A new study published in the Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory has revealed compelling evidence indicating that the first Pacific cities emerged much earlier than previously believed.
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU) utilized advanced aerial laser scanning technology to meticulously map archaeological sites on Tongatapu, the main island of Tonga, revealing a sophisticated urban landscape dating back to CE 300, approximately 700 years earlier than previously estimated.
The island of Tongatapu, known as the heart of Tonga and home to its capital Nukuʻalofa, boasts a rich history dating back to 900 to 850 BCE, with numerous archaeological sites such as the Haʻamonga ʻa Maui trilithon, ancient burial mounds, and the Papae ‘o Tele’a Tombs.
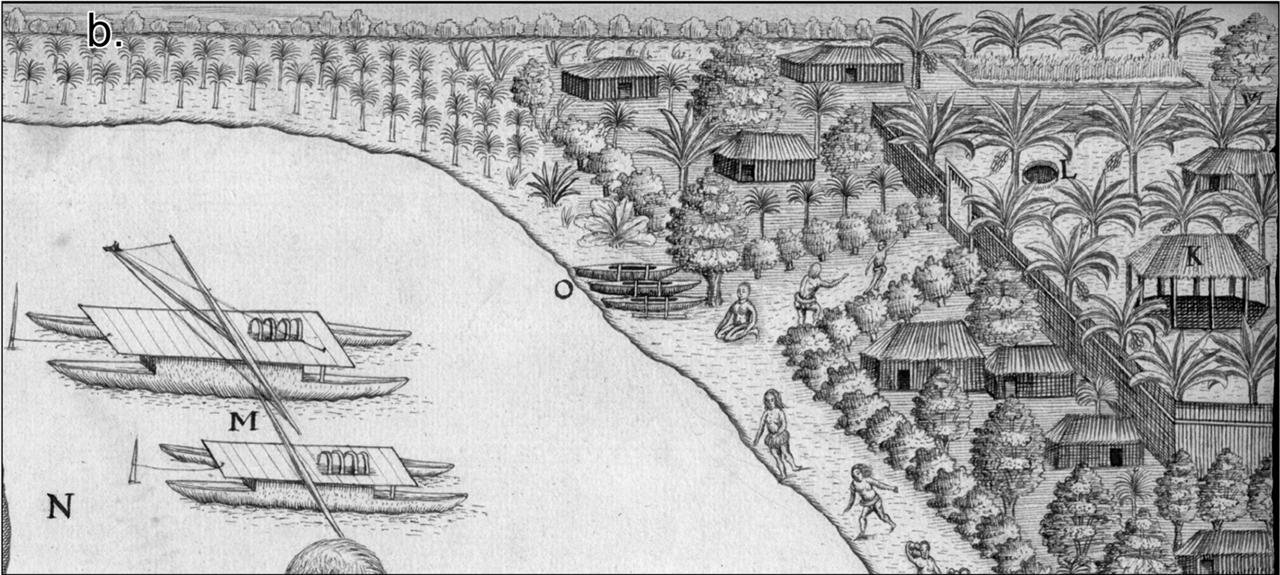
Through meticulous analysis of data obtained from airborne lidar surveys and ground investigations, researchers have revealed an urbanized landscape characterized by clusters of earth mounds interconnected by a sophisticated transport network, corroborating descriptions found in the journals of Captain James Cook during his expedition in 1773.

Lead author, Phillip Parton from The Australian National University, said: “Earth structures were being constructed in Tongatapu around CE 300. This is 700 years earlier than previously thought.” He further explained that as settlements expanded, innovative solutions were devised to accommodate the growing population.
According to Parton and Professor Geoffrey Clark, co-author of the study, the ancient city reflected a natural response to the increasing population density on an island constrained by limited space. It appears that the city planners aimed for gradual urbanization, resulting in a settlement with a lower population density compared to both contemporary urban centers and ancient cities elsewhere. This form of urban development catalyzed substantial social and economic transformations, fostering increased interaction among the inhabitants.
Parton added: “When people think of early cities, they usually think of traditional old European cities with compact housing and windy cobblestone streets. This is a very different kind of city.” He emphasized the need to recognize the Pacific’s contributions to urban science and its enduring influence on settlement patterns across the southwest Pacific Ocean.
The collapse of this early form of urbanization, according to the researchers, was primarily attributed to the arrival of Europeans, bringing with them introduced diseases that destabilized indigenous societies.
Parton expressed optimism about future discoveries, noting, “This is just the beginning in terms of early Pacific settlements. There’s likely still much to be discovered.”