An archaeological excavation at Nowe Objezierze in northwestern Poland has uncovered a Neolithic rondel that offers new perspectives on the ceremonial and social practices of early agricultural communities. The discovery, led by Dr. Lech Czerniak of the University of Gdańsk, reveals the architectural, cosmological, and societal complexities of these monumental structures, dating back to approximately 4800 BCE.
What Are Rondels?
Rondels, circular structures characterized by concentric ditches and wooden palisades, are unique ceremonial centers that emerged within Danubian Neolithic societies around 4800 BCE. They were prominent across regions stretching from the middle Danube to the Vistula and the Rhine rivers. These structures are thought to have been spaces for communal rituals, often aligned with astronomical events such as the winter solstice. Their use spanned about 300 years, gradually declining around 4500 BCE due to shifting social and environmental factors.
Key Features of the Nowe Objezierze Rondel
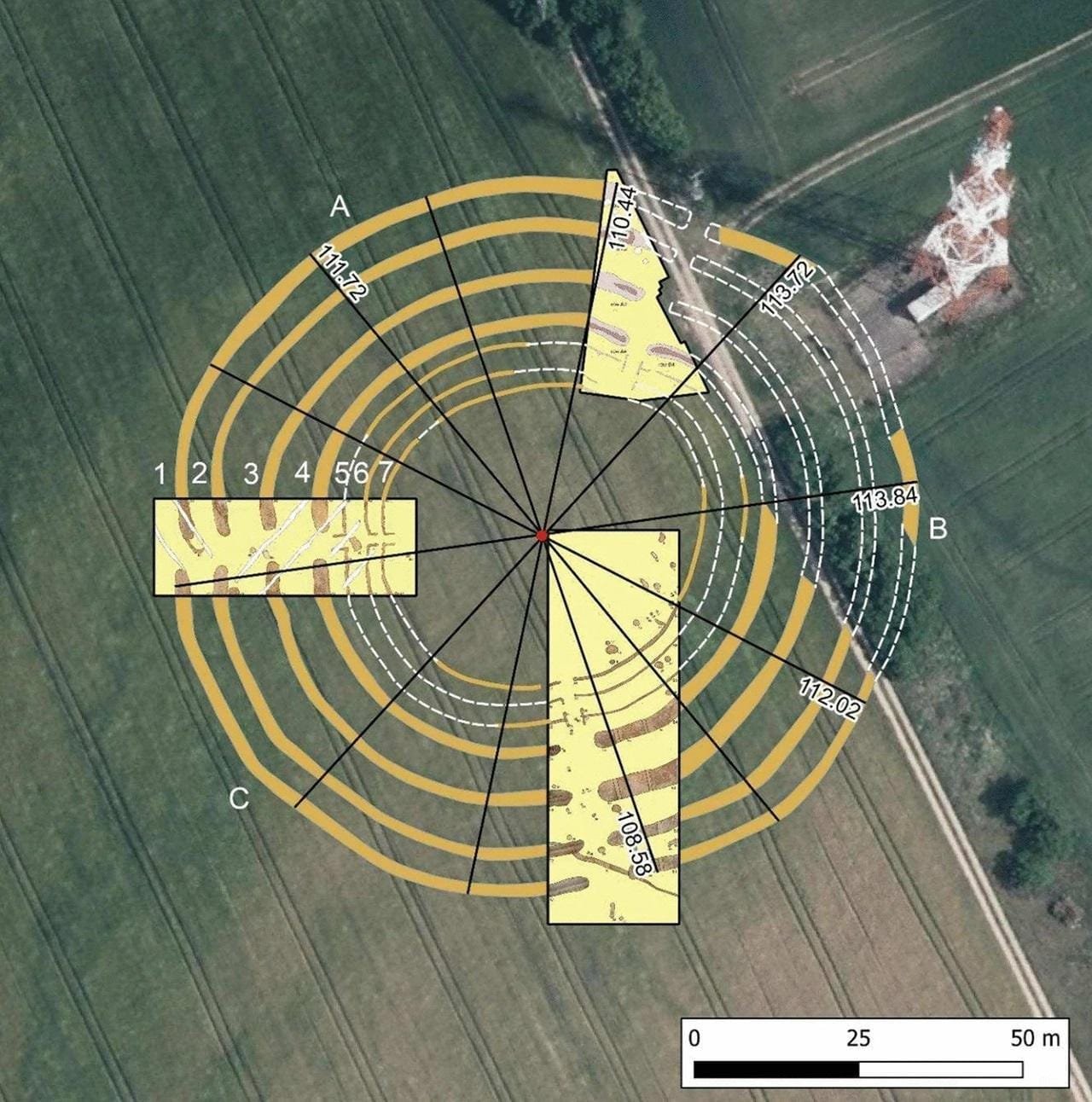
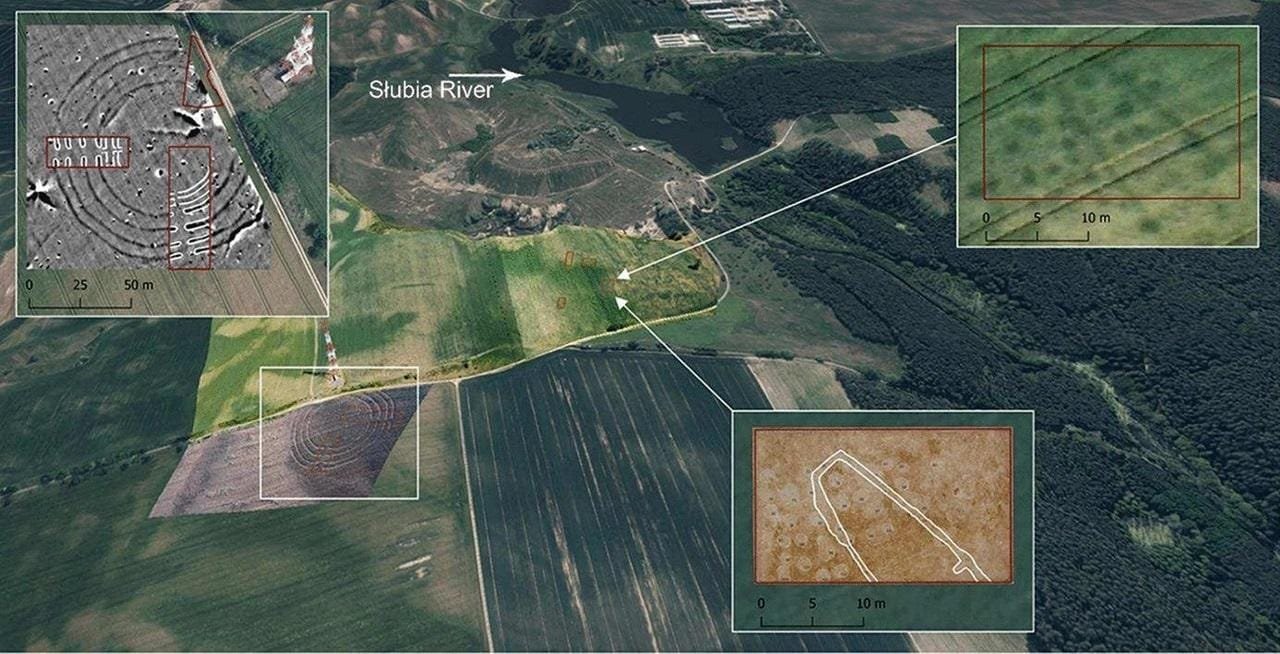
The rondel at Nowe Objezierze stands out for its size and complexity. Measuring 112 meters in diameter, it comprises four concentric ditches and multiple trenches that supported wooden structures. Researchers used the chaîne opératoire method to reconstruct its construction, revealing a meticulous process that involved extensive planning, technical expertise, and social collaboration.
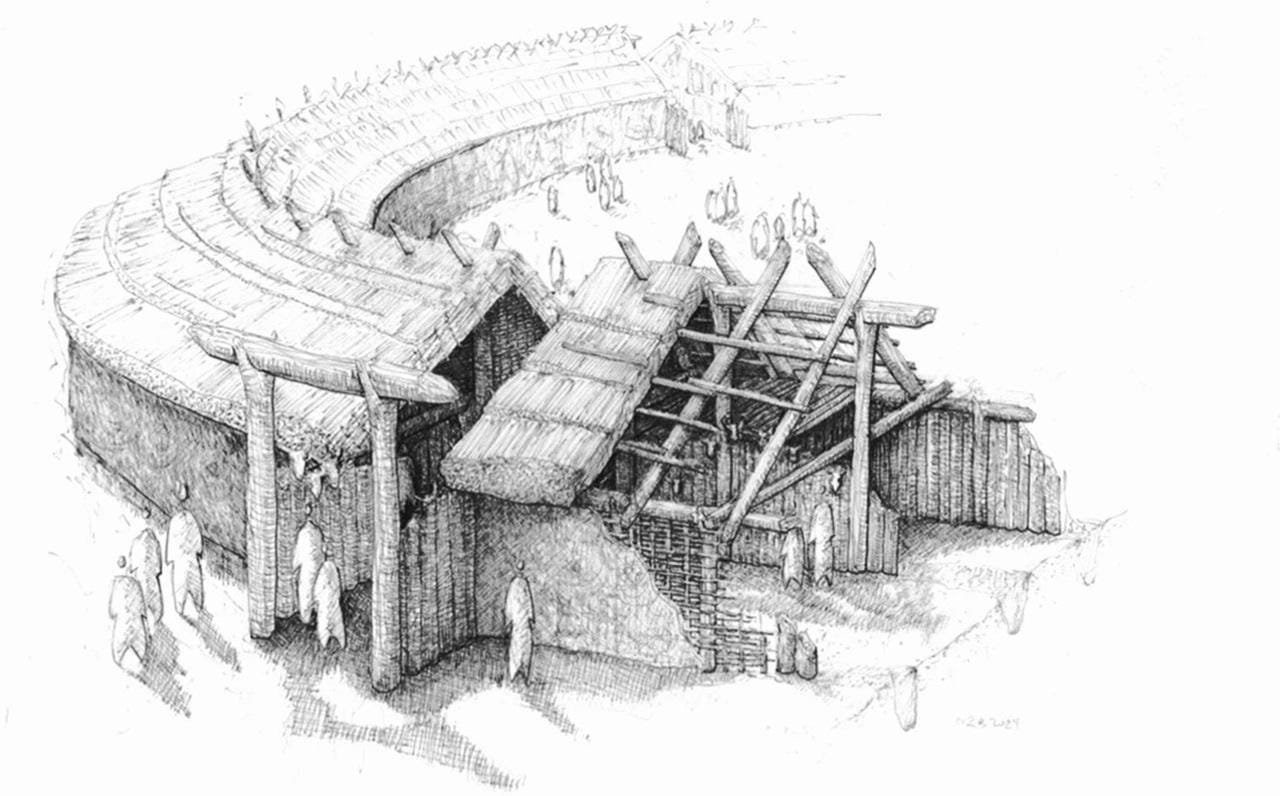
The construction likely involved hundreds of community members over several years. The process began with marking the central circle and preparing the land, possibly accompanied by initial rituals to mobilize the community. Wooden structures, likely reinforced with clay and reed roofs, were built over the trenches to withstand environmental challenges.
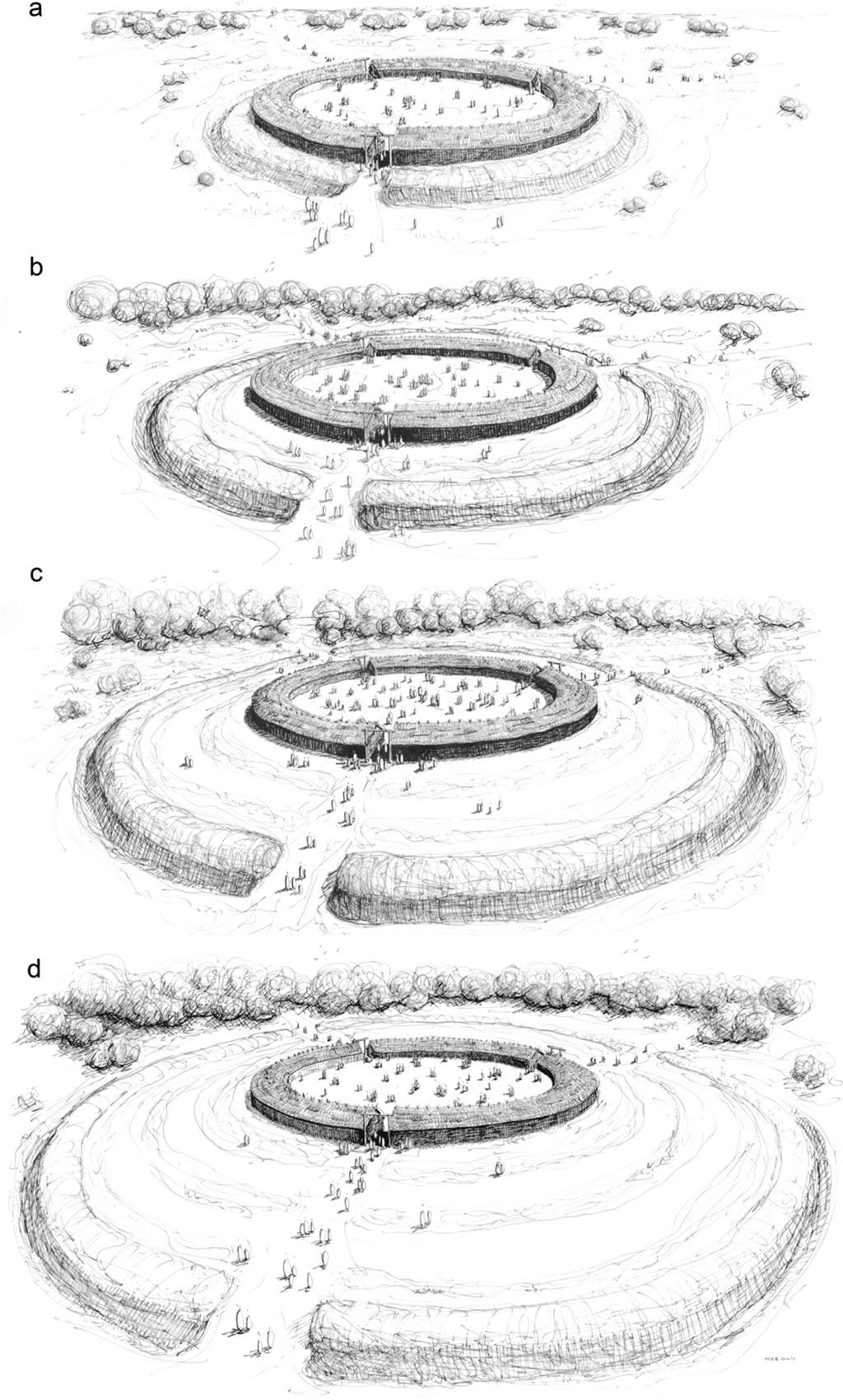
One of the most remarkable aspects is the evidence of cyclical rituals tied to the rondel’s construction and use. The ditches, for instance, were periodically dug, backfilled, and reopened in coordination with ceremonies. This cyclical activity points to the rondel’s role not only as a site for rituals but also as a symbol of continuity and renewal.
Social and Ritual Significance
The rondel served as a hub for communal gatherings, celebrations, and possibly sacrifices, as evidenced by animal remains and pottery found in the ditches. These ceremonies reinforced social cohesion, established communal hierarchies, and possibly resolved territorial disputes.
While some researchers argue that rondels were displays of political power, the evidence from Nowe Objezierze suggests a more egalitarian society. The collective effort in its construction and maintenance hints at a shared sense of purpose, possibly managed by groups akin to secret societies that preserved ritual knowledge.
Astronomical Alignment and Ritual Cycles
The orientation of the rondel’s entrances reveals the builders’ advanced knowledge of astronomy. Aligned with cardinal points, the entrances likely synchronized ceremonies with solar events, such as the winter solstice. This alignment underscores the integration of cosmological understanding into Neolithic architecture.
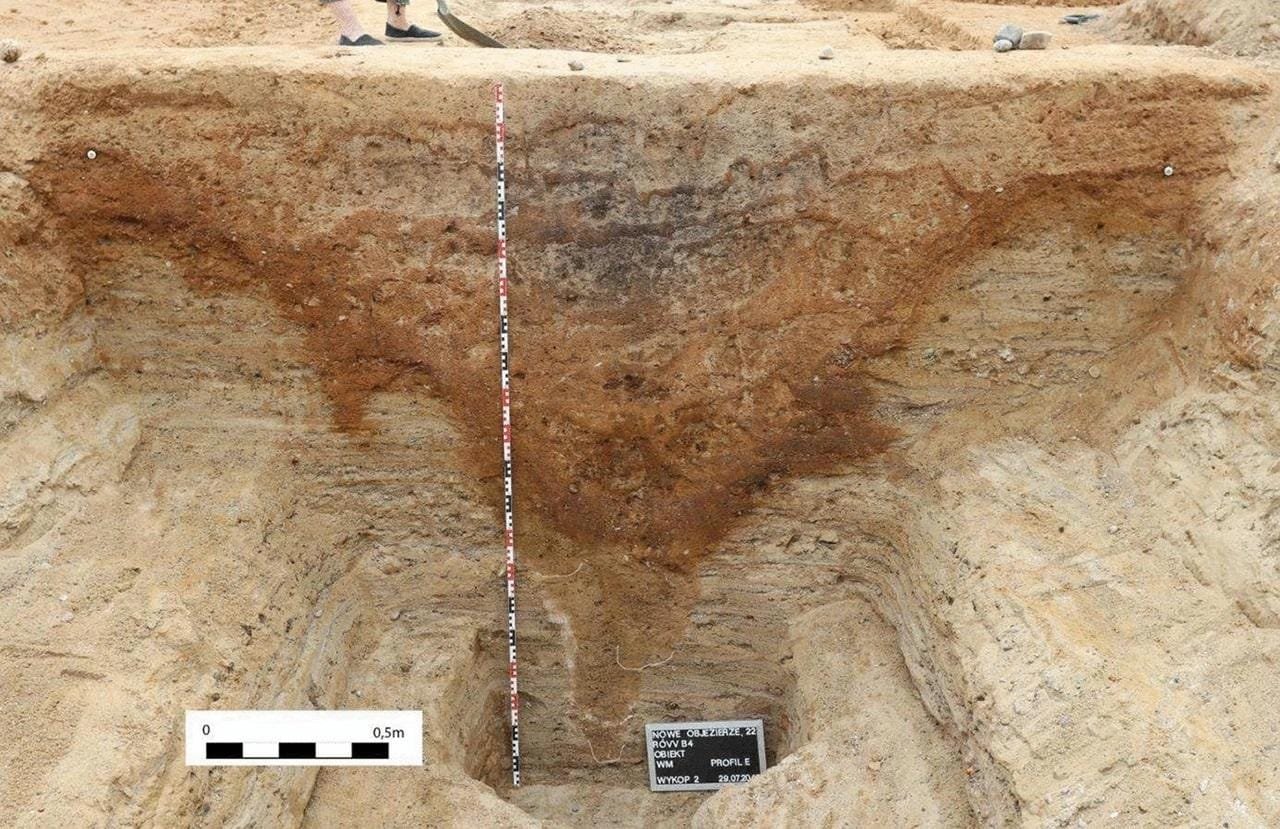

The decline of the Nowe Objezierze rondel
The decline of the Nowe Objezierze rondel mirrors broader changes in Neolithic societies. Pollen analysis indicates reduced agricultural activity, suggesting population decline and potential migration. Over time, the rondel was gradually abandoned, reflecting shifts in social structures and rising internal conflicts.






















