Excavations at the Papowo Biskupie site in northern Poland have uncovered evidence challenging previous beliefs about the burial rituals of the Chełmno group, a northern community of the Lusatian culture from 1200 to 450 BCE.
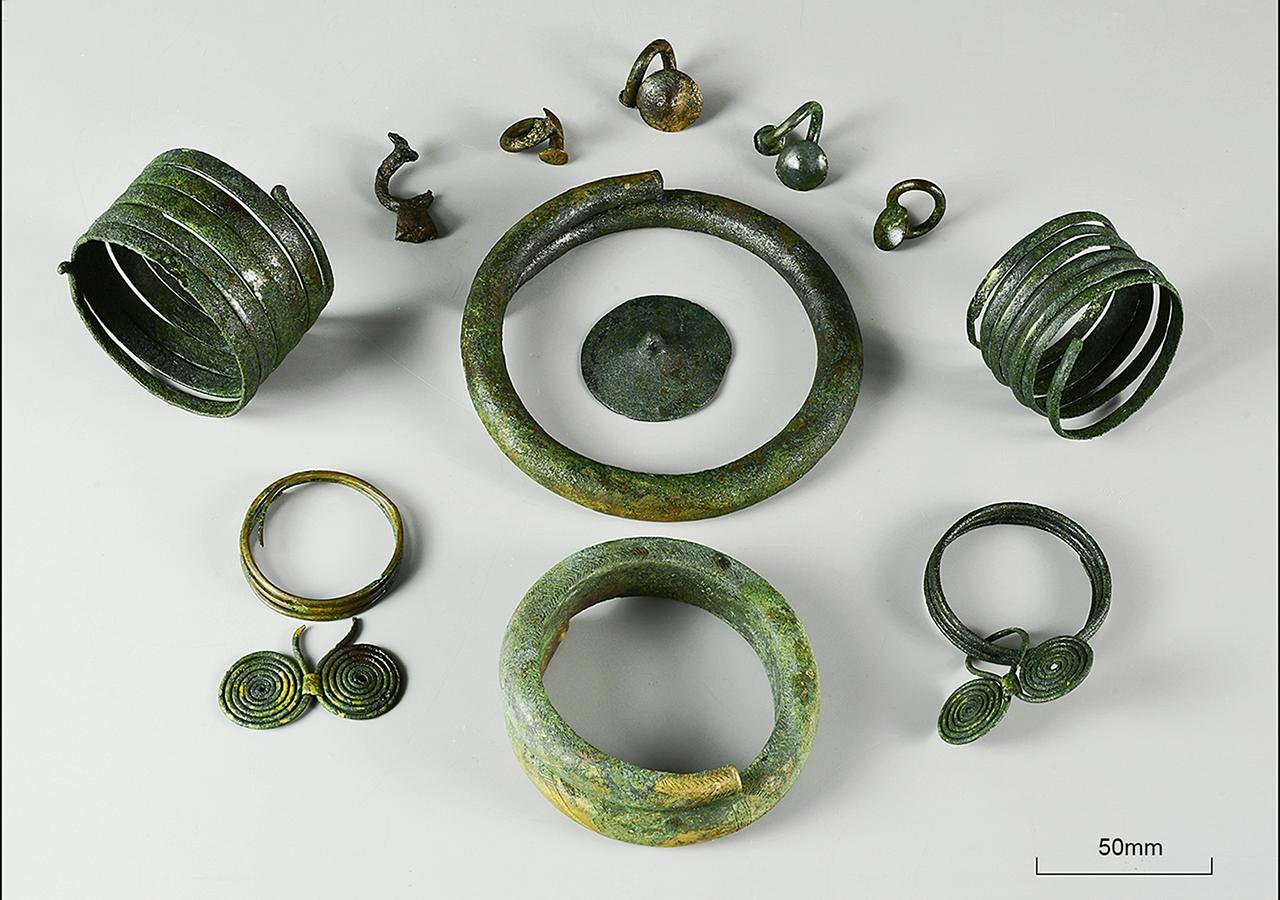

The Chełmno group, traditionally thought to be unaffected by social and economic changes, had been considered distinct from other Lusatian communities due to a lack of widespread metal hoarding. However, recent excavations at Papowo Biskupie have upended this perception, revealing over 550 bronze artifacts, primarily arm and neck jewelry, associated with the skeletal remains of at least 33 individuals.
Researchers initially doubted the ritual significance of metal in the Chełmno community, but the discovery challenges this assumption. The artifacts, dated through radiocarbon analysis, suggest a chronological sequence where human remains were initially placed in the lake before the deposition of metal objects. This hints at a potential transition in burial practices from lake burials to metal votive depositions, aligning the Chełmno group’s beliefs with broader Lusatian practices.
The study indicates a unique connection between the placement of human remains and metal objects during the later prehistoric period in Central Europe.
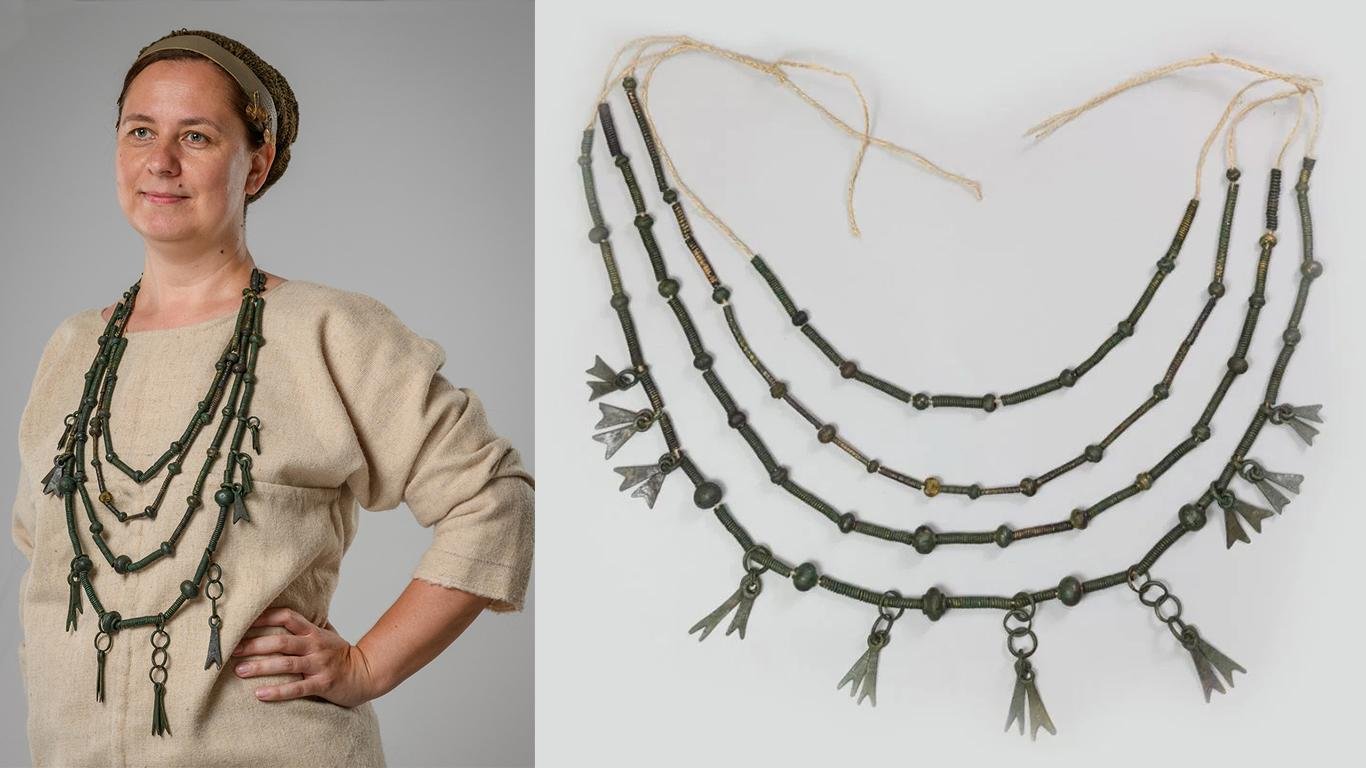

The excavation also revealed a significant quantity of bronze artifacts including a multi-turn necklace with Eastern Mediterranean origins, horse gear, and metal waste. The site’s exceptional nature lies in its skeletal remains, encompassing individuals of various ages and sexes, hinting at possible sacrificial practices.
The discovery prompts a reevaluation of the Chełmno group’s role in the broader Lusatian culture. “This site at Papowo Biskupie is one of the most eloquent testimonies of ritual activity from the Lusatian period in Poland,” said the researchers.
Furthermore, the Papowo Biskupie findings challenge the prevailing belief that the Chełmno group was disinterested in metal-related rituals. The shift from lake burials to metal offerings, as indicated by the archaeological record, suggests a cultural transformation within the Lusatian power elites during the transition to the Hallstatt culture in the Early Iron Age.
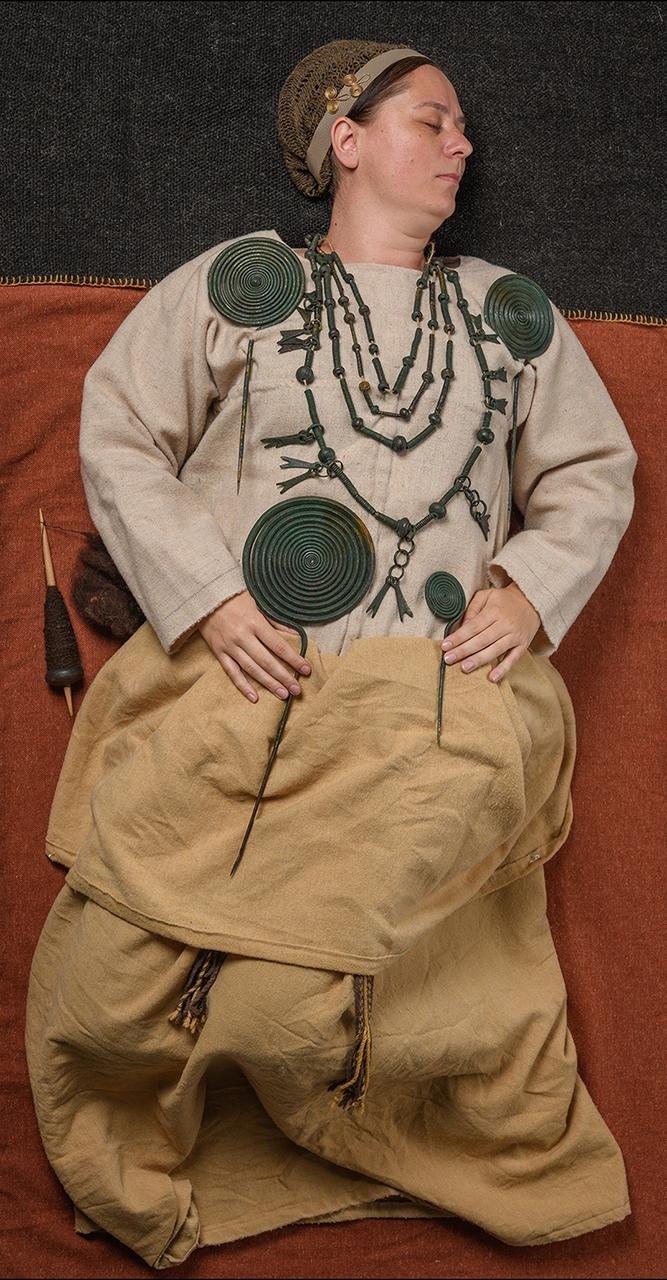

The artifacts, including female ornaments and horse-related accessories, align with a wider pattern observed in Hallstatt finds, pointing to the significance of women in votive depositions. This aspect adds a new dimension to the understanding of social and ritual practices during the Lusatian era, emphasizing the role of women in the evolving belief system.
The findings are detailed in the journal Antiquity.