Bush Barrow is an archaeological site located in Wiltshire, England. It is best known for the discovery of a rich burial mound dating back to the early Bronze Age, around 4,000 years ago.
The burial mound was first excavated in 1808 by Sir Richard Colt Hoare, who found a chamber containing the remains of a man and a woman, along with a variety of grave goods. The man had been buried with a bronze dagger, a gold-decorated lozenge-shaped belt plate, a shale wrist guard, and a beaker. The woman had been buried with a jet button, a bronze awl, and a gold-decorated lozenge-shaped belt plate.

The Bush Barrow burial is one of the most important archaeological discoveries from the early Bronze Age in Britain. It provides valuable insights into the burial practices, social hierarchy, and material culture of the period. The sheer scale of the burial, the richness of the grave goods, and the level of craftsmanship suggest that the individuals buried at Bush Barrow were of high status within their community.
Bush Barrow Lozenge
The Bush Barrow Lozenge is a small, intricately decorated gold artifact that was discovered in 1808 in the Bush Barrow burial mound. The lozenge is made of thin sheet gold and measures approximately 3.6 inches by 2 inches.
The lozenge is decorated with a series of raised lines and dots arranged in a complex pattern. The decoration is divided into four sections, each with a central motif surrounded by smaller motifs.
The significance of the Bush Barrow Lozenge is debated among archaeologists and historians. Some believe that it may have been used as a decorative element on a piece of clothing or armor, while others suggest that it may have had a ceremonial or ritual purpose.
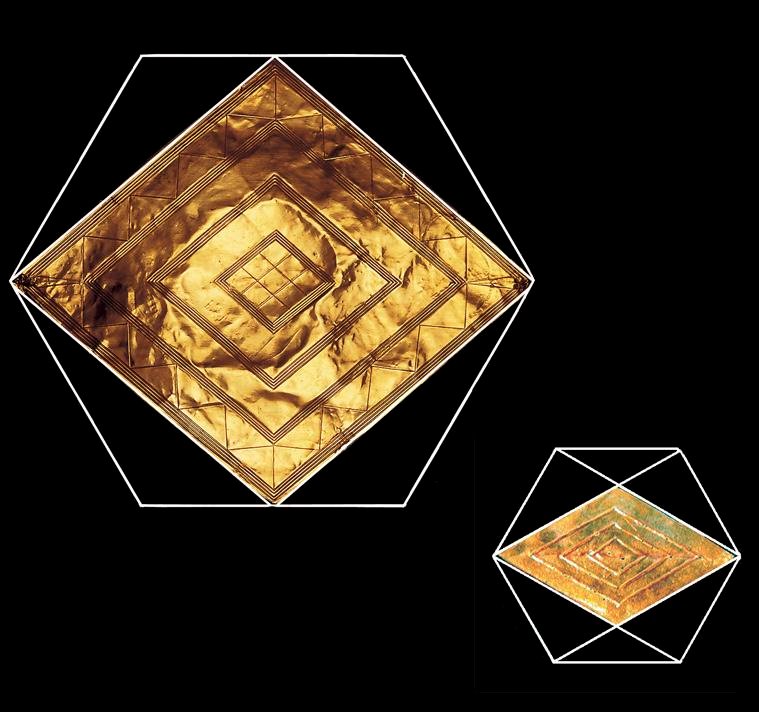
One theory is that the lozenge represents a map or plan of the cosmos, with the central motifs representing the sun and moon, and the smaller motifs representing stars or constellations. Others have suggested that the lozenge may have had connections to shamanism or other spiritual practices.
Despite its small size, the Bush Barrow Lozenge is considered to be one of the most important artifacts from the Bronze Age in Britain, and it continues to be the subject of ongoing research and study.
The artifacts found at Bush Barrow are now on display at the Wiltshire Museum in Devizes, England. The site itself is managed by English Heritage and is open to the public. Visitors can see the outline of the burial mound and explore the surrounding landscape, which includes other important prehistoric monuments such as Stonehenge and Avebury.





















