The excavation in the ancient city of Aspendos, located in Türkiye’s Antalya province, unearthed a stunning marble statue of Hermes, the messenger god of Greek mythology. The find is part of the “Heritage for the Future” project run by the Turkish Ministry of Culture and Tourism, which also uncovered fragments of statues depicting Aphrodite, Eros, Artemis, and Nemesis.
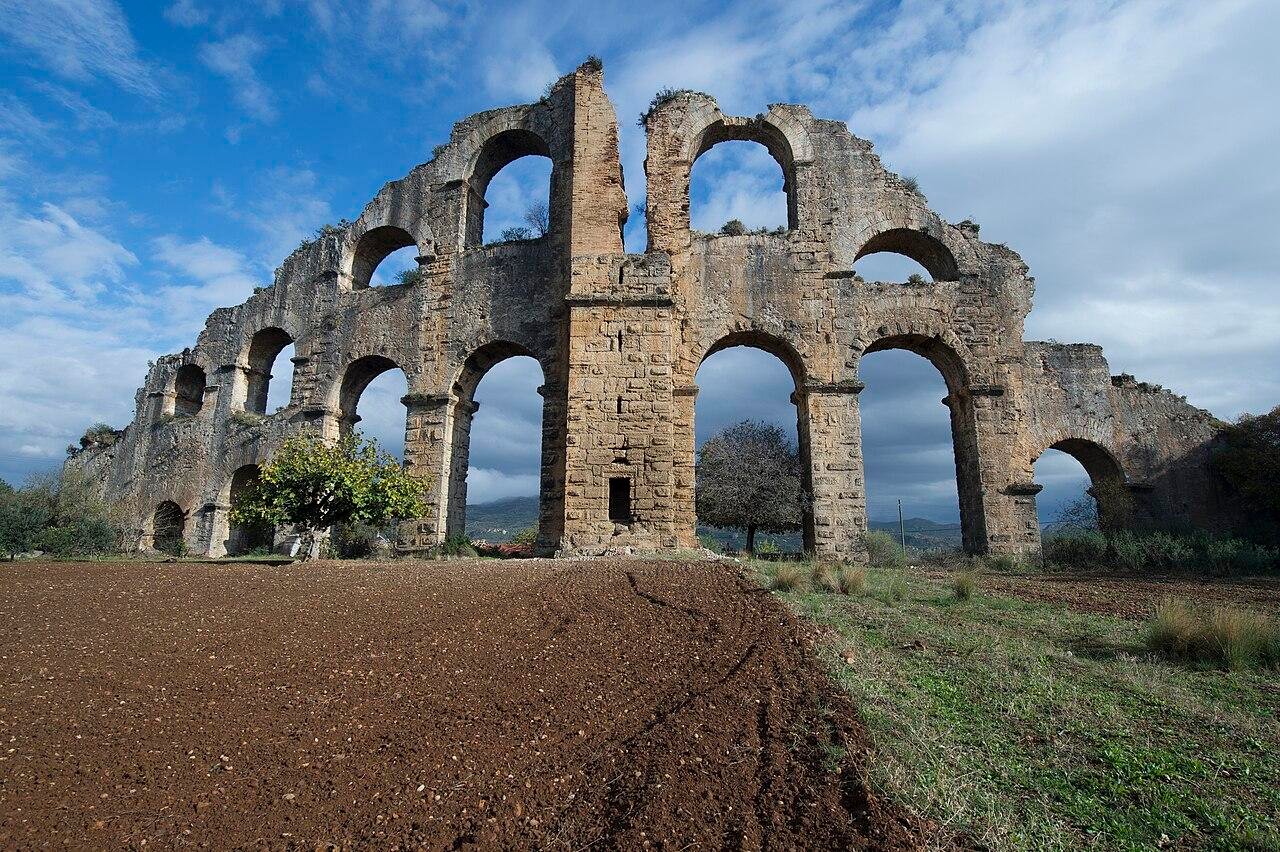

Aspendos is a key Greco-Roman city that flourished under Roman rule after its annexation in 190 BCE. It is known for its magnificent architectural heritage, including its remarkably well-preserved theater, built in 155 CE by the architect Zenon, which could accommodate up to 15,000 spectators. Other notable ruins include a stadium, baths, a basilica, an agora, a nymphaeum (monumental fountain), and an elaborate aqueduct system demonstrating advanced Roman engineering.
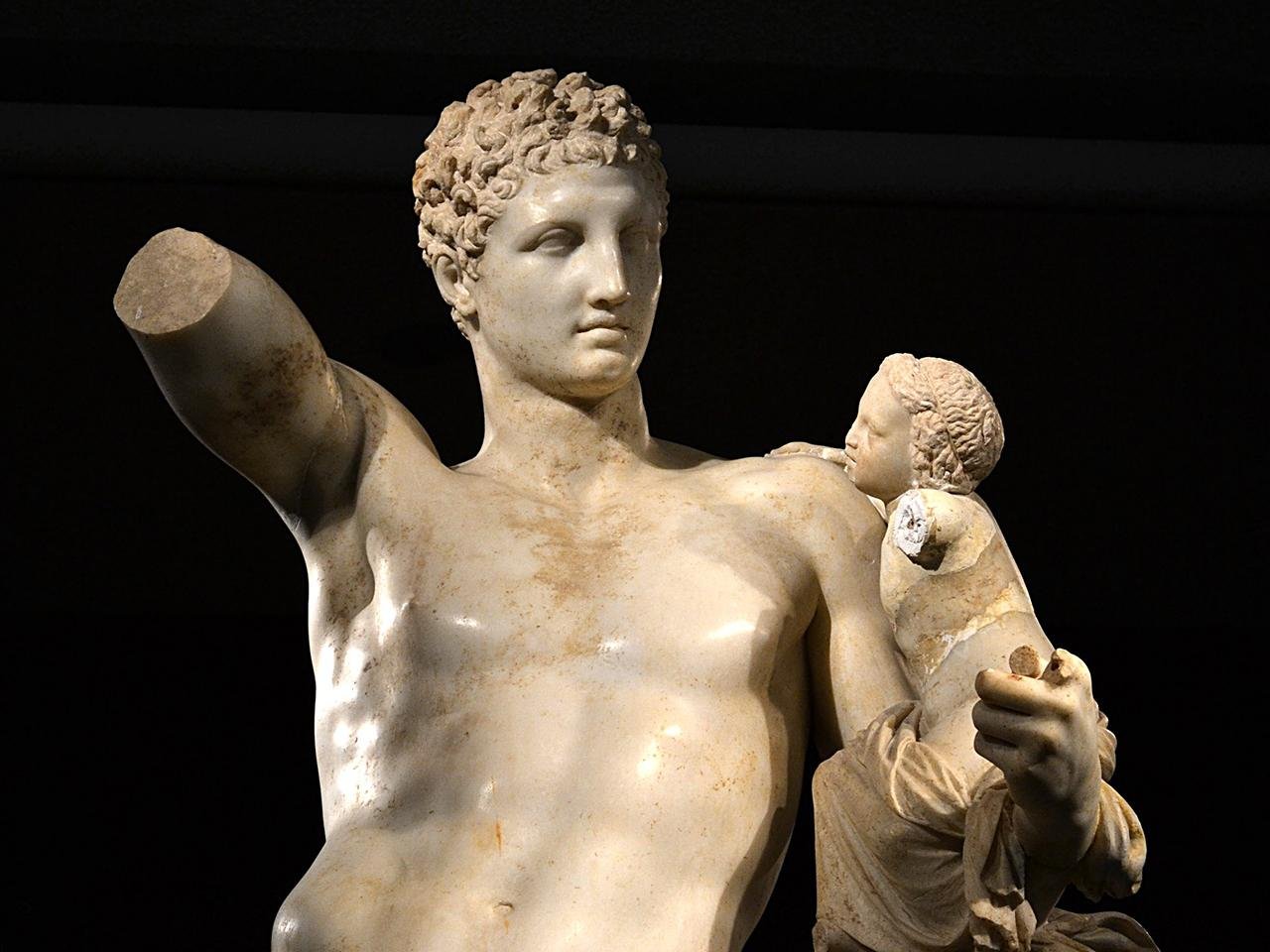
The Hermes statue was found amid the ruins of the monumental nymphaeum, located near the southern entrance gate of Aspendos. It is 1.65 meters tall and depicts Hermes wearing a draped cloak, with a pouch for money in his right hand and a caduceus (his signature staff) in his left hand. At his left foot, a ram, a symbol of strength and protection in Greek culture, is sculpted resting beside him. Stylistically, based on their analysis, archaeologists estimate this statue dates to the late 2nd to early 3rd centuries CE, a period marked by Roman artistic influences.
Zamanın sessiz tanığı Aspendos’ta, yüzyıllardır gömülü kalan figürler gün ışığına kavuştu.
Aspendos Antik Kenti’nde #GeleceğeMiras projemiz kapsamında süren kazılarda, Roma İmparatorluk Dönemi’ne ait Hermes heykeli gün yüzüne çıktı.
Aynı alanda Aphrodite ve Eros’un başları… pic.twitter.com/Cdv4Hd6z5t
— Mehmet Nuri Ersoy (@MehmetNuriErsoy) March 3, 2025
Turkish Minister of Culture and Tourism Mehmet Nuri Ersoy shared the news via social media, stating: “In Aspendos, the silent witness of time, figures that have remained buried for centuries have come to light. I extend my gratitude to the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums for their contributions to this project, and I hope these artifacts will enrich our country’s cultural and tourism landscape.”
The excavation team reassembled the fragmented statue at the restoration depot on-site. Experts believe the statue’s pose—weight on the left foot, right knee bent slightly—reveals the movement and naturalism inherent in Roman sculptural techniques.
In addition to the Hermes statue, archaeologists also recovered the marble heads of Aphrodite, the goddess of love and beauty, and Eros, the god of love. This collection is said to have a distinctive regional stylistic character that reflects the aesthetic ideals of the era. The same area has yielded fragments of statues representing Artemis, the goddess of hunting and wildlife, and Nemesis, the goddess of justice and retribution.

Aspendos’ history dates back to the 5th century BCE when it was a member of the Delian League and minted its own currency. After the defeat of the Persian fleet along its shores in 468 BCE, the city gained prominence. It finally came under Roman control in 133 BCE and experienced a period of architectural and economic growth during the 2nd and 3rd centuries CE. Today, Aspendos remains one of Türkiye’s most important archaeological sites.
More information: Turkiye’s Ministry of Culture and Tourism