Researchers have found a sacred road system near Chaco Canyon in New Mexico, revealing the cosmological and spiritual significance of these ancient pathways. A team from Dartmouth College used advanced lidar technology to identify a new road running parallel to an existing one at the Gasco site. Their research points to these roads being built for Indigenous rituals, not for transportation. The paths seem to align with significant celestial events.
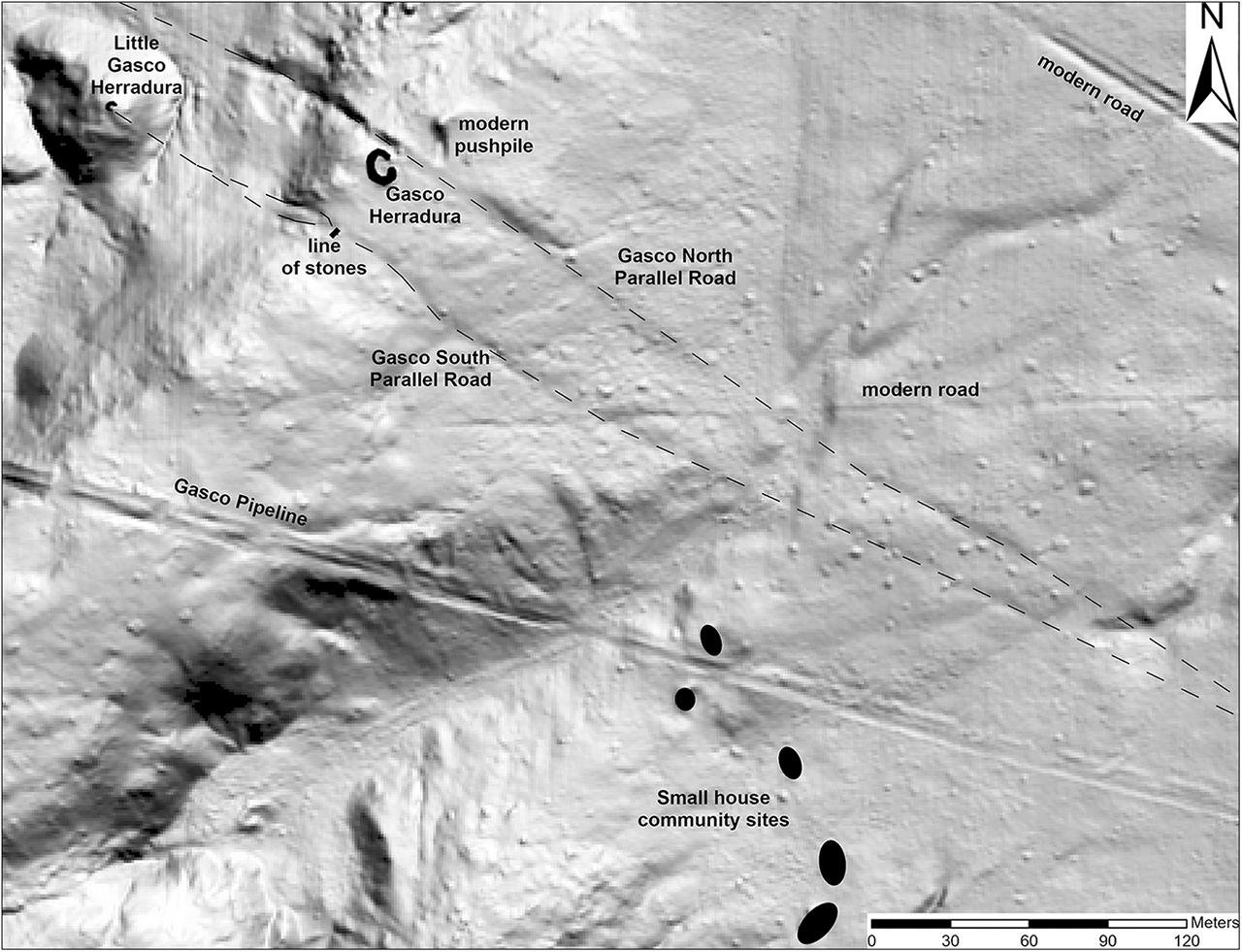
The research published in Antiquity shows that the road at Gasco is longer than experts previously thought. It stretches nearly four miles, not just a few hundred feet as once believed. What’s more, researchers found a second road about 115 feet south of the first one. Both of these roads align with where the sun rises over Mount Taylor during the winter solstice. This mountain is still sacred to Indigenous communities. These discoveries suggest that the Chacoan people integrated their spiritual beliefs into the very landscapes they lived on.
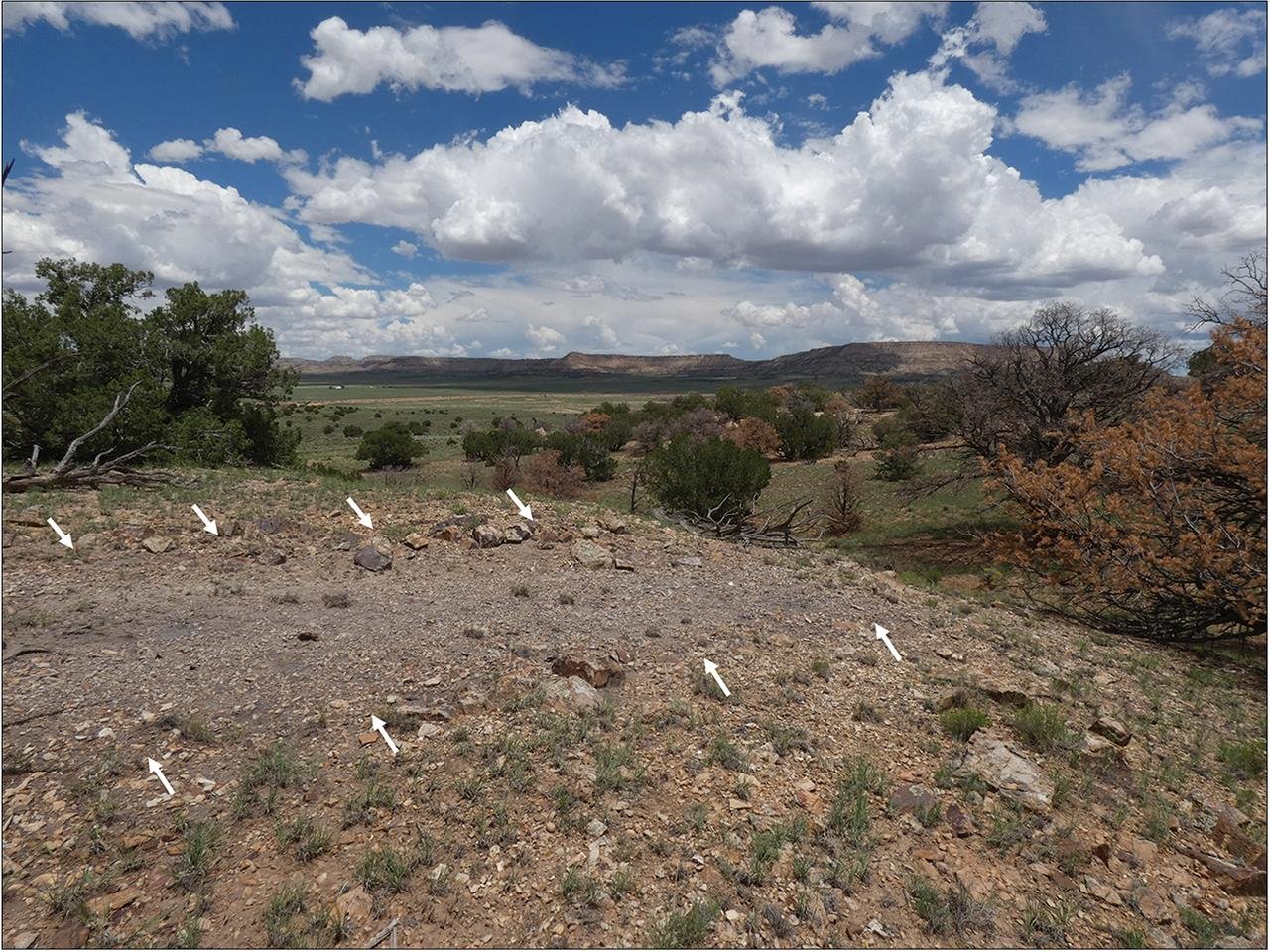
Robert Weiner, who led the research at Dartmouth College, highlighted the significance of these findings. He said, “One of the really exciting things about the work we’ve been doing with Chacoan roads is that they’re forcing us to reconceptualize what a road might be, what a road might mean.” Weiner explained that these roads were monumental constructions. Workers carved them into the sandstone bedrock, reaching widths of up to 30 feet—an impractical size for a society that had no wheeled vehicles or pack animals. Instead, their design and orientation suggest they had a ceremonial purpose, possibly involving processions and rituals tied to seasonal changes.
More evidence supporting the spiritual nature of these roads comes from finding herraduras—horseshoe-shaped rock structures—alongside them. These features might have been shrines for ritual offerings. The research uncovered ceramics and shaped stones close to the herraduras, hinting they were focal points for religious ceremonies. One road might have been used in winter and the other in summer, reinforcing a dualistic principle seen in other aspects of Chacoan culture.

The Chacoan culture flourished in the American Southwest from 850 to 1250 CE. They built impressive pueblo structures and vast ceremonial centers. But long dry spells and tough environmental conditions caused their decline. Despite this, their cultural and spiritual traditions persist among modern Indigenous groups like the Hopi, Zuni, and Diné (Navajo).
In the past, some experts thought these roads just linked settlements. But new discoveries show they played a key role in religious observances. The Gasco site sits near two natural springs, which adds to its sacred status. The study reveals that the Chacoan people didn’t make these roads to assign sanctity to the location. Instead, they recognized and responded to the inherent spiritual power of the place where natural elements like the sun, mountains, and water converged.
Sacred roads weren’t unique to the Chacoan people. Other ancient cultures had their own ritual paths too. For instance, the Stonehenge Avenue in Neolithic Britain. People built it along natural glacial striations that line up with the summer solstice sunrise. The Mississippian culture did something similar. They put their Emerald Acropolis on a hilltop with an orientation corresponding to lunar standstills. These examples show how different societies throughout history created large roads and ceremonial complexes to reflect celestial and environmental forces.
This latest research challenges conventional ideas about road construction, demonstrating that for the Chacoan people, roads were not merely routes for travel but pathways connecting their communities with the cosmos.
This study challenges old beliefs about road construction, showing that the Chacoan people saw roads as more than just ways to travel. These pathways connected their communities with the cosmos.
























Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
The prevailing theory now is that the Chacoan people didn’t “decline” but rather moved. This view has been reinforced by the recent DNA study involving the Picuris Pueblo.