Montale, located in northern Italy, is believed to have been a pioneering center for wool production during the Bronze Age, possibly on an industrial scale. Serena Sabatini, an archaeologist, reached this conclusion by examining archaeological discoveries, including textile tools and teeth from sheep and goats.

The presence of a significant number of textile tools at the Montale settlement indicated intensive wool production. To gain a deeper understanding of how this production was organized, researchers analyzed the teeth of sheep and goats from the Bronze Age.
Modern archaeological research increasingly incorporates methods from the natural sciences. Serena Sabatini, an archaeologist and associate professor at the Department of Historical Studies, collaborated with researchers at the Danish National Museum to employ strontium isotope analysis in her investigation.
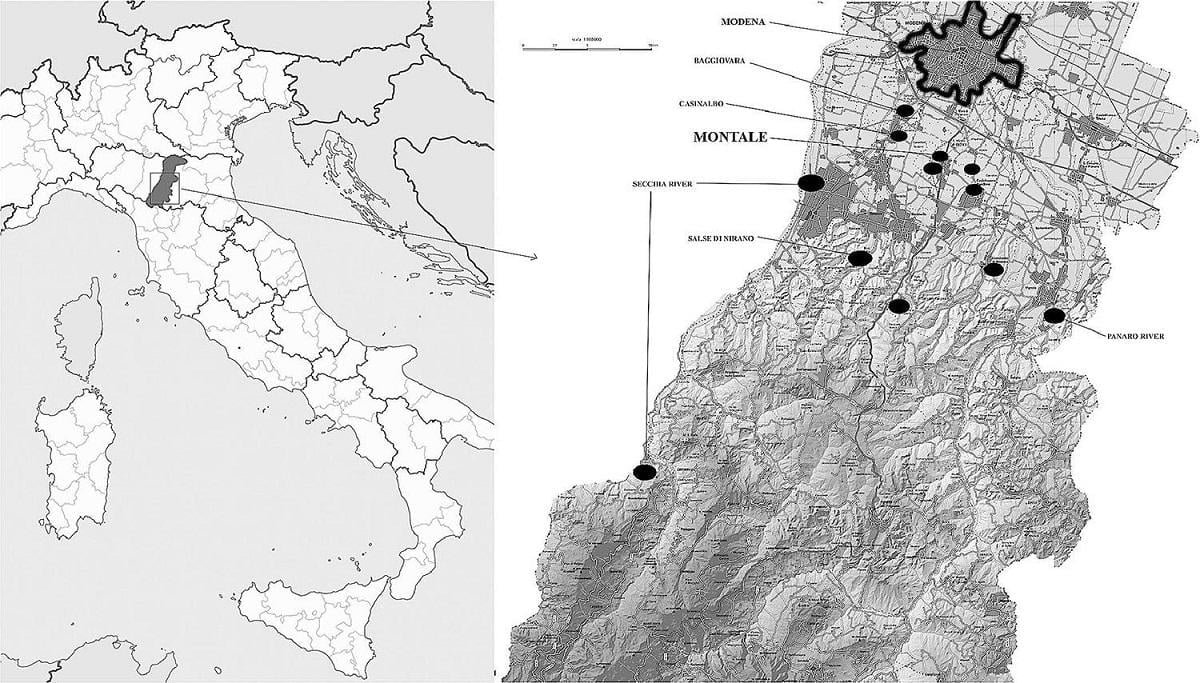
As part of the research project “Bronze Age wool economy: production, trade, environment, husbandry, and society,” Sabatini collected teeth from sheep and goats from the Bronze Age settlement at Montale in northern Italy. These teeth were then analyzed to measure the strontium isotope values present in them.
Strontium is a mineral found in both food and water, and it becomes integrated into the tissues of humans, animals, and plants. Strontium values in teeth and bones accumulate during childhood and remain relatively stable in adulthood.
This allows researchers to determine whether individuals spent their childhood in the same area where they were later buried or if they migrated there as adults or adolescents. A similar principle applies to animals, making it possible to investigate the mobility of animals within the landscape.
During the Bronze Age, it is likely that both humans and animals consumed locally sourced food and water, leading to the recording of specific strontium isotope values in their bones and tissues corresponding to their place of birth and upbringing.
The analysis results indicate that most of the sheep and goats were raised and ultimately died in the Montale region, suggesting close management by the community residing at the site. This finding aligns with previous theories about the pivotal role of these animals in large-scale local wool production.

It’s worth noting that Bronze Age sheep did not produce wool to the extent of modern breeds. Historical records from the Mediterranean region, where written sources are available, reveal that producing 3 kilograms of wool took a full year and required a mixed flock of ten sheep, including both adults and lambs. Crafting a simple 3.5-meter by 3.5-meter cloth necessitated 4 kilograms of raw wool.
This underscores the complexity of organizing an economically viable and profitable wool production system, which, in turn, demanded the management of substantial sheep flocks.
The study of textile production, particularly wool production, throughout history has garnered increasing interest in recent years. The aim of the project is to emphasize the significance of wool and wool textile production during the European Bronze Age.
Recent research suggests that during the 2nd millennium BCE, specific continental centers like Montale in northern Italy, which was part of the Terramare culture, recognized the economic importance of wool. Favorable social and environmental conditions allowed them to specialize in wool production, potentially exporting wool, wool yarn, or even finished wool textiles. This specialization enabled trade, as they exchanged wool and textiles for goods not readily available in their region.
More information: Serena Sabatini et al, (2021). Investigating sheep mobility at Montale, Italy, through strontium isotope analyses, Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports. DOI: 10.1016/j.jasrep.2021.103298