Ostia Antica, an ancient Roman harbor town at the mouth of the Tiber River, has yielded a significant archaeological discovery. A team of archaeologists has excavated a well near the Temple of Hercules, revealing a collection of artifacts linked to ritual feasting and cult activities.
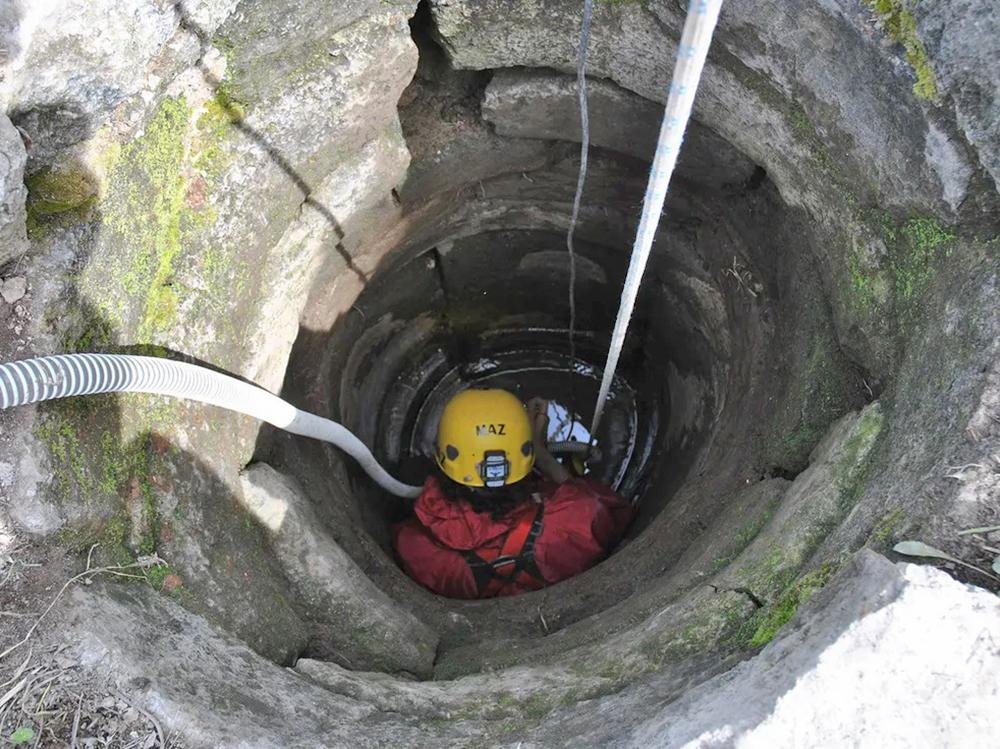

The well, approximately ten feet deep, is located in Regio I – Insula XV, a sacred area within Ostia Antica. This area, once home to several temples and sanctuaries, is dominated by the Temple of Hercules, a monumental structure dating back to the Republican Era. The well, situated at the temple’s base, was filled with water and oxygen-poor mud, which helped preserve the artifacts found within.
Among the most notable finds are various ceramics, lamps, glass containers, marble fragments, and burnt animal bones, predominantly from pigs and cattle. These artifacts date from the 1st to 2nd century CE. Archaeologists believe the burnt bones and ceramics indicate that animal sacrifices and ritual banquets took place at the site.

The remains of these feasts were likely discarded into the well when their function ceased. The Ministry of Culture noted, “The discovery of burnt bones confirms that animal sacrifices were carried out in the sanctuary, while the common ceramics, also bearing traces of fire, indicate that the meat was cooked and consumed during banquets in honor of divinity.”

A particularly intriguing find is a wooden funnel or chalice-like object, whose exact purpose remains unknown. This rare artifact, along with several interlocking wooden items, was remarkably well-preserved. Alessandro D’Alessio, director of the Ostia Antica archaeological park, speculated on its function, suggesting, “We believe it may have been used as a musical instrument such as a pipe.” The discovery of these wooden artifacts is especially significant, as wood typically deteriorates over time.
The Temple of Hercules, built in the third century BCE, was part of a larger complex that included other cult buildings. This area was a hub of religious activity, where oracles and priests predicted future events and advised generals. The site’s importance is underscored by its location along the Via Ostiensis, the main road connecting Ostia to Rome, making it a vital port for the Roman Empire.

Ostia Antica, founded in the seventh century BCE by Ancus Marcius, the fourth king of Rome, peaked in the second century CE. with a population of around 50,000. The city’s strategic position and its sacred precincts played crucial roles in its development and influence.
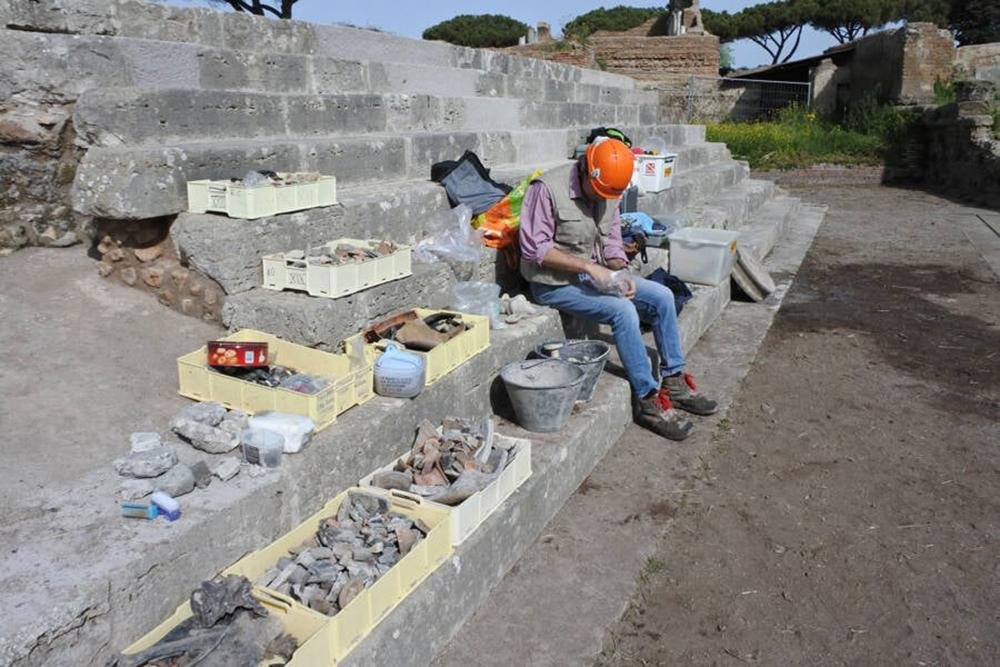
The well excavation is part of a broader restoration project at Ostia Antica. Archaeologists and specialists are meticulously studying and restoring the artifacts, which will eventually be displayed at the nearby Ostiense Museum. This museum, which is undergoing refurbishment, is expected to reopen by the end of June after a three-year closure.