Underwater archaeologists from Bournemouth University have successfully retrieved two medieval grave slabs from the Mortar Wreck, a 13th-century shipwreck located off the coast of Dorset, England.

The Mortar Wreck, named for its cargo of grinding mortars, sank in Studland Bay during the reign of Henry III (1216-1272). The site was initially discovered in 1982 but was presumed to be a mere pile of rubble until its true significance was uncovered in 2019. The ship is now recognized as England’s oldest intact wreck.
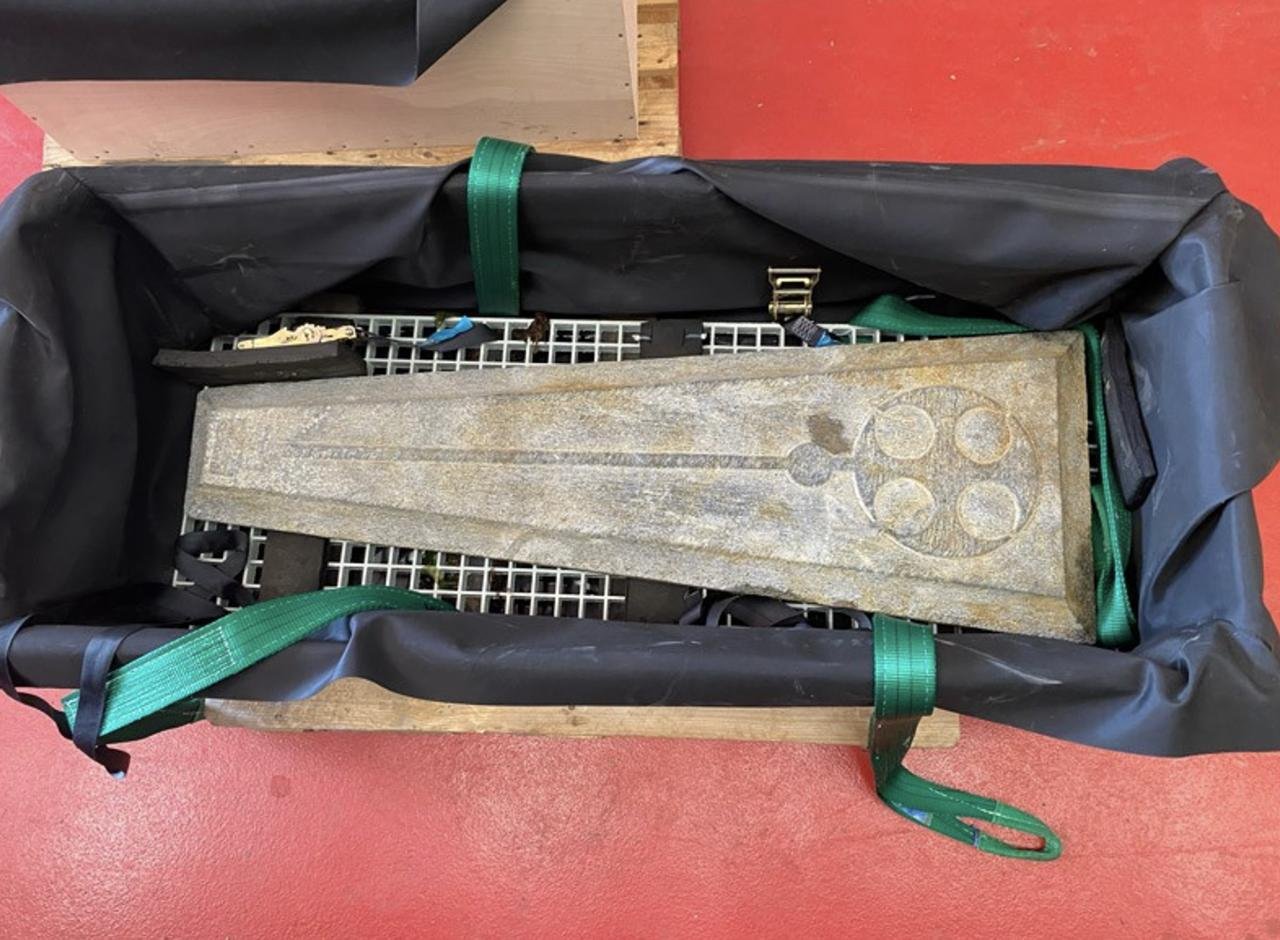
On June 4, 2023, a team of divers and archaeologists led by Tom Cousins, a maritime archaeologist at Bournemouth University, conducted a two-hour recovery operation from a depth of around seven meters. Using a barge, crane, and metal crates, the team brought the slabs to the surface. One slab, in immaculate condition, measures 1.5 meters and weighs approximately 70 kilograms. The other, much larger slab, is broken into two pieces with a combined length of two meters and a weight of around 200 kilograms.

Both slabs are crafted from Purbeck marble, a fossiliferous limestone quarried in the Isle of Purbeck, Dorset. This stone was highly prized during the medieval period for its use in architectural elements, including gravestones, due to its distinctive decorative qualities. The slabs feature carvings of Christian crosses, a common grave symbol in the 13th century, indicating they were intended as coffin lids or crypt monuments for high-ranking members of the clergy.

According to Tom Cousins, “The wreck went down in the height of the Purbeck stone industry, and the grave slabs we have here were a very popular monument for bishops and archbishops across all the cathedrals and monasteries in England at the time.” He noted that similar slabs have been found in renowned sites such as Westminster Abbey, Canterbury Cathedral, and Salisbury Cathedral.
The Mortar Wreck’s cargo, including the grave slabs and other items like cauldrons, cups, pottery, and domestic objects, offers a glimpse into 13th-century life and the transportation of goods during that era. Although the slabs were carved locally, they had not yet been polished to their usual glossy finish, suggesting that some finishing work was done at their final destinations.
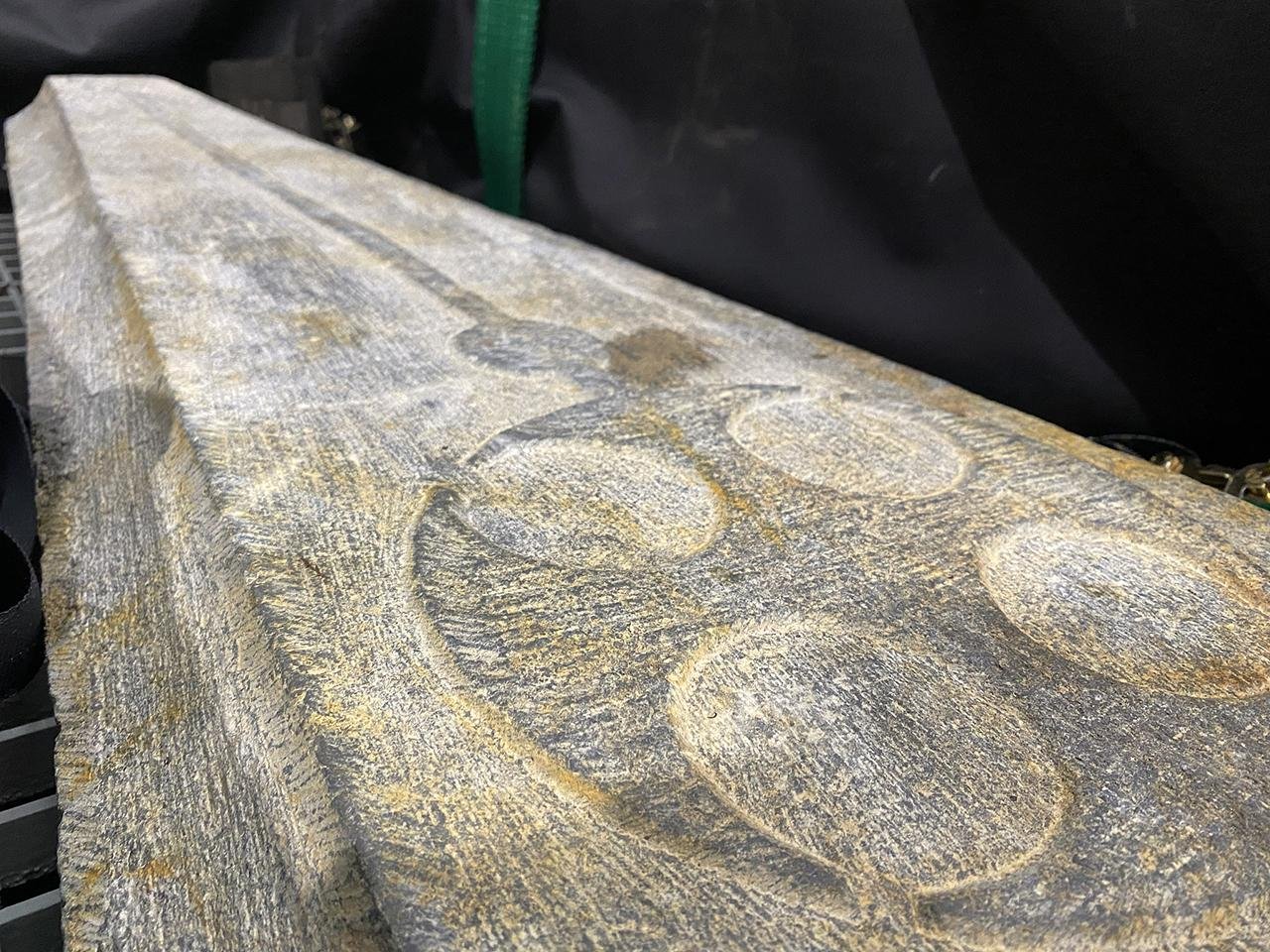

The grave slabs, along with other recovered artifacts, are set to be desalinated and conserved by the Bournemouth University team before being displayed in the new Shipwreck Gallery at Poole Museum, which is scheduled to reopen next year.
The Mortar Wreck site has been granted official protection since 2022. Cousins and his team plan to continue exploring and protecting the wreck over the coming years. They aim to document the well-preserved timber frames of the ship’s hull still embedded in the sand.

Moreover, the project serves as a valuable training ground for the next generation of maritime archaeologists. “The future aim of the project is to train the next generation so that they get the same opportunities I had. We’ve already started teaching our second-year students to dive and as they get into the third year we’re going to take them out to sea and teach them their first steps to becoming maritime archaeologists,” Cousins said.