Archaeologists from the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1266 of Kiel University (CAU) and the Archaeological Institute of the Slovak Academy of Sciences (Nitra) unearthed the remains of 38 individuals in a ditch surrounding the settlement during this year’s excavation in Vráble, Slovakia. Their well-preserved skeletons were jumbled together, and all of them, with the exception of a young child, were missing their heads.
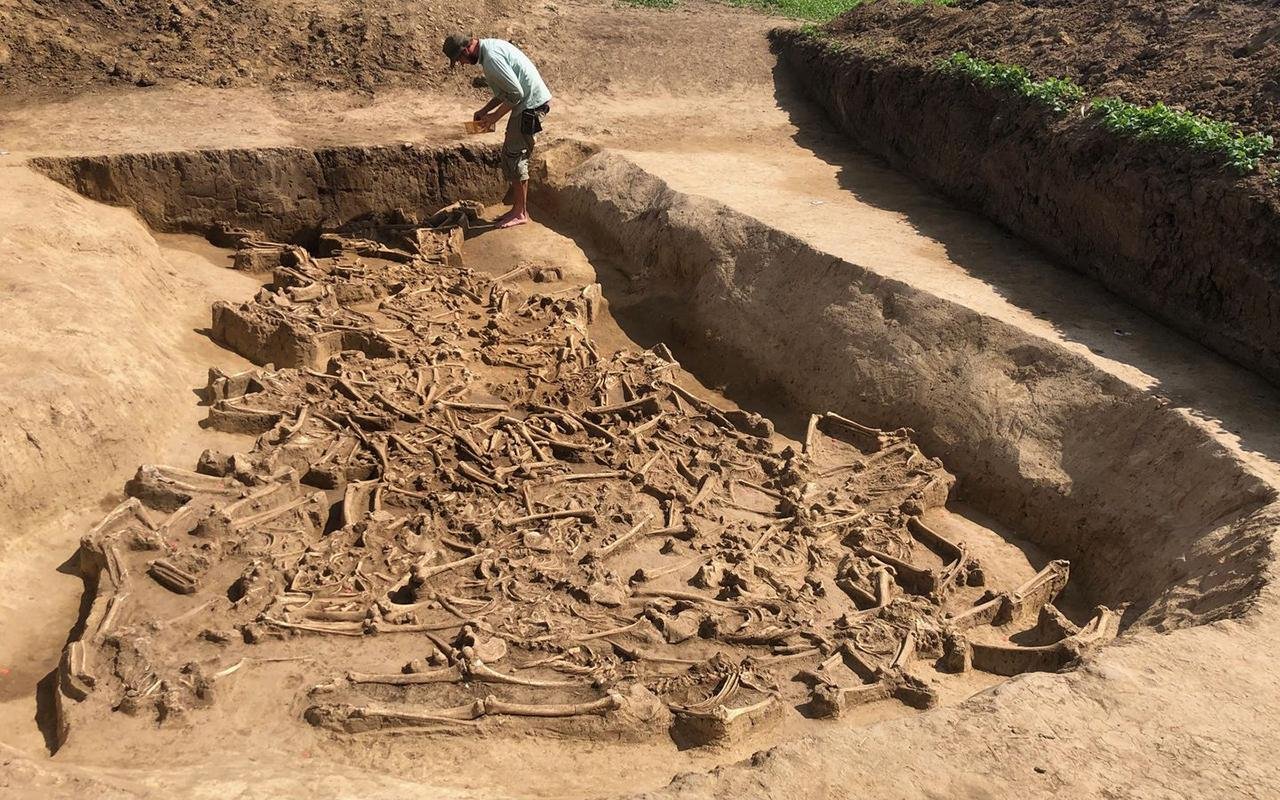

Future investigations will focus on how, when, and why these people’s heads were removed. The team discovered headless skeletons there last year. “We assumed to find more human skeletons, but this exceeded all imaginations,” reports project leader Prof. Dr. Martin Furholt.
An important Neolithic settlement site
A significant Neolithic settlement site Vráble-Ve’lke Lehemby (5,250-4,950 BCE) was one of the largest Early Neolithic settlement in Central Europe and has been a research focus of the CRC 1266 for several years. The archaeological artifacts are associated with the Linear Pottery Culture (LBK). Geomagnetic measurements were used to identify 313 houses in three neighboring villages. Up to 80 houses were inhabited at the same time, which was an exceptional population density for the time period.
The southwestern of the three settlements was separated from the others by a 1.3 km-long double ditch. Some areas were reinforced with palisades, which should not be interpreted as a defensive structure, but rather as a boundary marking of the village area.
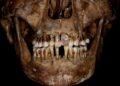
During the summer of 2022, the Slovak-German team discovered the remains of at least 38 people distributed across an area of around 15 square meters. One on top of the other, side by side, stretched out on their stomachs, crouched on their sides, on their backs with their limbs splayed out—the position of the skeletons does not suggest that the dead were carefully buried. Instead, the positions indicate that the majority of them were thrown or rolled into the ditch.
With the exception of one infant, all of them are missing their heads, including their lower jaws. “In mass graves with an unclear positioning, the identification of an individual is usually based on the skull, so for us this year’s find represents a particularly challenging excavation situation,” explains Martin Furholt.
Many unresolved questions: massacre, head-hunters, or peaceful skull cult
While the skeletons were being found, the first questions arose: Were these people killed violently, perhaps even decapitated? How and when were the heads removed? Or did the removal of the heads take place only after the corpses had decomposed? Are there any indications of the causes of death, such as disease? In what order were they placed into the ditch, could they have died at the same time? Or is it not a single mass burial at all, but the result of several events, perhaps even over many generations? A few clues to answering these questions already exist.
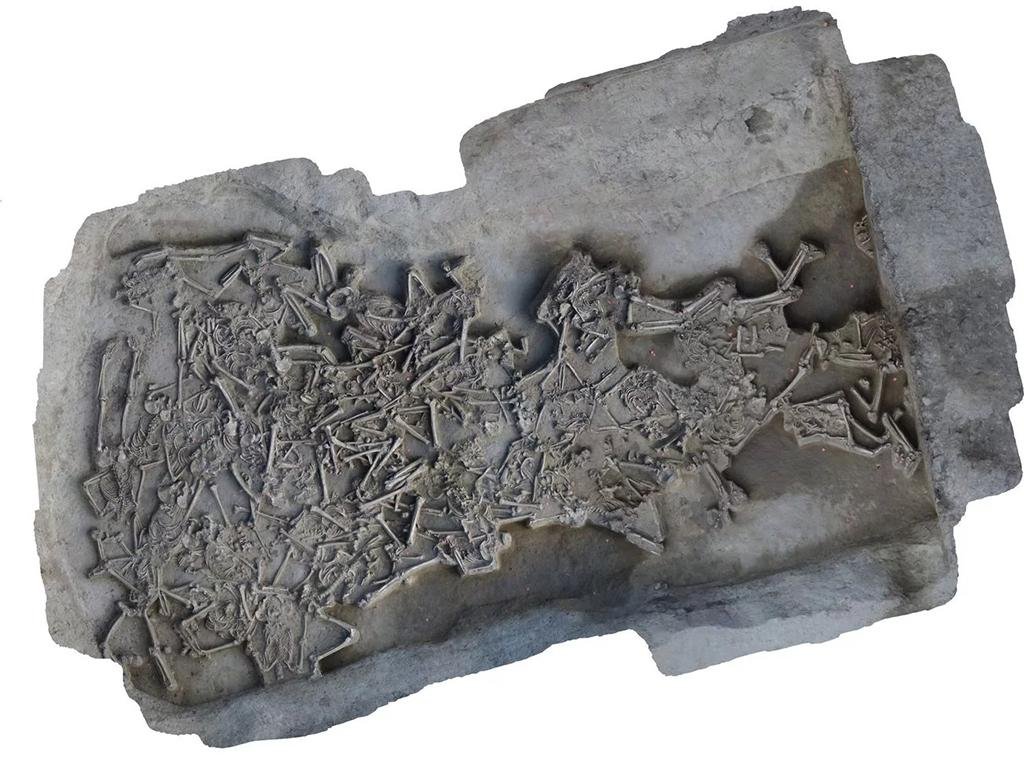

“Several individual bones out of anatomical position suggest that the temporal sequence might have been more complex. It is possible that already-skeletonized bodies were pushed into the middle of the trench to make room for new ones,” anthropologist Dr. Katharina Fuchs of Kiel University elaborates.
“In some skeletons, the first cervical vertebra is preserved, indicating careful removal of the head rather than beheading in the violent, ruthless sense—but these are all very preliminary observations that remain to be confirmed with further investigation.”
Interdisciplinary examinations of the skeletons should provide answers
An important part of further research is to find out more about the dead. Were they all of a similar age or a cross-section of society? Were they related to each other or to other Vráble dead? Were they natives or did they come from far away? Did they share a similar diet? Can any social significance be inferred from the treatment of the dead?
Answers can only be found in the interaction of detailed archaeological and osteological investigations, aDNA analyses, radiocarbon dating, and stable isotope analyses. The Kiel interdisciplinary research network of the Johanna Mestorf Academy, the CRC 1266, and the Cluster of Excellence ROOTS, in collaboration with the Slowakian Academy of Sciences in Nitra, offers excellent conditions for this further research.

Further considerations on meaning and interpretation are only meaningful based on such interdisciplinary research results.
“It may seem obvious to assume a massacre with human sacrifices, perhaps even in connection with magical or religious ideas. Warlike conflicts may also play a role, for example, conflicts between village communities, or even within this large settlement. Did these people fall victim to head-hunters, or did their fellow villagers practice a special death cult that had nothing to do with interpersonal violence? There are many possibilities and it is important to remain open to new insights and ideas. But it is indisputable that this find is absolutely unique for the European Neolithic so far,” explains project leader Dr. Maria Wunderlich. — Kiel University