A recent study has unveiled a disturbing trend of sacrificial murders spanning over 2,000 years. The research, published in Science Advances, delves into the horrible tradition of “incaprettamento” — a method of murder involving tying victims’ necks to their legs behind their backs, effectively causing them to strangle themselves.

The study, led by Eric Crubézy, a biological anthropologist at Paul Sabatier University in Toulouse, France, and forensic pathologist Bertrand Ludes of Paris Cité University, focuses on a tomb discovered over two decades ago near Avignon, in southern France.
This tomb, resembling a silo used for grain storage, contained the remains of three women buried around 5,500 years ago. Through a reevaluation of this tomb and an examination of similar cases across Europe, researchers identified a pattern of sacrificial killings.
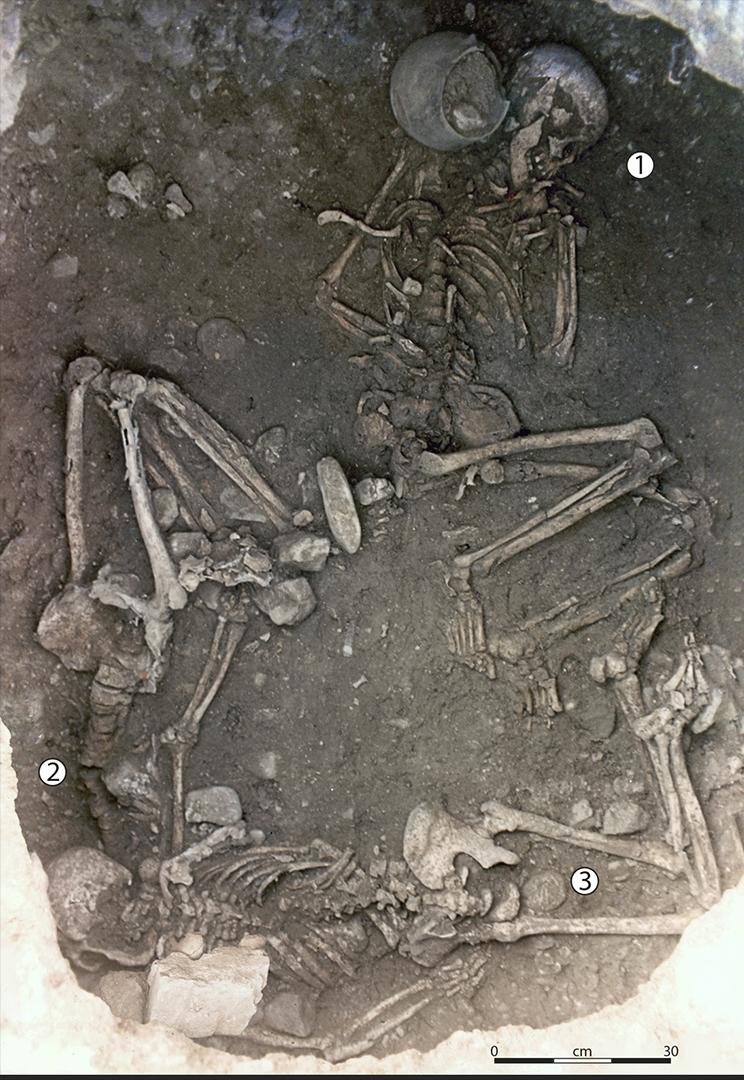

The victims, believed to have been deliberately killed, were bound in the incaprettamento manner before being buried, likely while still alive. The positioning of the victims, with two women buried in a prone position under the overhang of the tomb and a third centrally positioned, suggests a ritualized form of homicidal strangulation. Moreover, heavy grinding stones found at the site indicate that despite being bound, the victims were likely alive when buried.

This gruesome practice of incaprettamento appears to have been widespread across Neolithic Europe, with evidence found at 14 sites spanning from the Czech Republic to Spain. The earliest known occurrence dates back to around 5400 BCE, while the latest discovery at Saint-Paul-Trois-Châteaux suggests that the practice persisted for over two millennia.
The study also highlights the presence of agricultural symbolism surrounding the tomb, indicating a possible connection to farming practices during the Neolithic period. According to Crubézy, the ritual might have originated as a sacrificial custom before the advent of agriculture and later became associated with agricultural rituals.
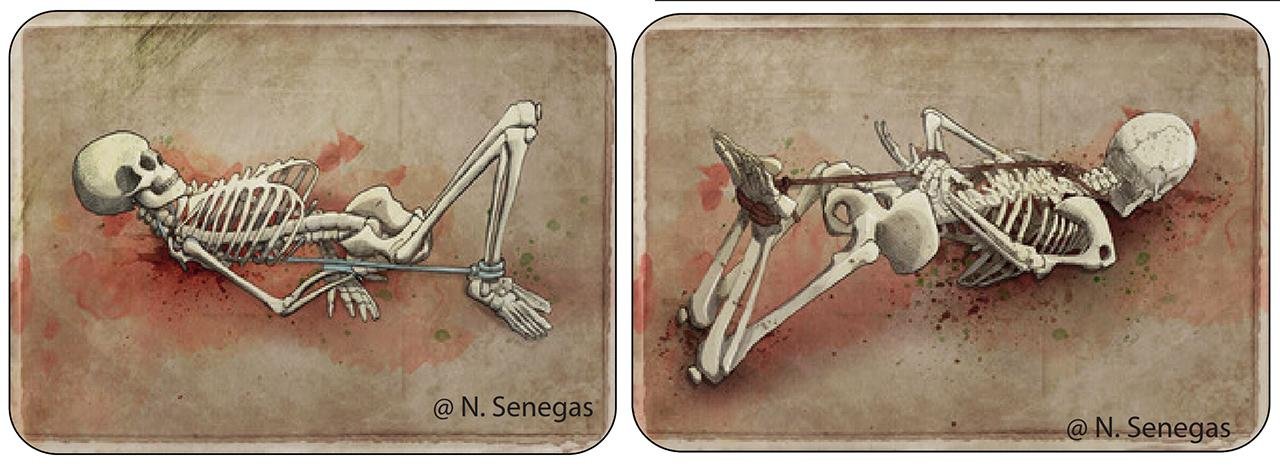

While the motivations behind these sacrificial killings remain unclear, researchers speculate that the method of incaprettamento may have been used to create the illusion of self-inflicted strangulation.
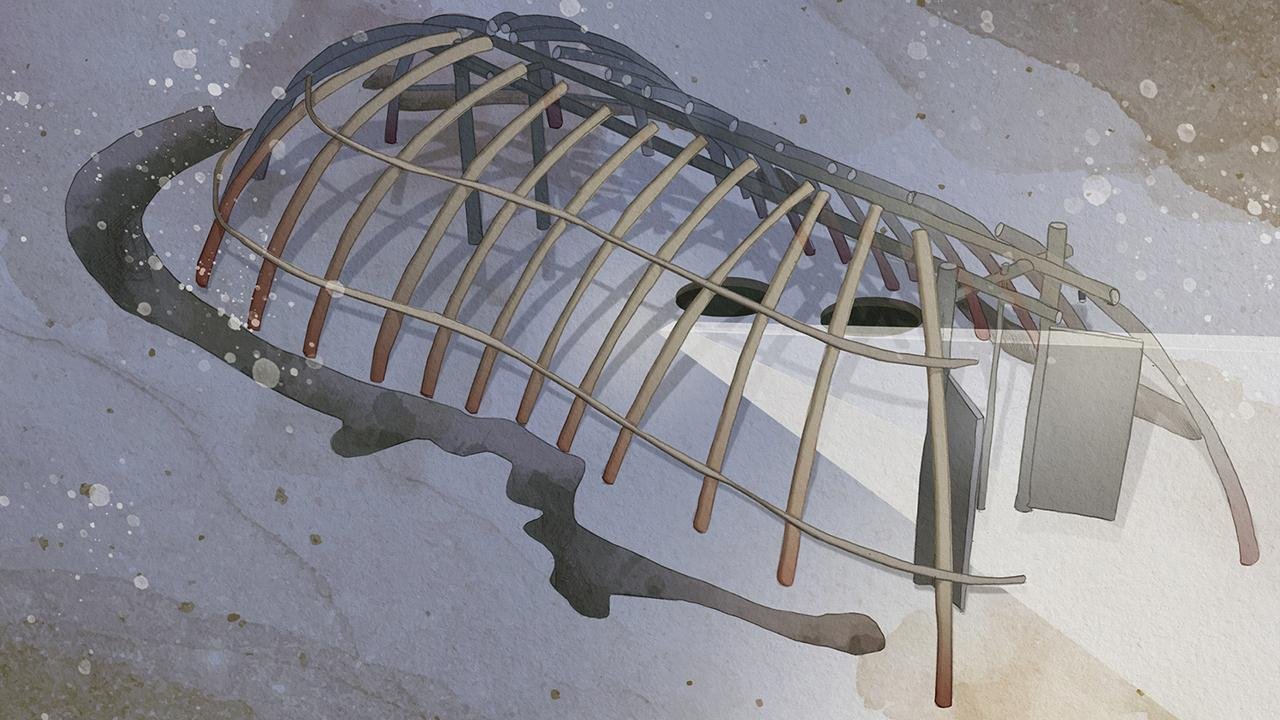

Further research is needed to fully understand the significance of these sacrificial murders and their connection to the development of agriculture during the Neolithic period.