Archaeologists have identified a previously unknown early modern fortification in Świerże, in the Dorohusk municipality of Chełm County, eastern Poland. The site lies within a historic manor and park complex near the Bug River, a region shaped by repeated military conflicts during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
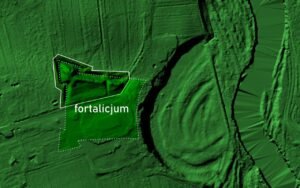
Researchers located the structure through airborne laser scanning and detailed LiDAR analysis, followed by field inspection. The earthworks had long been visible in the terrain, yet earlier surveys had misidentified them as the remains of an early medieval stronghold with a horseshoe plan. The new study shows a different picture. The preserved forms match a bastion fortification, or fortalicium, built for gunpowder warfare.
Today, only part of the northwestern section survives, including one corner bastion. The remaining ramparts rise to about two meters and cover roughly 0.4 hectares. Based on the layout of the visible embankments, the original complex likely covered around 1.5 hectares and measured close to 120 by 140 meters. The plan appears rectangular, with projecting bastions at the corners. Such arrangements reflect principles linked to the French school of fortification engineering, associated with Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban. Comparable fortified residences exist in Tykocin, Krynice in Tomaszów County, and Duba in Zamość County.
Historical maps confirm the structure’s existence. The Austrian military map West Galizien, prepared between 1801 and 1804, marks the site as a ruin. By the turn of the nineteenth century, the fortification had already lost its defensive role. Nineteenth-century maps show further damage, especially in the southern section. Farming activity and landscape changes tied to the creation of the manor park contributed to the gradual leveling of the earthworks. The southern part lay outside the protected park area and deteriorated further. Construction of the Church of Saints Peter and Paul in the nineteenth century likely erased what remained of that sector.
Archival sources support the dating. A document from 1694 mentions an entrenchment near the Bug River. An eighteenth-century record refers to nearby fields known locally as the rampart, preserving the memory of the former defenses. The fortification may be connected to the Olędzki family, who owned the estate in the late seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, or to Mikołaj Firlej of Dąbrowica, who held part of the property before the mid-seventeenth century.
The proposed date range fits a period marked by Cossack uprisings, the Swedish Deluge, and wars between Poland and Russia. Landowners in border regions often fortified their residences during these conflicts. In 1792, during the Polish–Russian War, Prince Józef Poniatowski established his headquarters at Świerże while commanding forces along the Bug River. The estate served as a base for operations linked to fighting near Dubienka.
Further archaeological work and archival study will clarify the sequence of construction, use, and abandonment. Excavation could also help explain how the earlier fortified residence related to the later manor and how the estate changed over time.
More information: Lublin Voivodeship Conservator of Monuments























Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.