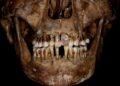
Scientists from Greece, Spain, and the U.S. have unveiled the identities of the occupants of the unspoiled 4th-century BCE Royal Tombs at Vergina in northern Greece. The study, recently published in the Journal of Archaeological Science, resolves nearly half a century of scholarly disputes over the specific individuals buried in each tomb.
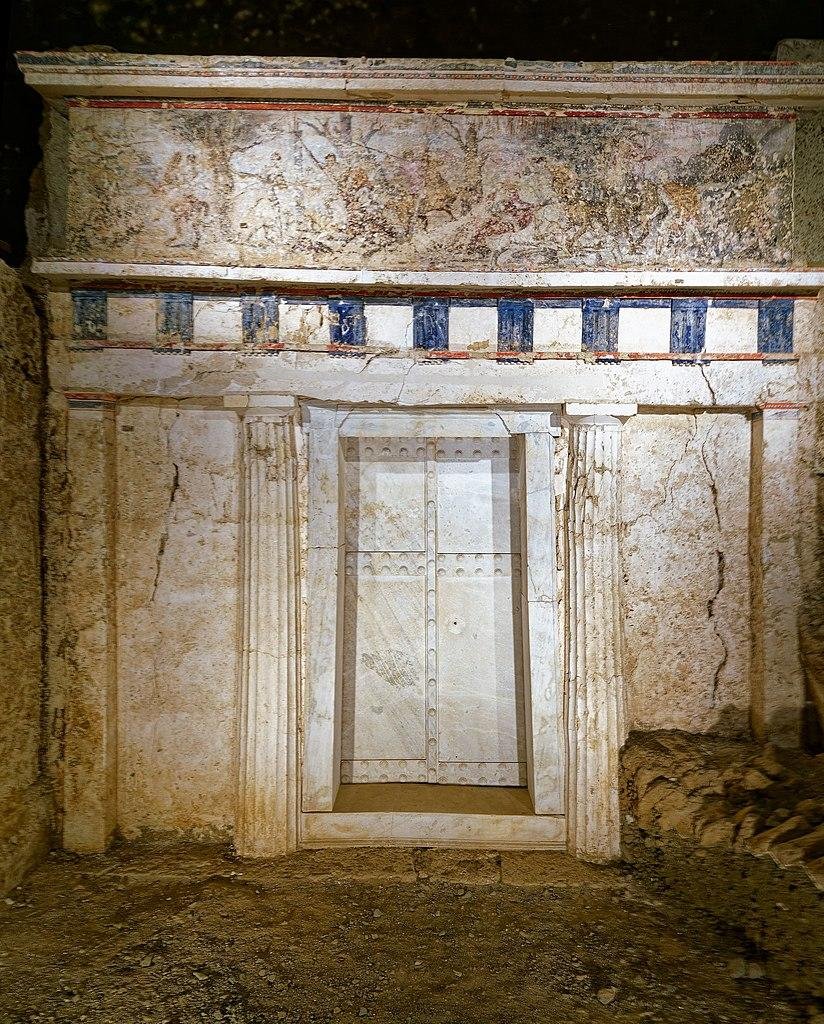

The tombs, known as Royal Tombs I, II, and III, contain the remains of Alexander’s father, stepmother, half-siblings, and son, along with various artifacts, including armor belonging to Alexander himself. The researchers employed a multi-faceted approach, utilizing macro photography, radiographs, anatomical dissection, and historical sources to analyze the skeletal elements.
Tomb I, as confirmed by the study, is the final resting place of King Philip II, Alexander’s father, alongside his wife Cleopatra and their newborn child. The male skeleton in Tomb I exhibits a knee fusion, consistent with historical evidence of King Philip II’s lameness. The infant’s extremely young age aligns with the narrative of Philip’s assassination in 336 BCE, ordered by his previous wife Olympias, Alexander’s mother.
Contrary to previous speculations, Tomb II does not house Philip II. Instead, researchers determined that it belongs to King Arrhidaeus, Alexander’s half-brother, and his wife Adea Eurydice. The presence of skeletal evidence for excessive horseback riding in Adea Eurydice supports the conclusion, dispelling the notion that Tomb II could be Alexander’s final resting place.

“Due to ancient depictions and descriptions, some scholars have suggested that some of the objects in Tomb II, such as the armor, belonged to Alexander the Great, which is possible only if this is the Tomb of Arrhidaeus, not Philip II,” write the authors in their paper.
Tomb III, according to the study, unequivocally contains the remains of Alexander IV, Alexander the Great’s teenage son. This finding challenges the theory proposed by historian Helen Glykatzi-Ahrweiler, suggesting that Alexander the Great himself was buried in one of the tombs.
The research, led by Antonis Bartsiokas from Democritus University of Thrace, Juan Luis Arsuaga from Universidad Complutense de Madrid, and Nicholas Brandmeir from West Virginia University, effectively refutes the long-standing speculation that Tomb II housed Philip II.
According to the researchers, the evidence presented supports the conclusion that Tomb I belongs to King Philip II, his wife Cleopatra, and their newborn child. Tomb II belongs to King Arrhidaeus and his wife Adea Eurydice. Tomb III to Alexander IV. Our hypothesis of Philip II in Tomb I remains unchallenged in peer-reviewed literature, and we believe the available evidence is conclusive.

Despite these groundbreaking revelations, the researchers acknowledge the need for further evidence, awaiting the publication of excavation diaries and addressing uncertainties regarding labels and genetic background.