A recent study published last year in the journal Cell has identified the ancient origins of a genetic mutation that confers resistance to HIV, and how it first appeared in an individual who lived near the Black Sea between 6,700 and 9,000 years ago. Named CCR5 delta 32, the uncommon genetic variant disables a key immune protein used by a large majority of strains of the HIV virus to enter human cells and therefore “locks out” the virus in individuals who carry two copies of the mutation.

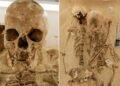
HIV is a relatively new disease. It was only identified in the last century, but the genetic mutation that defends against it has existed for thousands of years. The international research team, led by Professor Simon Rasmussen and senior researcher Kirstine Ravn of the University of Copenhagen’s Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Basic Metabolic Research (CBMR), confirmed this through the analysis of over 3,000 genomes of ancient and modern humans. The study used a new AI-based method to detect the mutation in the often degraded DNA of ancient bones.
The researchers analyzed DNA from more than 900 ancient people, ranging from the early Mesolithic era to the Viking era. They found that the CCR5 delta 32 mutation emerged abruptly and rapidly spread in human populations, particularly after humans transitioned from a nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle to more densely settled agricultural societies. That shift in lifestyle likely put humans in contact with new pathogens, imposing evolutionary pressure that favored individuals with the mutation.
“People with this mutation were better at surviving, likely because it dampened the immune system during a time when humans were exposed to new pathogens,” explained Leonardo Cobuccio, a co-author of the study and postdoctoral researcher at CBMR, in a statement. “While it might sound negative that the variation disrupts an immune gene, it was probably beneficial. An overly aggressive immune system can be deadly — think of allergic reactions or severe cases of viral infections like COVID-19, where the immune system often causes the damage that kills patients.”

CCR5, the protein affected by the mutation, helps direct immune cells to areas of inflammation within the body. Disabled by the delta 32 mutation, however, it becomes harder for HIV to infect these cells. This discovery has already been put to use in medicine: scientists have used the protective properties of the mutation to successfully treat a handful of HIV patients.
One of the most fascinating findings of the research is that every modern carrier of this mutation, found in approximately 10 to 16 percent of Europeans, and up to 25 percent of Danes, probably descends from that single individual living around the Black Sea thousands of years ago. Previous hypotheses had suggested that the mutation had spread in response to more recent events such as the Black Death or Viking-era pandemics. The new genetic evidence, however, defies such a supposition and shows that the mutation became widespread between 8,000 and 2,000 years ago, long before such events.
The study redefines our understanding of how humans have learned to live with disease and demonstrates the power of combining ancient DNA and modern technology to uncover hidden pages of human history.






















Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
An interesting hypothesis to test would be whether that mutation is present with others that enhance other ways to combat infection.
What does this genetic discovery have to do with “Viking Age “ ?
Thank you for your comment. As indicated in both the title and the content of the article, the research involved analyzing human remains from a broad time span, ranging from prehistoric periods up to the Viking Age. Notably, the remains from the Viking Age played a significant role in the discovery and conclusions about the ancient HIV-resistant gene.
What was the reservoir for the type of HIV found around the black sea 6000 to 9000 years ago
We think now that the current HIV was from Simian /animals
in other words are there any ideas of where this more ancient form of HIV came from?
This HIV resistant gene has been found in .. where exactly in the near Black Sea?
So what it has to do with vaccine of hiv… i mean cure..
nice information and good article thank you
The Delta32 mutation at its origin had nothing to do with HIV; HIV is much more recent. Delta32 had to do with improved immune tolerance or other indications.
Seems to me that this gene was stolen and swaped out by the parasites it seems to me they have been steadily degenerating our dna but telling us we are evolving but instead.its the opposite so why the big cover up and i already know the answer and it has to do with the one thing that causes all disease and feeds upon us creating viral plasmid trojan horse viruses from the ionized miasma coming off the parasites inside the body and they get absorbed by a cell and reproduce causing stds cancer mental illness shylock type behaviour serial killer rabid urges sexual deviance you know the typical celebrity and elite class individuals life style on the weekends. Interesting for sure though it kinda proves my theory amoung other aspects and anomalies that have been covered up and sanatized that i would have never known if i didnt spend my free time learning all i can from books uploaded to internet archive and thank god for that especially since the only free to download stuff if pre 20 th centriry and i pretty much have a saying everything past 1920 is basically fiction. Malaria is the main culprit that tampered with our dna and capped the telemers and flipped the chromosomes inside itself while loosing the ability to repair and heal damged dna and now our dna is at around 7% or 8% virus
Your more than the average conversation or commentor Hans please stay intelect! You have done your digging in medical school or something huh! Nice to read a comment not from the average Joe
Thank you for your contribution.
For everyone asking about the HIV virus, it’s not actually a recent virus, it was just recently identified. But it’s been traced back much further than this article about the discovery of DNA mutations. So a human having the immunity to HIV is not new news. There are people out there that have this same mutation. When HIV first got identified in the late 70s the immunity mutation was found not long after. A gay man living in the San Francisco area whom frequently visited the bathhouses in the areas that were gathering spots for gay men. As many of the man’s friends were dying around him, he never got sick, that’s when it was found he had the immunity to HIV. This isn’t something new at all. The article is just making a statement about how the mutation has been found in ancient DNA.
Yes, it was first recognised in 1981 but been around for a number of years before that so no doubt there would’ve been cases of immunity, however, this article is about the archaeology that identified the genetic mutation that’s been around for thousands of years and how that discovery has finally allowed for several patients to be treated.
Having knowledge of the immunity without understanding it isn’t exactly helpful. Identifying it’s origins is pretty amazing stuff with new developments in archaeology.
Hello, I’d like more information about “the reconstructed Viking Age village” pictured – location and provenance, thanks