A recent study examines the running capabilities of Australopithecus afarensis, the species of the renowned fossil “Lucy,” who lived over 3 million years ago in East Africa. The findings, published in Current Biology, combine advanced 3D modeling techniques and musculoskeletal simulations to explore how Lucy’s body moved, uncovering critical details about the evolution of human running.
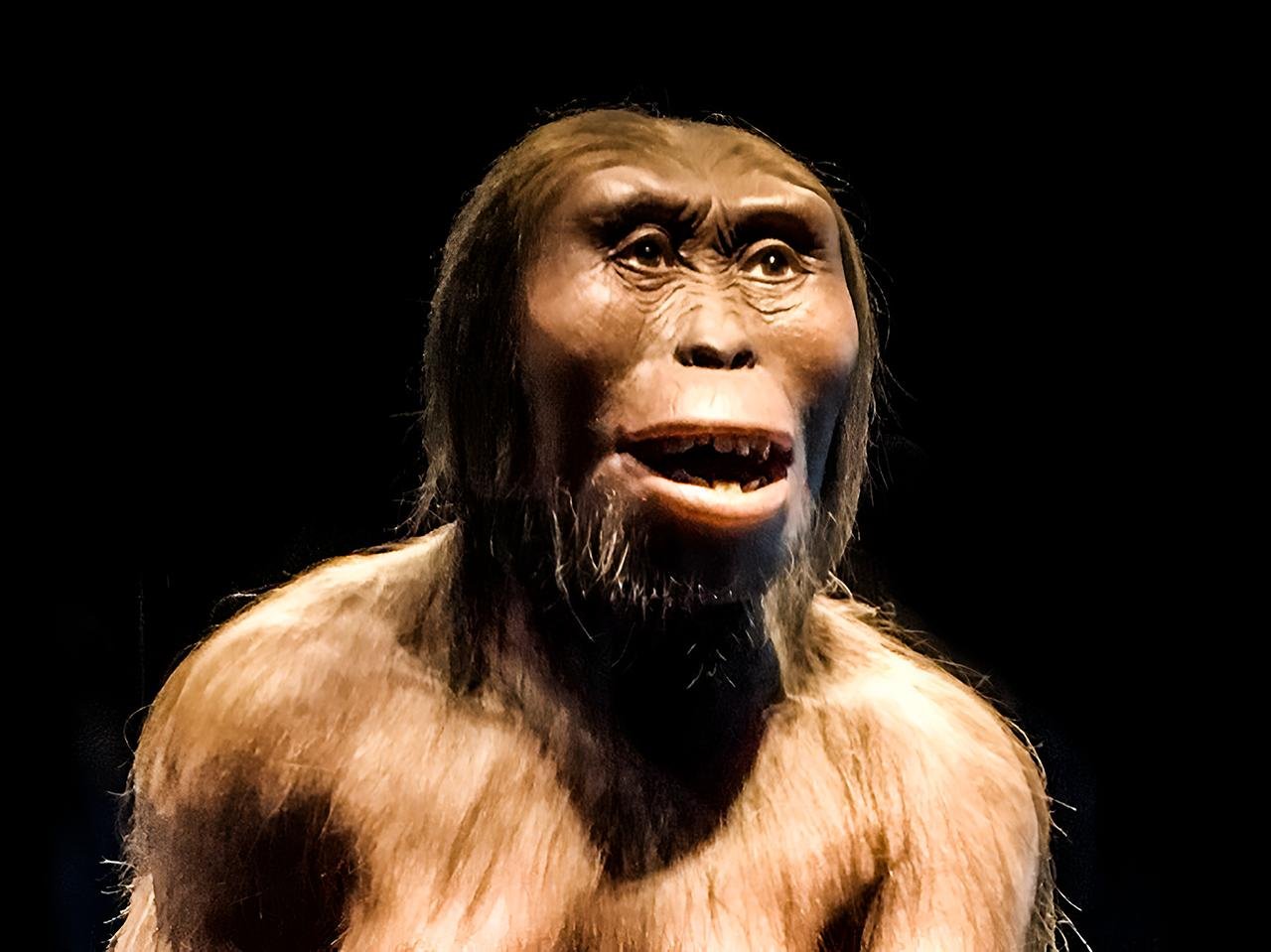

Lucy’s skeleton has long been studied as a key to understanding bipedalism in early hominins. While she and her kind could walk upright, their running capabilities were far from those of modern humans. According to Karl Bates, an evolutionary biomechanics researcher at the University of Liverpool and a co-author of the study, “Even if you jack up all the muscles, she was still slower.”
Related: Study reveals Lucy and early hominins may have used tools 3.2 million years ago
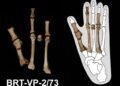
Simulations based on Lucy’s fossilized bones revealed her top speed was approximately 11 mph (5 m/s), significantly slower than modern humans, whose sprinting speeds often exceed 18 mph (8 m/s) and peak at over 27 mph in exceptional athletes like Usain Bolt. Furthermore, running required Lucy to expend 1.7 to 2.9 times more energy than a modern human, making her locomotion far less efficient.
Video of the optimal maximal-speed running gait (4.26 m/s) for the Au. afarensis
model iteration with modern human-like triceps surae architecture and muscle masses.
Credit: K. T. Bates et al., Current Biology (2024)
The study attributes Lucy’s slower pace and higher energy cost primarily to her body proportions and muscle architecture. With long arms, a smaller frame, and a differently shaped Achilles tendon, Lucy lacked the spring-like mechanics that modern humans rely on for efficient running. Modern humans possess a more elastic Achilles tendon paired with shorter muscle fibers, enabling efficient energy storage and release during running, which decreases the effort needed to propel forward.
The Achilles tendon and surrounding calf muscles—collectively known as the triceps surae—play a vital role in modern running performance. These adaptations allow for both speed and endurance, features absent in A. afarensis. Even when researchers simulated Lucy with human-like muscle configurations, her running remained slower, further underscoring the impact of her smaller stature and unique skeletal structure.

The findings emphasize that the traits enabling modern humans to excel at running did not emerge as a simple byproduct of bipedal walking but required specific evolutionary adaptations. Bates and his team argue that modifications in body proportions, particularly the development of longer legs and efficient ankle structures, were critical for improved running performance. These changes likely arose with the genus Homo, around 2 million years ago, as early humans adapted to new environments and challenges.
Running offered significant advantages to our ancestors, from pursuing prey over long distances to escaping predators and exploring new territories. Lucy’s less efficient running, however, suggests her species primarily relied on other strategies for survival, such as climbing or gathering food within shorter ranges.
While the current study provides unprecedented insight into Lucy’s running ability, the researchers aim to expand their work to include factors like fatigue, bone strain, and upper body dynamics. These additional variables could further clarify the evolutionary transition from the upright walking of early hominins to the running prowess seen in modern humans.
Lucy’s story reminds us that human evolution was a gradual process, marked by subtle yet impactful changes over millions of years.




















Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
This is very intresting
Well if she was a kind of orangutan, as it was ascertained by Dr. Zuckerman, it certainly could run.