Archaeologists are exploring the sacred landscapes where the Incas once walked during their Capacocha rituals. This ancient sacrificial ceremony involved offering children to the gods on top of high mountains and volcanoes. New studies are looking at the pathways that lead to these sacred sites. They pay special attention to tambos, which are rest stations built along the way to aid pilgrims on their arduous journey.
The Capacocha ritual stood out as one of the most significant ceremonies in the Inca Empire. People performed it to appease the gods and ensure prosperity. The Incas selected both boys and girls from noble families for these sacrifices, seeing this as a great honor and a means of securing political favor for their families. The journey began in Cusco, the Inca capital. There, the children were ceremonially paraded around four grand statues. These statues represented the Creator, the Sun God, the Moon God, and the Thunder God. After this, the children began a lengthy pilgrimage to remote shrines known as huacas. At these sites, the final sacrifice took place.
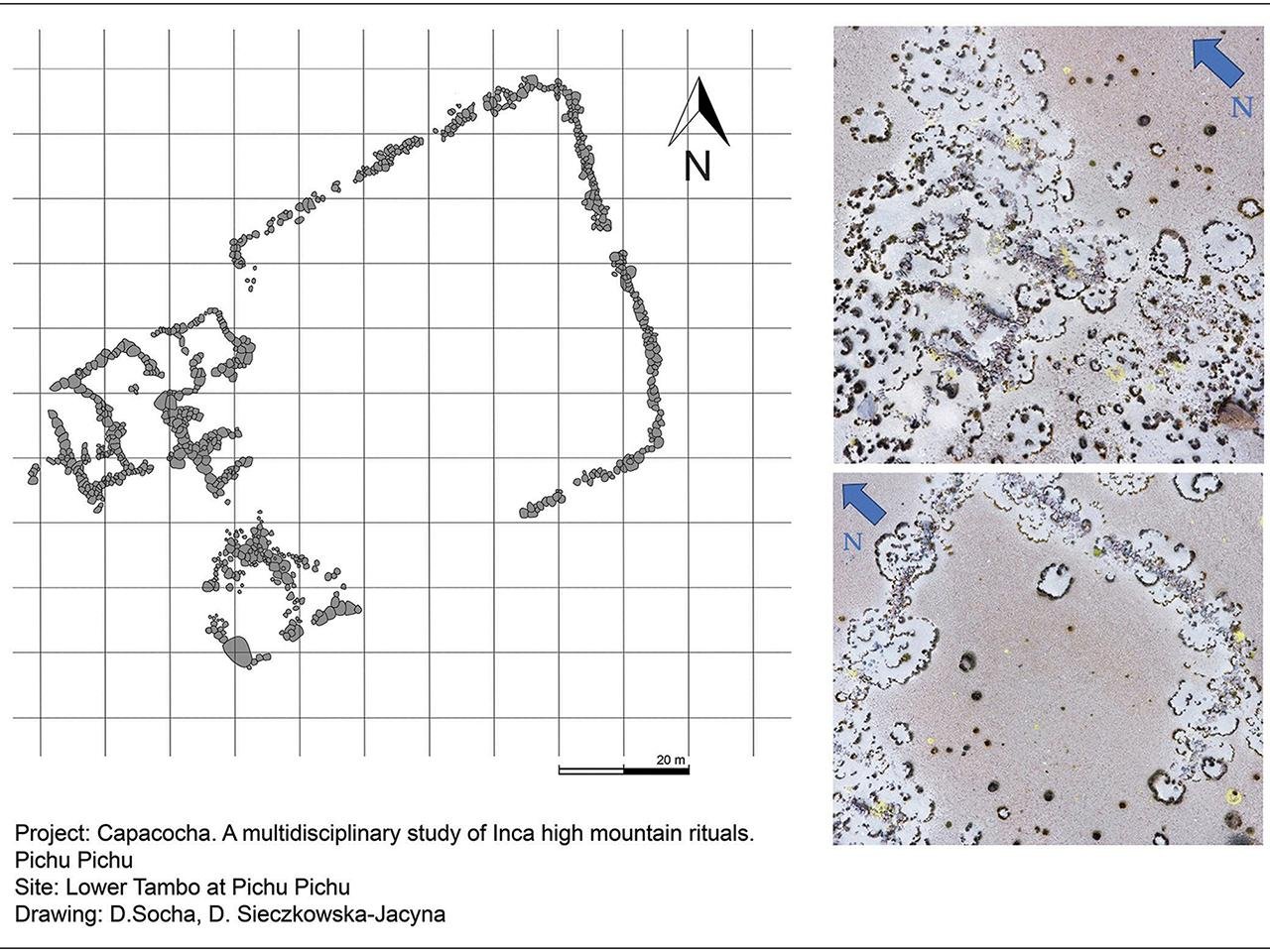
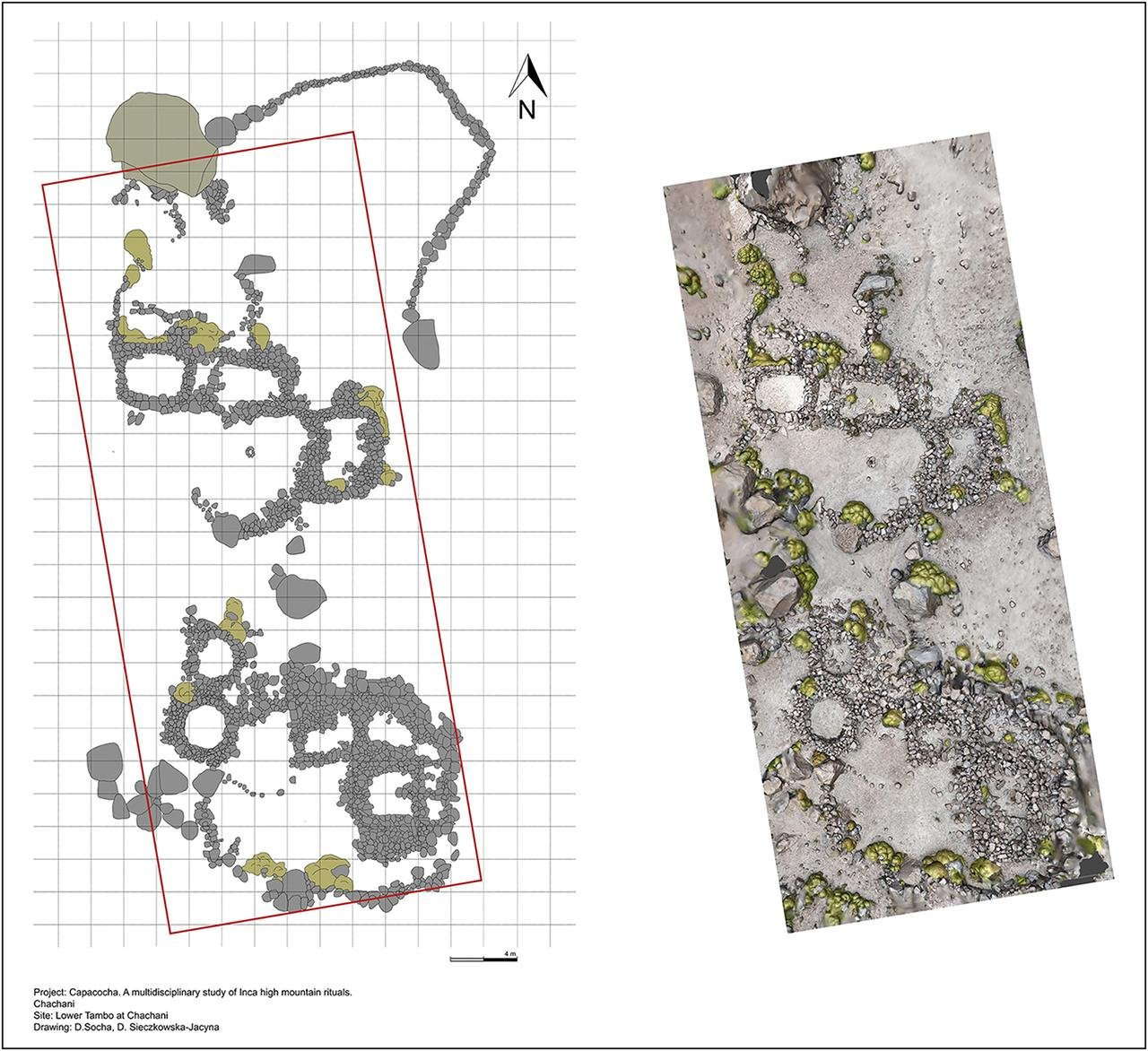
A recent study published in the journal Antiquity has provided new insights into the tambos along these pilgrimage paths. It focused on the Chachani volcanic group and the dormant Pichu Pichu volcano in southern Peru. The research team used satellite mapping and photogrammetric imaging to examine the spatial arrangement of these structures. Their findings show a hierarchical organization reflecting the social divisions among the pilgrims.
The tambos were found to be divided into two distinct sections: a larger, lower-altitude area with several buildings and a smaller, higher-altitude section with fewer structures. At Chachani, the lower tambo had 14 buildings around a central courtyard, or kancha, which served as a gathering place for large groups of travelers. On the other hand, the higher tambo had just one building beside a large rock marking the final stop before the summit, which took about six hours to reach. The Incas built small shelters along the way to give pilgrims a place to rest, and some of these shelters still stand today.
A similar pattern was seen at Pichu Pichu, where the lower tambo had eight buildings around a kancha, while the upper tambo consisted of a three-room structure located next to a rock shaped like the volcano. The spatial organization of these tambos suggests that they were designed to accommodate pilgrims from different social statuses, such as priests, sacrificial victims, their families, and others involved in the huaca cult. The researchers think the lower tambos likely served as communal gathering points, while the upper tambos were reserved for smaller, more exclusive rituals.
One crucial aspect of the Capacocha ritual involved divination, which was conducted in secluded spaces. Oracles played a vital role in Inca society. Their prophecies influenced major religious, political, military, and economic decisions. Historical records, such as those from chronicler Hernández Príncipe, indicate that the oracle of the Capacocha mummy Tanta Carhua was located below the hill where the mummy was buried. The boulder at Chachani, which exhibits signs of water flow, might have been used in ritual liquid ceremonies linked to divination. These ceremonies invoked the power of the mountain deities to ensure water and fertility.

Archaeologists have found Capacocha sites on mountaintops in northern Chile, southern Peru, and northwestern Argentina. The team aims to conduct biochemical analyses of artifacts found at the tambos to determine the origins of the pilgrims and establish a chronological framework for these sacred journeys. They also want to find other places related to Capacocha rituals to study architectural patterns and the Inca state’s management of these religious ceremonies.























