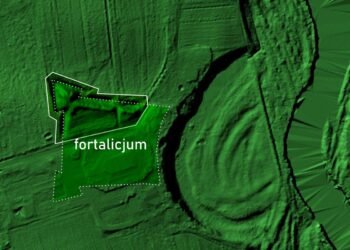
Archaeologists working at Hala Sultan Tekke on the southern coast of Cyprus uncovered two chamber tombs filled with high-status grave goods from the Late Bronze Age. The harbor city, also known as Dromolaxia Vyzakia, covered at least 25 hectares and thrived from around 1650 BCE until its destruction around 1150 BCE. Wealth in this center grew from copper production and export. Excavations across the settlement have produced slag heaps, furnaces, ore fragments, and crucibles, clear signs of large-scale metalworking within the city.

Fieldwork during May and June 2025 focused on an extra-urban cemetery in Area A. Surveys guided trench placement. Teams exposed eroded architectural remains, an abandoned well, and two chamber tombs dating to the 14th century BCE. Groundwater tests near the well showed high salinity about ten meters below the surface, a condition that likely led to abandonment in antiquity.
Both tomb roofs collapsed in ancient times. Fallen debris sealed interior layers and protected burial deposits. Although some objects suffered damage, overall context remained intact. This sealing provides a clear view of funerary practice across multiple generations. Stratigraphy shows repeated use over long periods. Earlier bones were often moved aside with care to make room for later burials. Such treatment points to strong family connections and long memory within kin groups.
Grave goods include fine local pottery, tools, jewelry, and personal items. Imported objects stand out for their number and geographic range. Pottery arrived from the Greek mainland, especially Berbati and Tiryns, and from Crete and other Aegean islands. Egyptian materials include ivory pieces and vessels carved from high-quality calcite. Deep blue lapis lazuli traced to mines in Afghanistan appears in bead form. Reddish carnelian from western India also occurs. Amber from the Baltic reached the site as beads and even a carved scarab. These materials traveled along complex exchange routes linking many regions of the eastern Mediterranean and beyond.
Pottery from Nuragic Sardinia adds further evidence for wide trade links. Similar finds elsewhere connect Sardinia with Cypriot copper in oxhide ingot form. Such parallels support a network in which metal moved west while prestige goods and ceramics moved east. Hala Sultan Tekke held a strong position within this system, aided by a protected harbor and access to copper ores from the Troodos Mountains.
Bioarchaeological study of human remains shows burials of all ages, from newborns to adults, rarely older than forty. This age profile fits patterns known from Bronze Age populations with high mortality. Ongoing laboratory work includes ancient DNA studies, which aim to clarify biological relationships among individuals placed in the same tombs and to explore mobility and ancestry.
Digital recording teams created detailed two-dimensional and three-dimensional documentation of structures and finds. Specialists also analyzed materials and conservation needs at museum facilities in Larnaca. The combined results build a detailed picture of social organization, trade connections, and daily life in a major Bronze Age port city.
Finds from these tombs point to the burial of elite families linked to copper trade and long-distance exchange. Variation in imported goods between tombs raises the possibility of distinct social roles or different cultural backgrounds among groups living in the city. Continued analysis promises finer dating and deeper insight into community structure at one of Cyprus’s most important Late Bronze Age centers.





















Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.