Archaeological excavations in western Ukraine have unveiled evidence of early human presence in Europe dating back 1.4 million years, marking a significant milestone in our understanding of ancient migrations. The findings, published in the journal Nature, suggest that these early humans, likely Homo erectus or a related species, ventured far beyond their African origins.
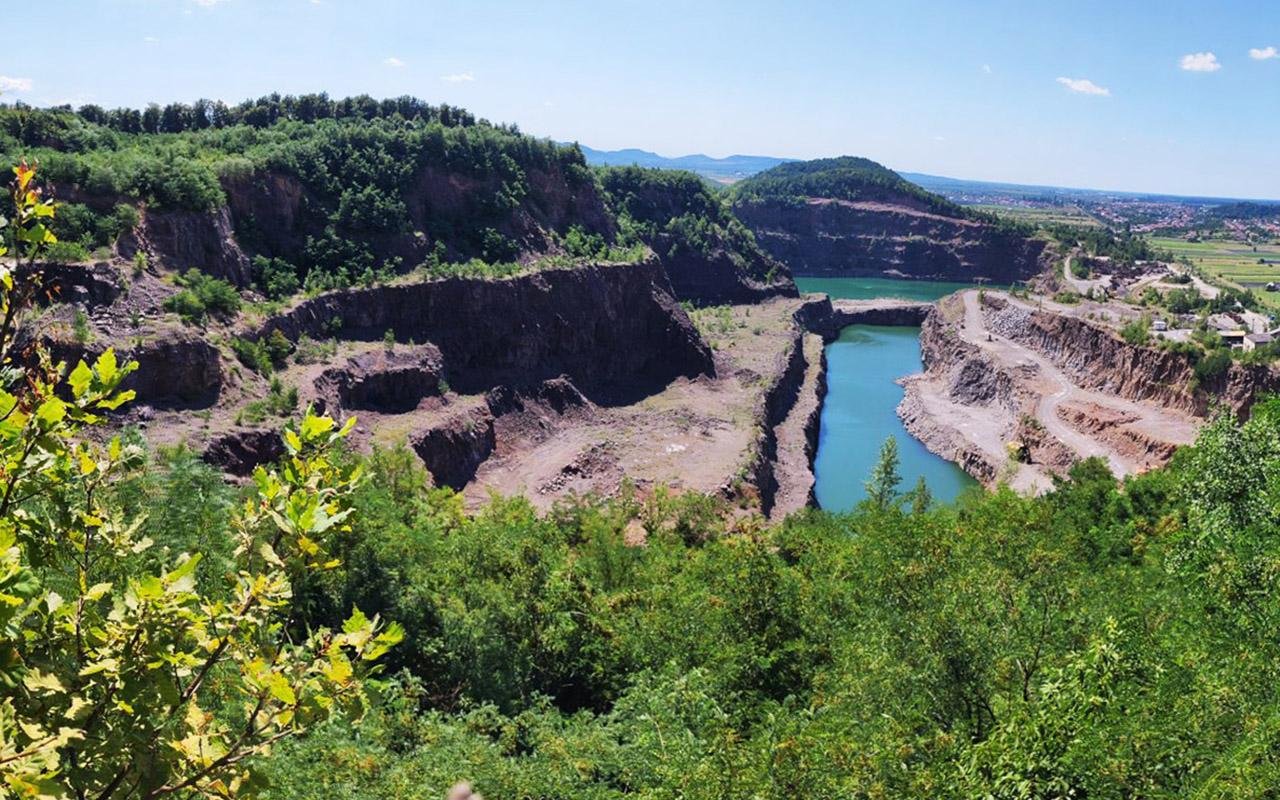

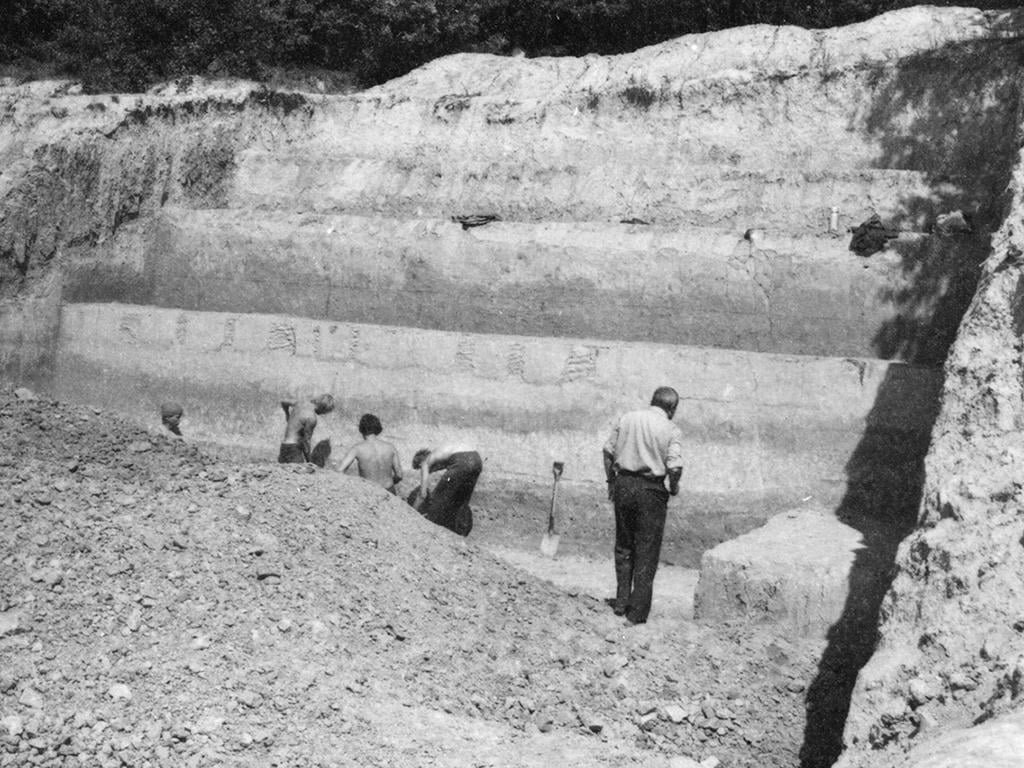
The site of Korolevo, located in the Carpathian Mountains, has been a focal point for archaeologists since its discovery in 1974. Recent analysis of stone tools unearthed at the site reveals their remarkable antiquity, pushing back the timeline of human habitation in Europe by hundreds of thousands of years.
Researchers utilized a technique called cosmogenic nuclide burial dating to establish the age of the artifacts with greater precision. This method, based on the decay of isotopes within quartz crystals, determined that the tools were buried approximately 1.4 million years ago. The significance of this discovery lies not only in its age but also in its implications for understanding early human migration patterns.
While the exact species responsible for crafting these tools remains uncertain, the evidence suggests they were created by a hominin, a group encompassing modern humans and their extinct relatives. The proximity of Korolevo to other key sites in Europe and Asia supports the notion of eastward migration routes taken by early humans.

“This is the beauty of this article: The outcomes are somehow just as everybody expected,” remarked Roman Garba, lead archaeologist on the project. The findings align with long-held hypotheses regarding the movement of hominins out of Africa and into Europe, shedding light on the ancient pathways traversed by our early ancestors.
However, not all experts are in agreement with the proposed timeline. Giovanni Muttoni, a geochronologist at the University of Milan, questions the reliability of the dating method and suggests a later arrival of hominins in Europe around 900,000 years ago. He emphasizes the importance of considering ecological factors in understanding ancient migrations and highlights the lack of significant climate shifts around the proposed dates.

Despite differing interpretations, the discovery at Korolevo represents a crucial piece of the puzzle in reconstructing the story of human evolution. The site’s location, nestled within the Carpathian Mountains, hints at the adaptability and resilience of early humans.