An archaeological excavation in Iraq’s historic Babylon Governorate has led to the discovery of 478 artifacts.

This significant find, led by archaeologist Quhtan Abbas Hassan Aboud, is part of an ongoing excavation at site 19/3 in the Al-Fayadiya district. The discoveries offer insights into two distinct historical layers: the Sasanian and Old Babylonian periods, providing a rare glimpse into the evolution of one of the world’s earliest civilizations.
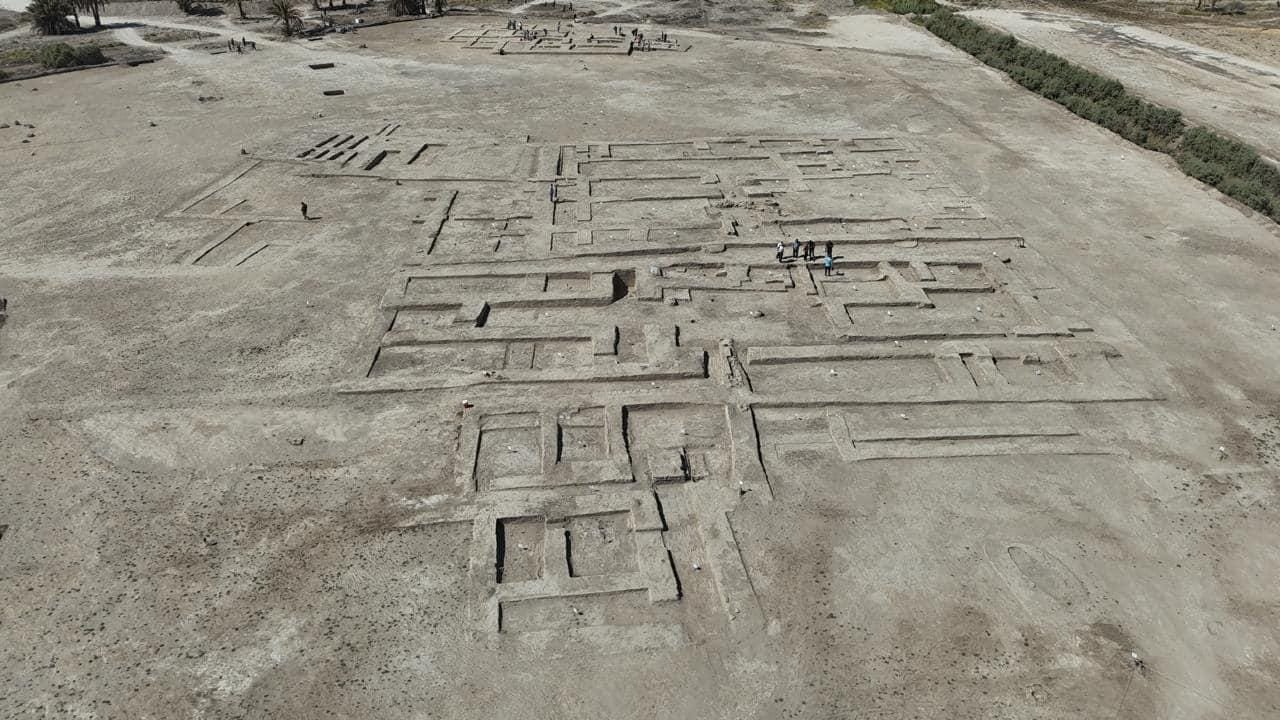
The excavation site is divided into two sectors, named A and B. Sector A covers an area of approximately 6,000 square meters and features two distinct archaeological layers. According to Soheil Al-Tamimi, Director of Iraq’s Department of Excavations, the upper layer corresponds to the Sasanian period, which lasted from 224 to 651 CE, but it has been significantly damaged by erosion and human activity over time. The deeper and better-preserved layer dates back to the Old Babylonian period, offering researchers a more intact snapshot of urban life during that era, which spanned roughly from 1894 to 1595 BCE.
Sector B, covering a larger area of 9,000 square meters, has proven even richer in its findings. Excavations here have uncovered two residential units featuring rooms of varying sizes, potentially used for different functions such as living spaces, storage, or work areas. These structures are believed to represent common Babylonian homes.
Among the artifacts unearthed, several stand out for their historical and cultural significance. Pottery vessels, cuneiform writing tablets, and cylinder seals were discovered in excellent condition. Cuneiform, the world’s oldest known writing system, was used more than 5,000 years ago and offers invaluable information about Babylonian governance, trade, and religious practices. The clay tablets often functioned as early legal documents, and some were encased in a clay outer shell—a precursor to the modern envelope.
Additionally, cylinder seals, small cylindrical objects carved with intricate symbols, were used to sign documents or mark ownership in ancient Mesopotamia. These seals, often made from stone or other durable materials, were essential tools for people across all levels of Babylonian society.
The artistry and craftsmanship of these artifacts, especially the cylinder seals, highlight the visual culture and aesthetic developments of the Babylonian period. The seals feature detailed iconography that has helped historians trace the evolution of Babylonian art and symbolism over time. According to a statement from Iraq’s General Authority of Antiquities and Heritage, the findings represent a breakthrough in the understanding of Babylonian urban development and material culture.