Archaeologists from the Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale have recently uncovered a significant Roman-era structure submerged near the coastline of Campo di Mare on Italy’s western coast. This discovery is part of a broader three-year program aimed at excavating and preserving the remnants of ancient Roman architecture that have succumbed to the sea over time.

The initial breakthrough occurred in 2021 when researchers identified a cipollino marble column complete with its Ionic capital. This column was associated with a circular structure, approximately 50 meters in diameter, which was entirely submerged and located a few meters from the coast. Subsequent excavations and underwater surveys revealed that the structure is likely a maritime pavilion that was part of a larger Roman villa complex.
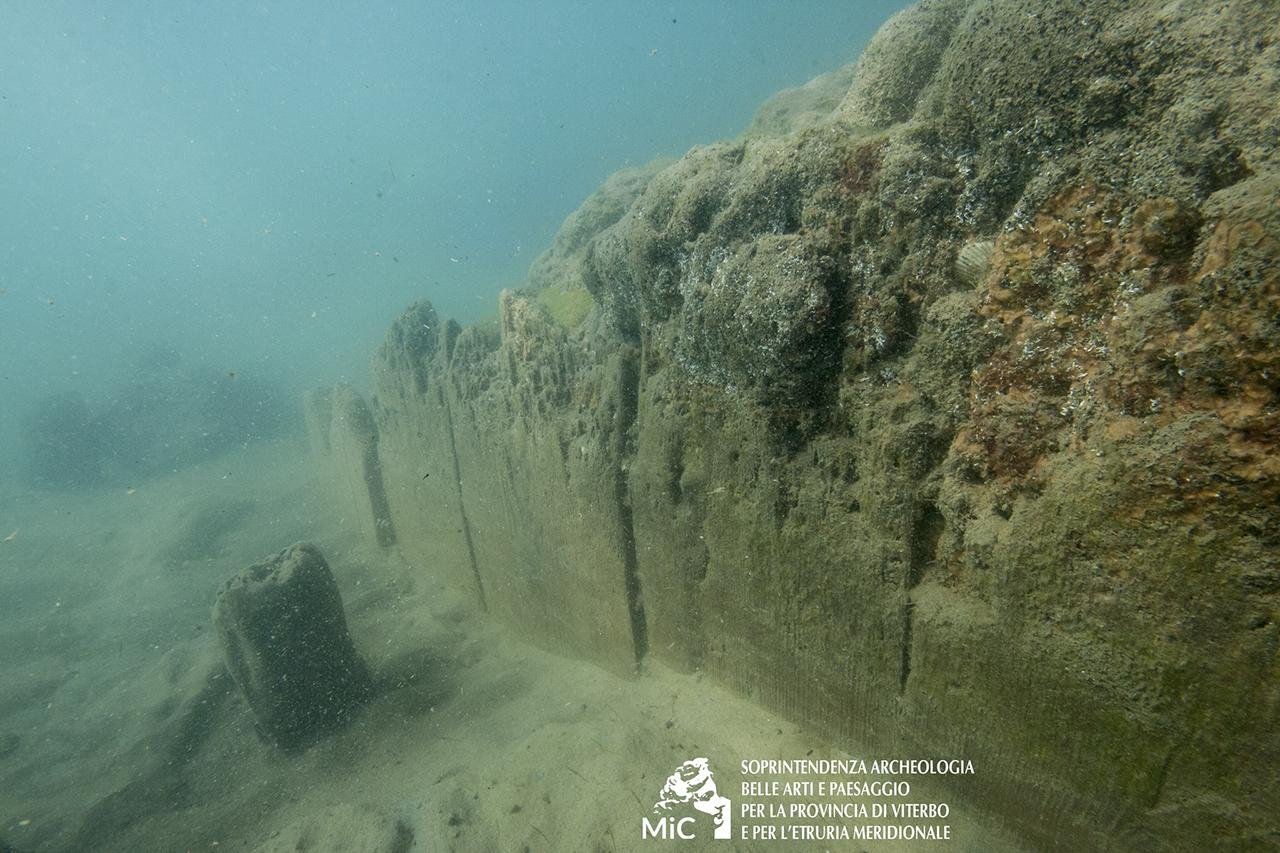
The submerged pavilion is constructed with notable architectural sophistication. The excavation team, led by the Underwater Archaeology Service of the Superintendency and supported by CSR Restauro Beni Culturali, uncovered two concentric belts of brick walls, built using a double layer of triangular bricks and mortar. These walls, spaced about three meters apart, were founded on a clay base that helped preserve wooden formwork and numerous foundation posts.
One of the significant findings within the structure includes opus spicatum flooring, a type of masonry where bricks are laid in a herringbone pattern. This pattern, primarily decorative during the Roman period, was often used for paving and occasionally as wall infill. The team also discovered traces of opus signinum, a Roman concrete made from small pieces of broken pottery, including amphorae, tiles, or bricks. Opus signinum was primarily used for its waterproofing properties in structures like baths, aqueducts, and cisterns.

Fragments of opus sectile pavement were also found, indicating the structure’s richness and elegance. Opus sectile is a decorative technique using cut and inlaid materials to create intricate designs, often found in luxurious settings.
Despite challenging marine conditions, characterized by constant waves and coastal erosion, the excavation and documentation of the site progressed efficiently. The structural remains, suffering from continuous coastal erosion, required meticulous cleaning, restoration, and consolidation, especially of the wooden parts. This delicate work was carried out by underwater restorers from CSR Restauro Beni Culturali. Additionally, the Municipality of Cerveteri and the Port Authority of Civitavecchia facilitated the interdiction of work areas to enable uninterrupted restoration activities.
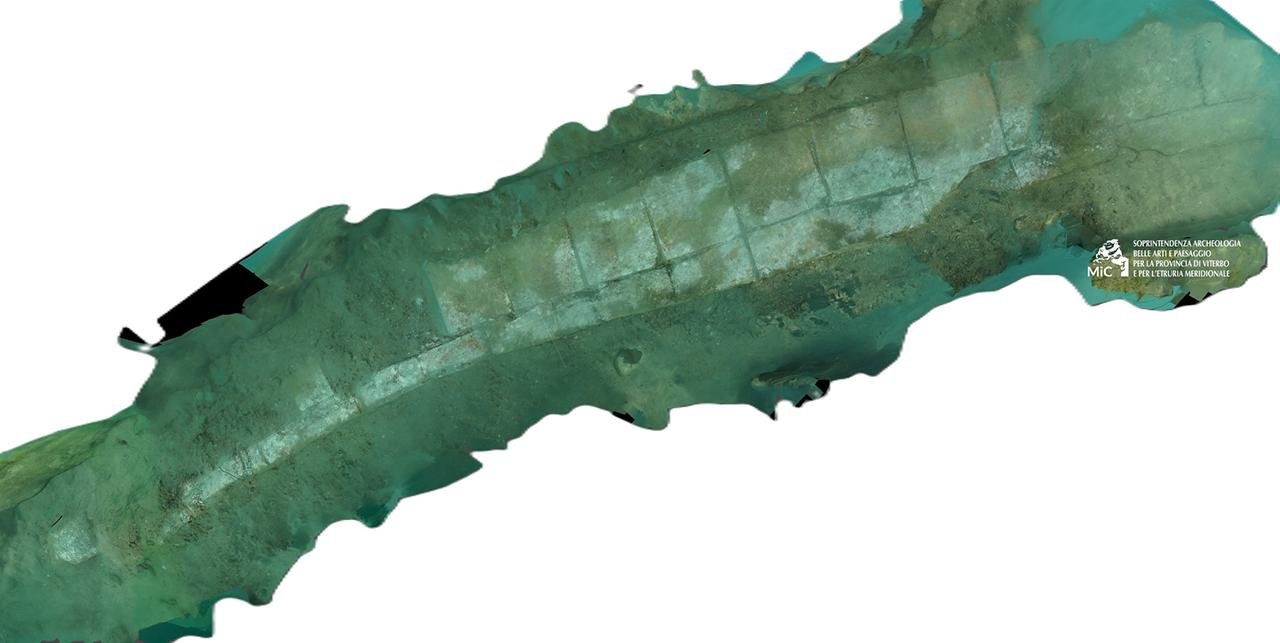

The discovery and subsequent analysis of the pavilion suggest it was a luxurious and representative part of a Roman villa, strategically located near the ancient route of Via Aurelia. This route was significant during the Roman era, connecting Rome with various coastal and inland regions. The opulence of the pavilion, as indicated by the architectural elements, implies that it may have belonged to a high-ranking member of the Roman aristocracy.
According to a press statement from the Soprintendenza Archeologia Belle Arti Paesaggio Etruria Meridionale, the architectural elements of the pavilion underscore its importance within the context of Roman villa architecture. The extensive use of opus signinum and opus spicatum, along with the presence of opus sectile, highlights the advanced construction techniques and the aesthetic sensibilities of the period.
Future geophysical surveys are planned in collaboration with the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV). These surveys aim to provide a detailed study of the site and ensure its preservation against relentless coastal erosion.