An intriguing archaeological discovery in an Early Medieval settlement near the village of Conington in Cambridgeshire, England, has shed light on burial practices, social dynamics, and possibly superstitions of the past.
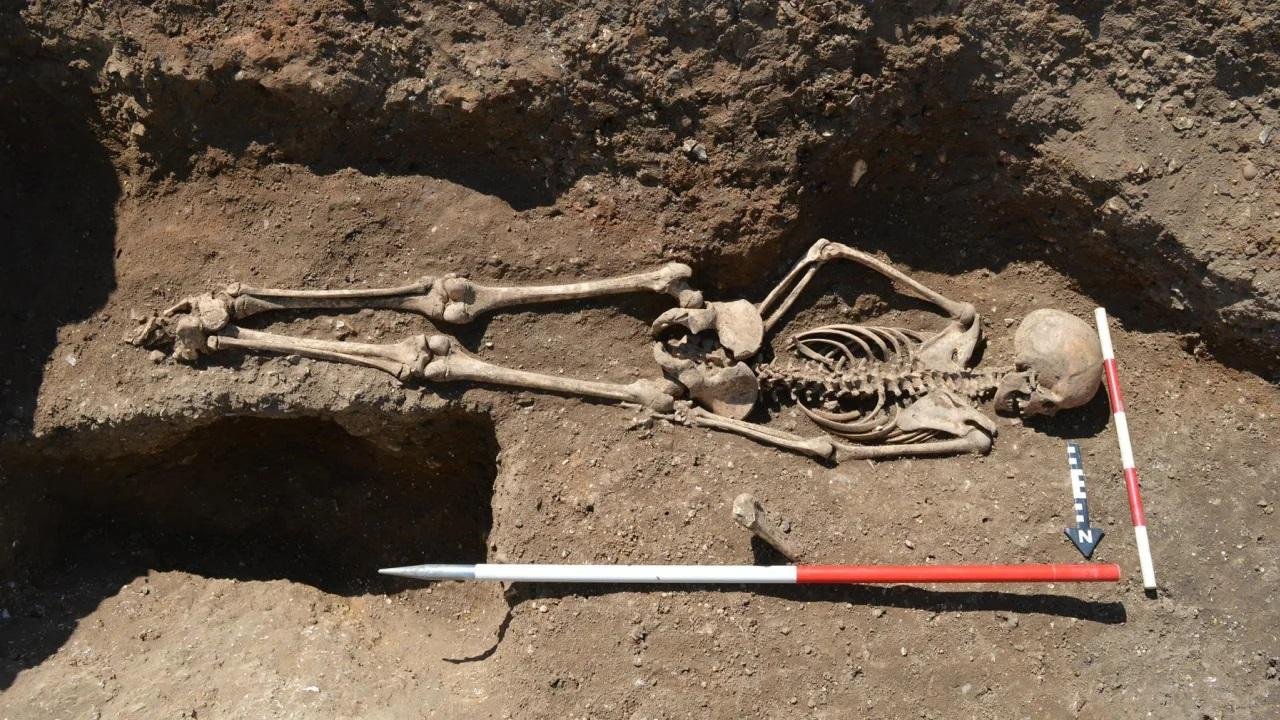

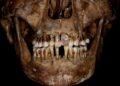
The skeletal remains of a 15-year-old girl were unearthed in a pit, revealing a burial position that deviates from the norm of the time. The girl was buried face down, with indications that her ankles may have been bound, leading experts to propose that these measures were taken to prevent her from ‘returning’ from the grave.
The excavation, which took place between 2016 and 2018, was conducted as part of an archaeological program linked to a national highways improvement project. The findings have since been meticulously analyzed by researchers at the Museum of London Archaeology (MOLA) and MOLA Headland Infrastructure.
Early Medieval England did not have uniform burial traditions, but it was common for the deceased to be buried with their faces upward. The case of the Conington girl, however, stands out as an exception.
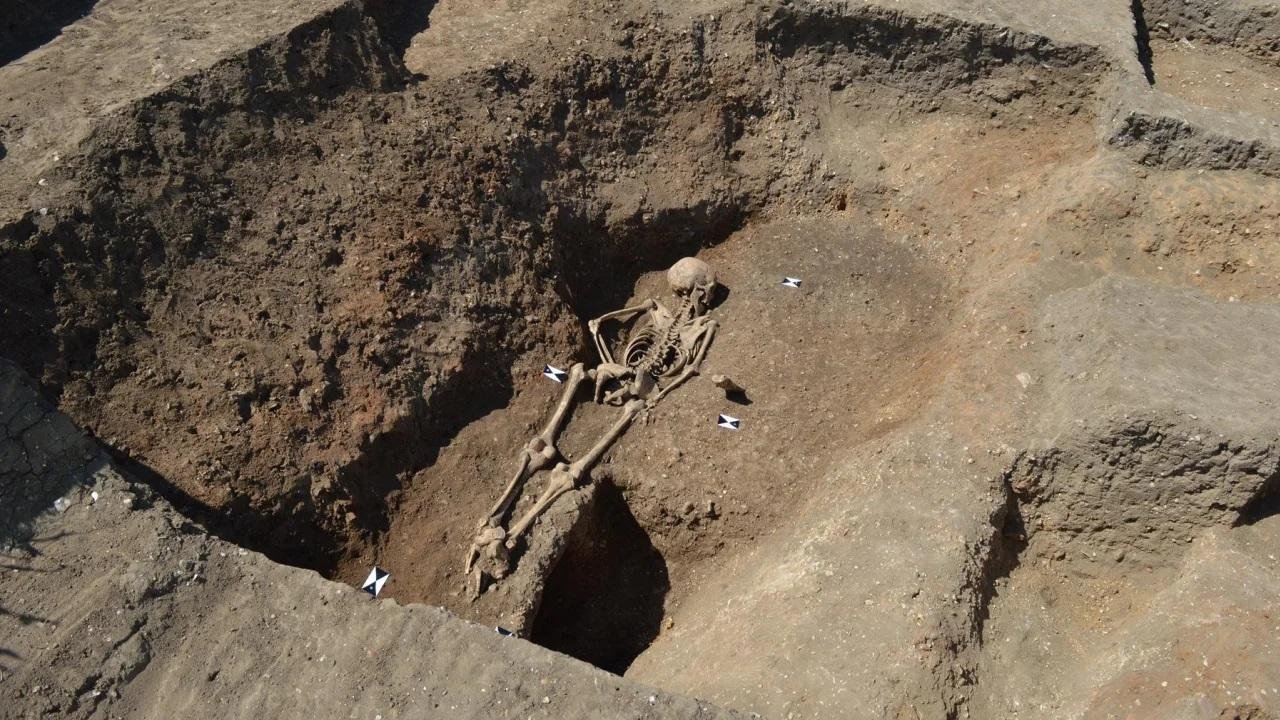

Her face-down burial is believed to signify an expression of ‘otherness,’ marking her as different from the community she belonged to.
Don Walker, a senior human osteologist at MOLA, suggests, “We will probably never know exactly how this young woman was viewed by the community she grew up in, but the way she was buried tells us she was almost certainly seen as different.”
The unique burial position and the potential binding of the girl’s ankles have prompted discussions about the reasons behind these measures. Similar to instances of ‘vampire’ burials found in later periods, the actions taken could have been driven by beliefs that the deceased might rise from the grave to harm the living.
Although ‘vampire burials’ are commonly associated with the 14th to 17th centuries, this earlier case points to a broader spectrum of fears and superstitions held by communities.
The analysis of the girl’s skeletal remains offers information about her life and social status. Evidence of childhood malnutrition and a spinal joint disease indicates that she likely belonged to a lower social stratum. The absence of signs of prolonged illness suggests a sudden or unexpected demise. Radiocarbon dating places her death between CE 680 and 880, aligning with the Early Medieval period.

The location of her burial adds another layer of significance to the find. Placed in a pit that once held an entry gate post, the burial carries echoes of another face-down interment discovered about 30 miles away.
According to MOLA, boundaries and borders seemed to be chosen for “significant or unusual” burials during this era.
The settlement near Conington served as an administrative center for the Kingdom of Mercia, an influential Anglo-Saxon realm. The timing of the girl’s burial, around the period of the settlement’s abandonment, suggests a symbolic closure of the site. As the power of the kingdom waned, the community’s actions signify a poignant farewell.