Tell Asmar, also known as Eshnunna, was an ancient city in Mesopotamia, located in what is now modern-day Iraq. The city was an important center of the Sumerian civilization and later the Akkadian Empire.
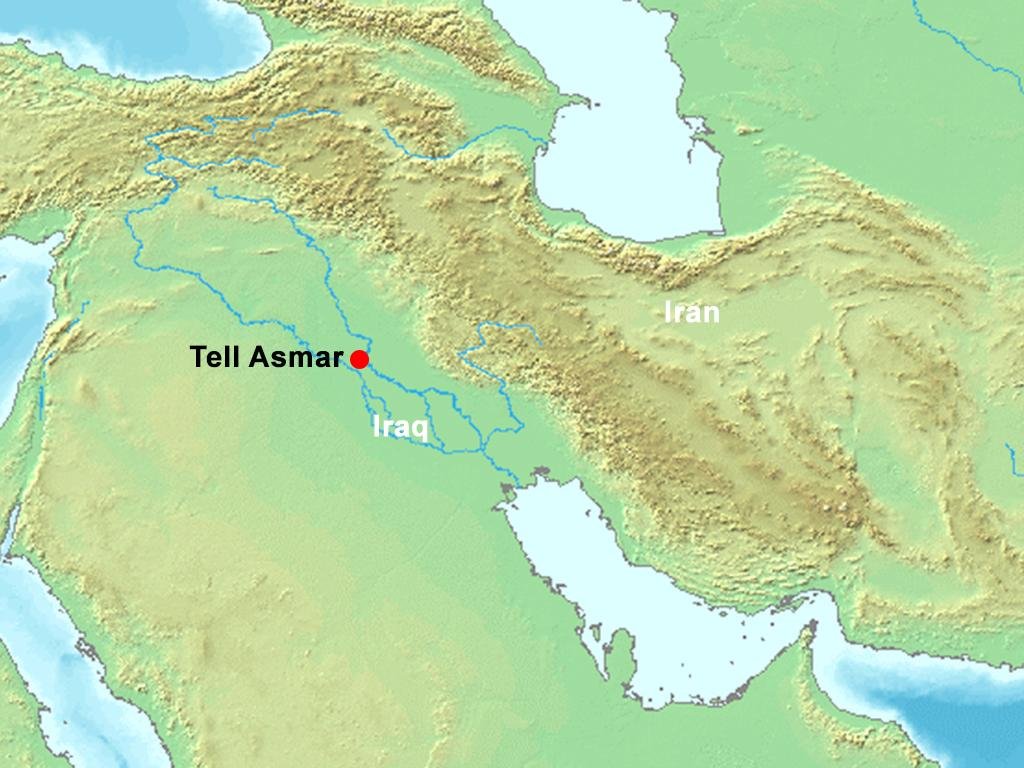
The city is named after a large mound or “tell” which contains the remains of the ancient settlement. The tell rises to a height of about 25 meters and covers an area of around 80 hectares. Archaeological excavations at Tell Asmar have uncovered numerous artifacts and structures that provide insight into the city’s history.
One of the most important discoveries at Tell Asmar is a series of temples that were built over several centuries, starting around 2900 BCE. These temples were dedicated to the goddess Inanna, who was a major deity in the Sumerian pantheon. The temples were built on top of one another, with each successive temple being larger and more elaborate than the last.

The excavations at Tell Asmar have also revealed a wealth of art and artifacts from the Sumerian period, including statues of gods and goddesses, jewelry, pottery, and tools. Many of these objects are now housed in museums around the world.
Overall, Tell Asmar is an important archaeological site that has contributed greatly to our understanding of the ancient Sumerian civilization and its religious practices.