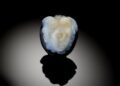
A 2100-year-old statue head of Hygieia, the Greek goddess of health, has been unearthed during ongoing excavations in the ancient city of Laodicea, located in the southwestern region of Turkey near Denizli.

The head of Hygieia, who symbolizes health and cleanliness, was discovered by an archeological team led by Prof. Dr. Celal Şimşek of Pamukkale University.
Laodicea, historically known as “Laodikeia on the edge of the Lycus,” was founded by Antiochus II between 263 and 261 BCE and named after his wife. This city, once a bustling hub in ancient times, is situated on the south side of the Lycus River, approximately six kilometers north of modern-day Denizli. Its strategic geographical location made it one of the most influential cities in antiquity, thriving particularly during the 1st century BCE due to its prominence on a major trade route, as noted by the historian Strabo.
The city boasted numerous impressive structures, including the largest stadium in Anatolia, two theaters, four baths, five agoras, five fountains, long colonnaded streets, and an array of temples, churches, and basilicas. Despite its prosperity, Laodicea was frequently beset by earthquakes, the most devastating of which occurred in 60 CE during Emperor Nero’s reign, completely destroying the city. Remarkably, the proud inhabitants of Laodicea declined imperial assistance and rebuilt the city themselves. Further calamities struck in 494 CE and between 602-610 CE, coupled with increasing threats from Arab raids, eventually leading to its abandonment.

The excavation efforts in Laodicea have been ongoing since 2003, and the recent discovery of Hygieia’s statue head adds to the historical richness of the city. Hygieia, whose name is the root of the modern word “hygiene,” was a significant figure in ancient Greek and Roman mythology. She was the daughter of Asclepius, the god of medicine, and played a crucial role in the philosophy of preventive medicine and cleanliness. Classical depictions of Hygieia often show her holding or feeding a large snake, a symbol associated with Asclepius, in her arms. Her statues were common in major healing centers, particularly in temples dedicated to Asclepius, with prominent ones located in Epidaurus, Corinth, Cos, and Pergamon.
Prof. Şimşek shared the news of the discovery on his social media X account, writing, “The meeting of the Sun and Hygieia with us in Laodicea after 2,100 years.” The statue head’s discovery is a notable addition to the collection of artifacts that narrate the rich history of Laodicea, further highlighting its importance as a center of ancient civilization.
Laodicea, which has been on Turkey’s Tentative List of World Heritage Sites since 2013, was once a vibrant center of trade, culture, and religion. The recent discovery of the Hygieia statue head underscores the city’s significant historical role in antiquity.























Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
Excellent updates!