A new study conducted by Dr. Ashleigh Wiseman from the University of Cambridge’s McDonald Institute for Archaeological Research has digitally reconstructed the leg and pelvic muscles of “Lucy,” a famous fossil specimen of the early human ancestor Australopithecus afarensis.
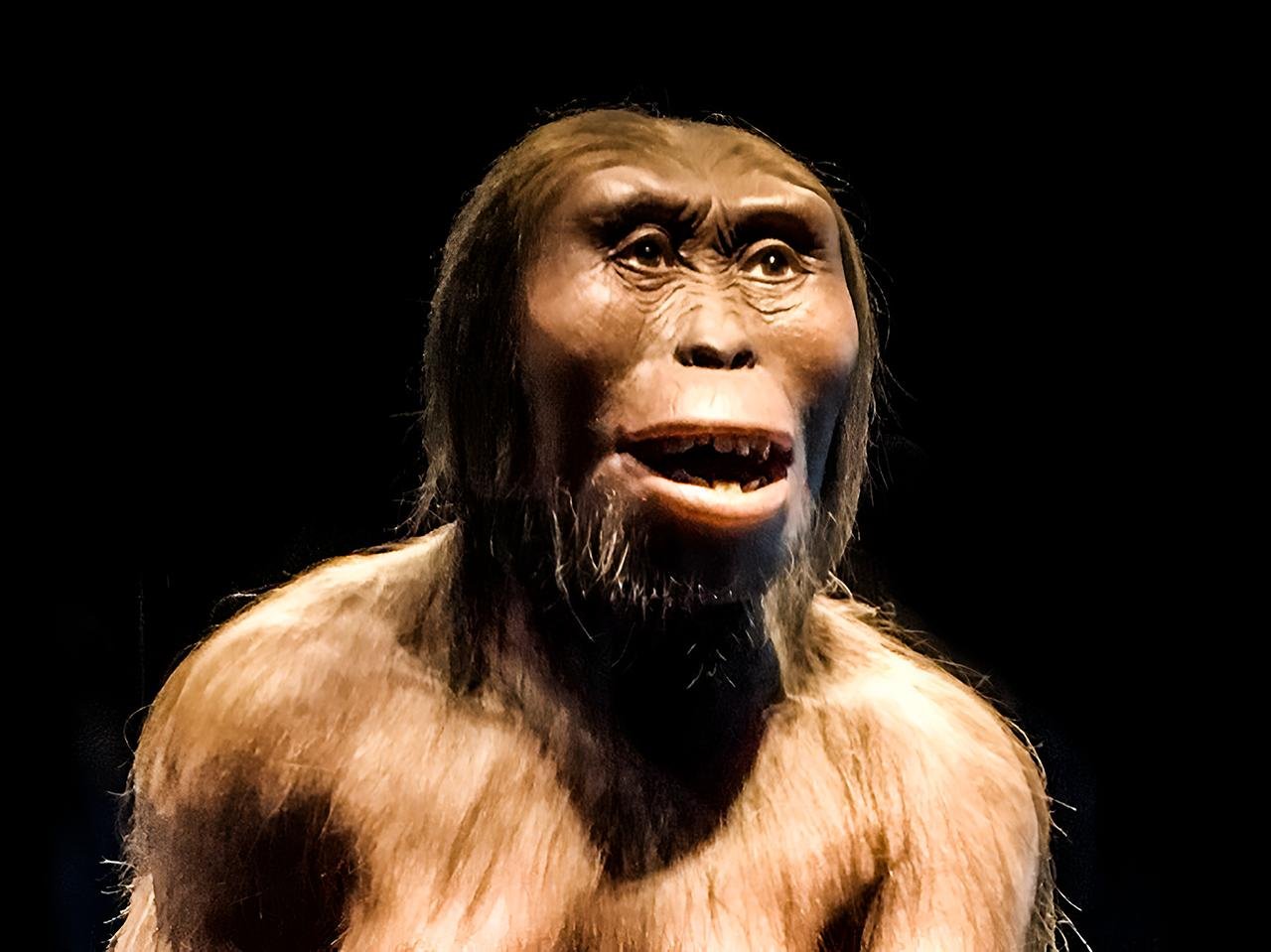

The findings suggest that Lucy had the ability to stand and walk upright, similar to modern humans. The research also indicates that Lucy likely had the capability to climb trees, indicating that the species thrived in both forest and grassland habitats in East Africa approximately 3 to 4 million years ago.
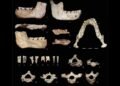
Lucy’s fossils are among the best-preserved remains of Australopithecus ever discovered, with 40% of her skeleton recovered from Ethiopia’s Hadar region in the 1970s.
The analysis of her bones revealed that she stood about 3.4 feet (1 meter) tall and weighed between 29 and 93 pounds (13 to 42 kilograms). These findings suggested that human ancestors could walk upright long before they evolved larger brains.
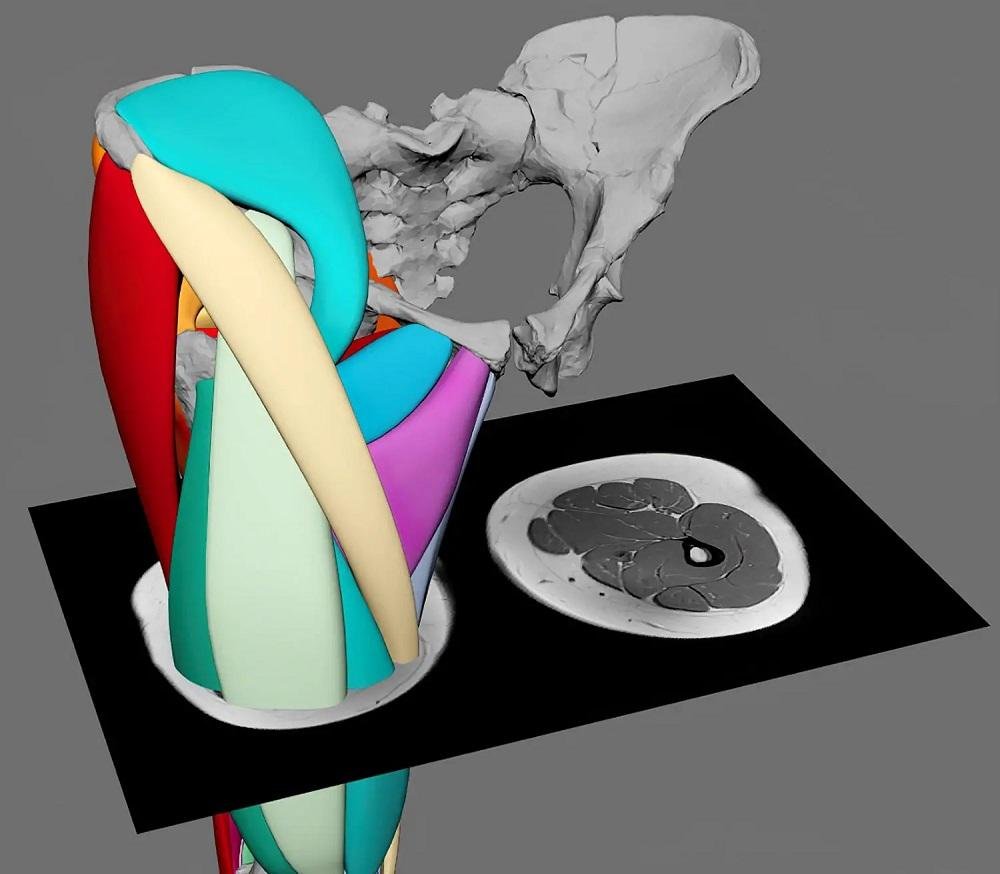
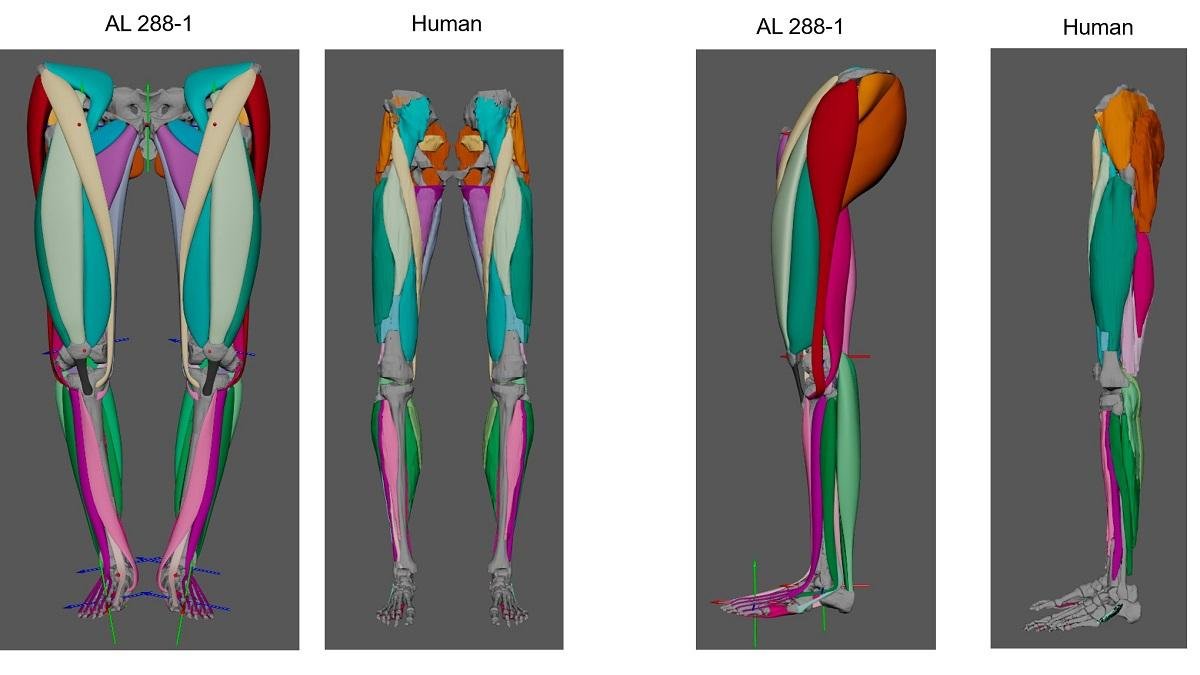
Using a digital modeling approach, Dr. Wiseman reconstructed 36 muscles in each of Lucy’s legs.
The models revealed that Lucy had the ability to straighten her knee joints and extend her hips, similar to modern humans, indicating an upright walking posture.
The proportions of fat and muscle in Lucy’s legs were also analyzed, showing that her muscles were far more developed and less fatty compared to modern humans. Some of her calf and thigh muscles occupied twice as much space as they do in human legs today.
The study supports the consensus among researchers that Lucy walked erect rather than with a crouching waddle like chimpanzees. The reconstruction of Lucy’s muscles suggests that she was proficient at bipedalism and could have effectively exploited both tree and ground habitats.
While the study is based on an incomplete skeleton, the results align with previous research. The research methodology of digitally reconstructing muscles is considered promising and goes beyond simplistic interpretations of paleontologists when inferring the locomotion of extinct species.
This study contributes to the understanding of our evolutionary history and opens the door for similar techniques to be applied to ancestral humans, shedding light on the range of physical movement that propelled our evolution.
The research was made possible through open-access science, emphasizing the importance of sharing scientific data for further advancements in the field. Muscle reconstructions have been previously used to study the movement capabilities of various species, such as estimating the running speed of a Tyrannosaurus rex.