Archaeologists with Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) at the ancient Maya city of Dzibanché have unearthed three stucco reliefs that depict scenes of the powerful Kaanu’l (or Snake) dynasty. Located in Quintana Roo, Mexico, Dzibanché—an early center for the Maya civilization dating back to 300 BCE—served as the initial stronghold of the Kaanu’l rulers, who later expanded their influence to vast regions in present-day Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala.

The new findings, which date to the Early Classic period (500-600 CE), were discovered on two platforms west of the site’s Ball Game II court, a ceremonial space for the Maya ballgame, an activity combining athleticism and ritual devotion. These platforms, each approximately 10 by 5 feet, display the first stucco reliefs ever uncovered on Dzibanché’s ballcourt, which archaeologists believe were meant to reinforce the dynasty’s authority.
Sandra Balanzario Granados, head of the INAH’s Archaeological Site Improvement Program (Promeza) at Dzibanché, described the discovery as a breakthrough: “Although we had found stucco reliefs on larger buildings, we would never have thought of finding such decorated façades on a ball court with such profound meanings as these ones apparently have,” she explained.
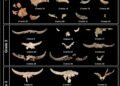
Each of the three relief scenes offers a glimpse into the mythological and celestial beliefs of the Kaanu’l dynasty. The first relief features two figures standing guard beside a pedestal, originally intended to support a sculpture, with symbols referencing a Kaanu’l ruler. The second scene depicts ancestral figures in a cosmic setting, surrounded by stars and intertwining serpents—motifs that reflect the Kaanu’l’s divine connection as rulers.
Epigrapher Alexander Tokovinine noted the striking blend of Maya and Teotihuacán iconography, particularly the serpent symbolism, which underscored the dynasty’s claim to a godly lineage. The third panel portrays a series of mythological animals linked to constellations, further emphasizing the rulers’ divine right and their cosmological power.
The prominence of intertwined snakes—a recurring theme across the reliefs—is especially significant, as it represents the “Snake” lineage of the Kaanu’l dynasty, affirming their place as divine intermediaries between the gods and the people. In pre-Hispanic Maya culture, rulers were often regarded as earthly representatives of the gods, and the Kaanu’l rulers viewed themselves as descendants of celestial beings. According to INAH, “This representation of intertwined snakes indicates that we are looking at images with which the rulers of Dzibanché sought to reaffirm their ancestry or lineage.”
The stucco reliefs, crafted from a mixture called sascab (a lime-based mortar common in Maya construction), still retain traces of red, blue, yellow, and black paint. However, centuries of exposure to the elements have eroded much of their vibrant colors. To preserve these artifacts, the archaeological team is employing advanced photogrammetry to create detailed models, ensuring that these intricate designs are documented accurately for future research.
This discovery is part of a broader research effort funded by the INAH and the ongoing Mayan Train project, an initiative aimed at connecting archaeological sites across the Yucatán Peninsula. Since 2023, a 100-person team has worked extensively at Dzibanché, uncovering relics of Maya civilization and restoring important structures, including the Temple of the Owl, the Temple of the Cormorants, and sections of the acropolis.
More information: INAH