Researchers from New York University’s Applied Mathematics Laboratory have brought a fresh perspective to the mysterious origins of the Great Sphinx of Giza, suggesting that the iconic monument’s distinctive form may have been significantly influenced by natural forces, specifically wind erosion.
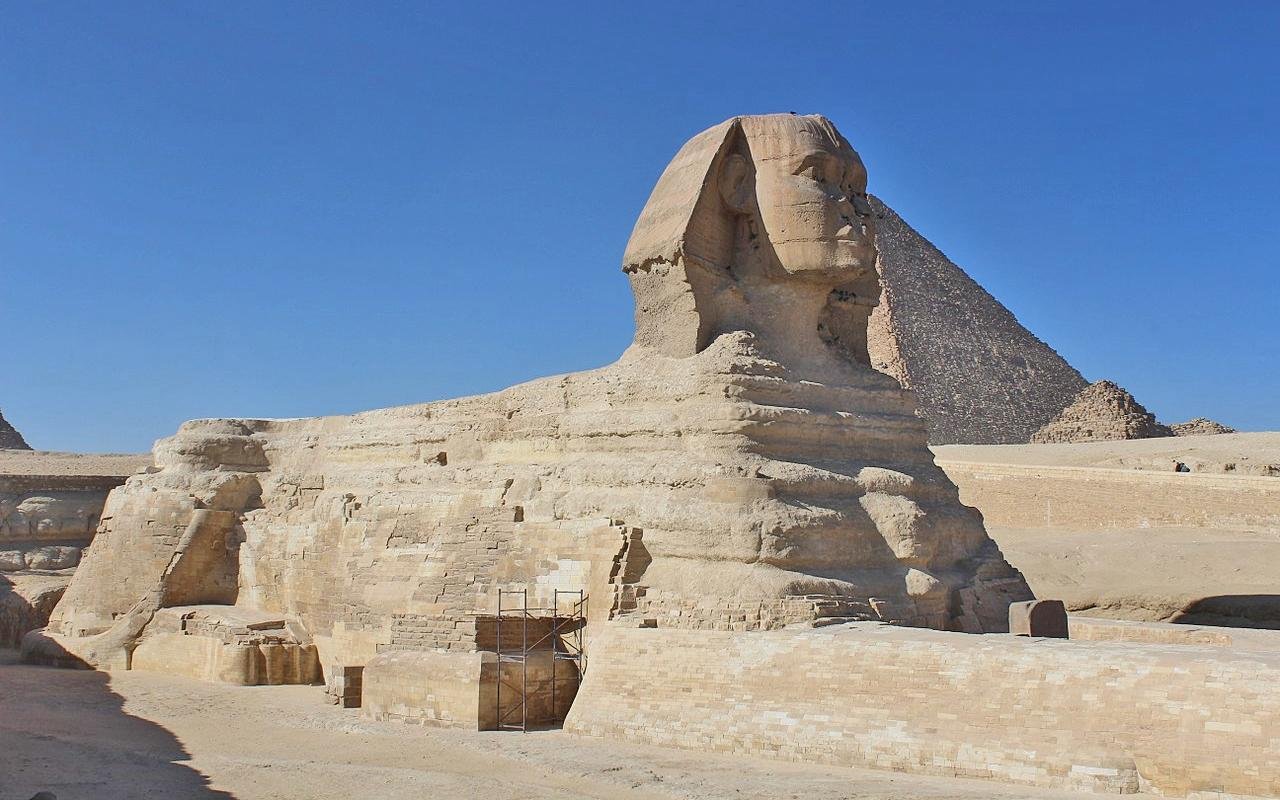

This theory, first proposed over 40 years ago by space scientist and geologist Farouk El-Baz, gains fresh evidence through meticulous experiments simulating the environmental conditions of 4,500 years ago, when the Sphinx is believed to have been constructed.
The Great Sphinx, a monumental limestone statue perched on the Giza Plateau, has long captivated historians and archaeologists, leaving unanswered questions about its original appearance, purpose, and the role of the surrounding landscape in its formation.
The NYU study explores the intriguing possibility that the Sphinx began as a natural rock formation called a yardang, shaped by wind-blown dust and sand.
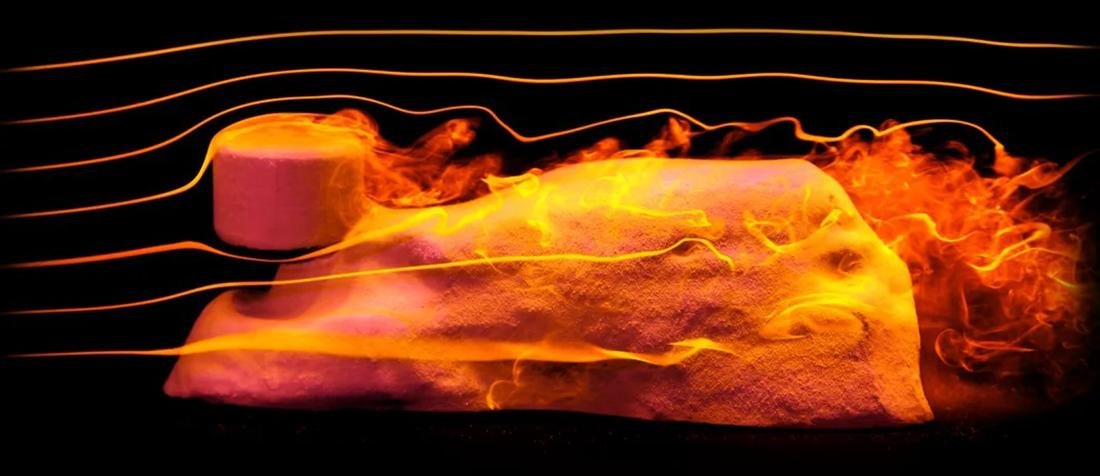


Dr. Leif Ristroph, associate professor at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the senior author of the study, explains, “Our findings offer a possible ‘origin story’ for how Sphinx-like formations can come about from erosion. Our laboratory experiments showed that surprisingly Sphinx-like shapes can come from materials being eroded by fast flows.”
To test this hypothesis, the research team replicated yardangs in the laboratory, using soft clay mounds containing embedded, less erodible material to mimic the landscape of northeastern Egypt where the Great Sphinx resides. By subjecting these formations to a rapid-flowing water stream, representing the erosive action of wind, the researchers observed the emergence of a structure resembling the Great Sphinx.
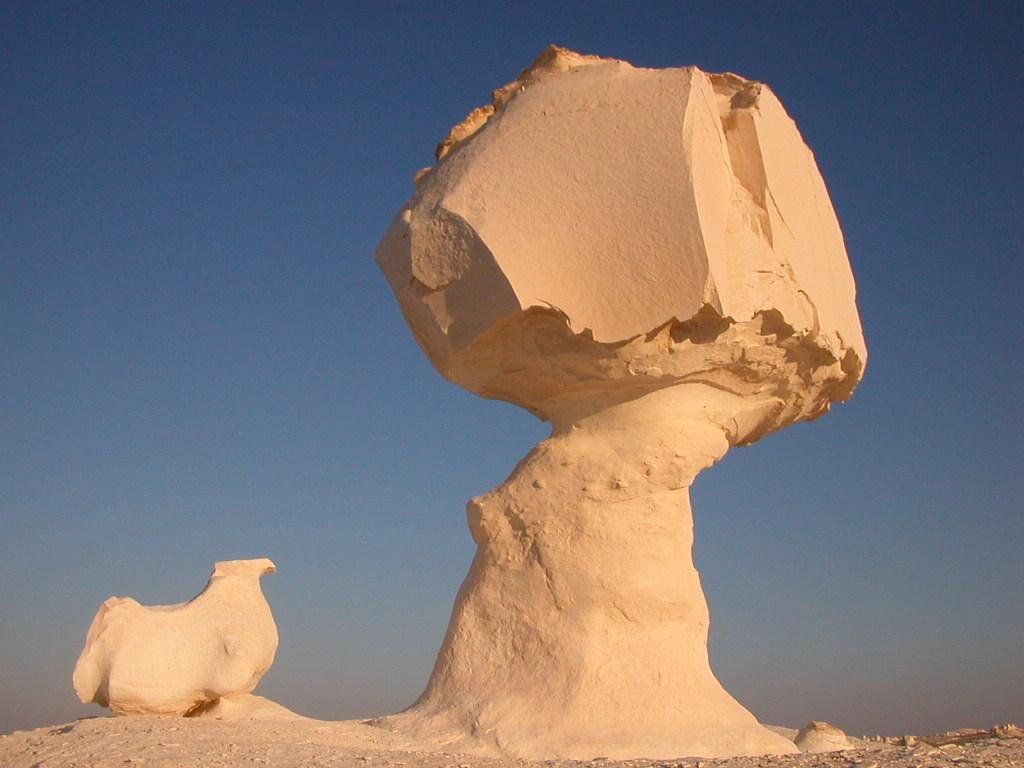
The study’s results provide a compelling argument for the role of wind erosion in shaping the Sphinx’s iconic features. Dr. Ristroph notes, “There are, in fact, yardangs in existence today that look like seated or lying animals, lending support to our conclusions.”
While the findings offer a new perspective, they don’t definitively settle the question of the Sphinx’s construction. Dr. Kathryn Bard, an archaeologist at Boston University, cautiously acknowledges the study’s contribution, stating, “The study shows a very real possibility of how a natural limestone formation came to have a kind of amorphous sphinx-like shape.” However, she points out that yardangs in Egypt’s Western Desert, where she has conducted research, differ from the one produced in the study.

The debate over the Sphinx’s origins persists, with experts emphasizing the undeniable contribution of skilled craftsmen to the monument’s intricate details. Dr. Ristroph acknowledges the nuanced nature of the discussion. “It’s not so black and white. No one says this is an entirely human-carved thing, and no one says it’s entirely nature-carved. The question is how much was naturally existing and then further modified,” he told CNN.
This study was published in Physical Review Fluids.