Archaeologists working in southern Iraq have identified the site of Alexandria on the Tigris, a large port city founded in the late fourth century BCE during the campaigns of Alexander of Macedon. The ruins lie at Jebel Khayyaber, near the modern border with Iran. Surveys show a planned urban center that linked river traffic from Mesopotamia with sea routes through the Persian Gulf and trade networks reaching India and Central Asia.
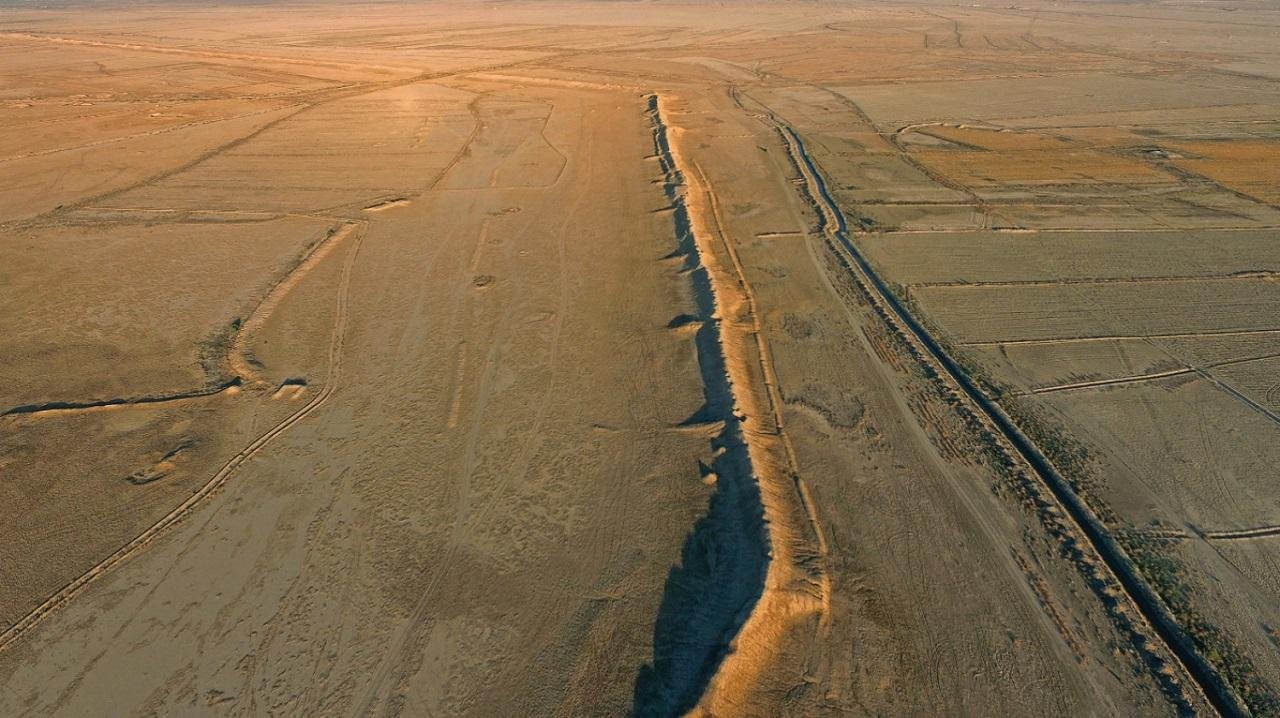

Ancient authors described a place called Charax Spasinou near the head of the Persian Gulf. Scholars argued for decades about its position. In the 1960s, British researcher John Hansman studied Royal Air Force aerial photographs and noted a huge walled enclosure and traces of settlement in this area. Field research stalled soon after. The war between Iraq and Iran turned the border zone into a military landscape, and armed forces built installations across parts of the ruins.
Research teams returned in 2014. Local heritage officials guided visiting archaeologists to the site. What looked like a low ridge in a flat plain proved to be a city wall stretching more than one kilometer, with sections rising up to eight meters. The scale pointed to a major urban center.
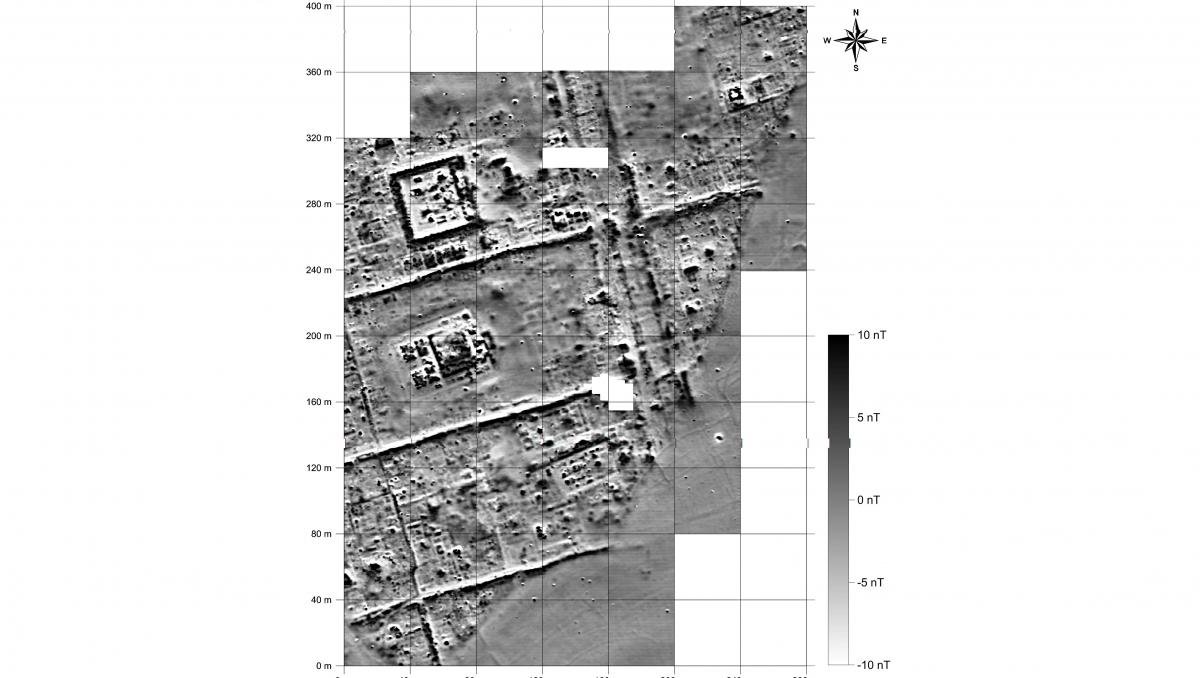
Teams then carried out large-scale surface surveys. Researchers walked across more than 500 square kilometers and recorded dense scatters of pottery, brick fragments, and industrial debris. Thousands of drone photographs helped build a detailed terrain model. Geophysicists used magnetometers to map buried structures. The results outline a city laid out on a grid, with wide streets, large housing blocks, temple compounds, workshops with kilns, canals, and harbor basins. One district includes house blocks of exceptional size, larger than most known from other cities of the same era.
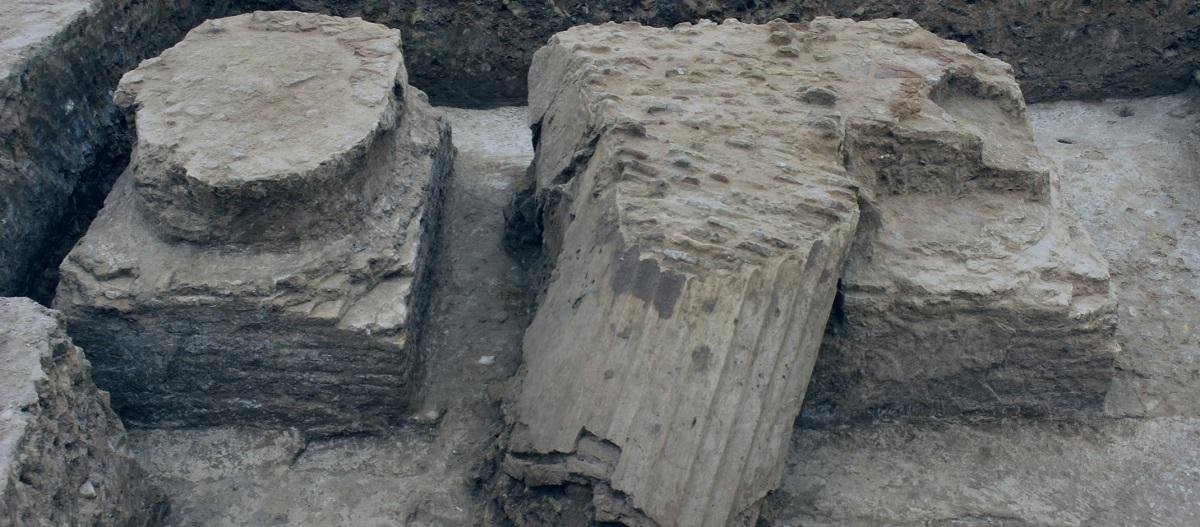

Analysis of street alignments shows four main grid orientations. These patterns reflect different building phases and land-use zones. Residential quarters stand close to religious buildings. Industrial sectors cluster near former waterways. Another enclosed area lacks a street network and appears to mark a palace complex or garden district. Satellite imagery also reveals canals north of the city, linked to large agricultural fields which would have supported a substantial population.
Historical context explains the city’s importance. Between about 300 BCE and 300 CE, long-distance trade expanded across the Indian Ocean and through overland routes into Central Asia. Goods such as spices, textiles, semi-precious stones, and metals moved toward major cities in Mesopotamia. Seleucia and later Ctesiphon, both on the Tigris, served as imperial capitals and large consumer markets. Ancient sources give population figures for Seleucia in the hundreds of thousands. A port at the junction of sea lanes and river transport offered an efficient transfer point for such trade.
Environmental change led to decline. Rivers in southern Mesopotamia shift course over time, while sediment pushes the Persian Gulf shoreline farther south. Geological cores and landscape studies indicate a westward movement of the Tigris by the third century CE. The harbor then lost direct access to the main channel, and the coastline lay far away. River shipping declined, and the economic base weakened. Most residents left, and urban life faded.
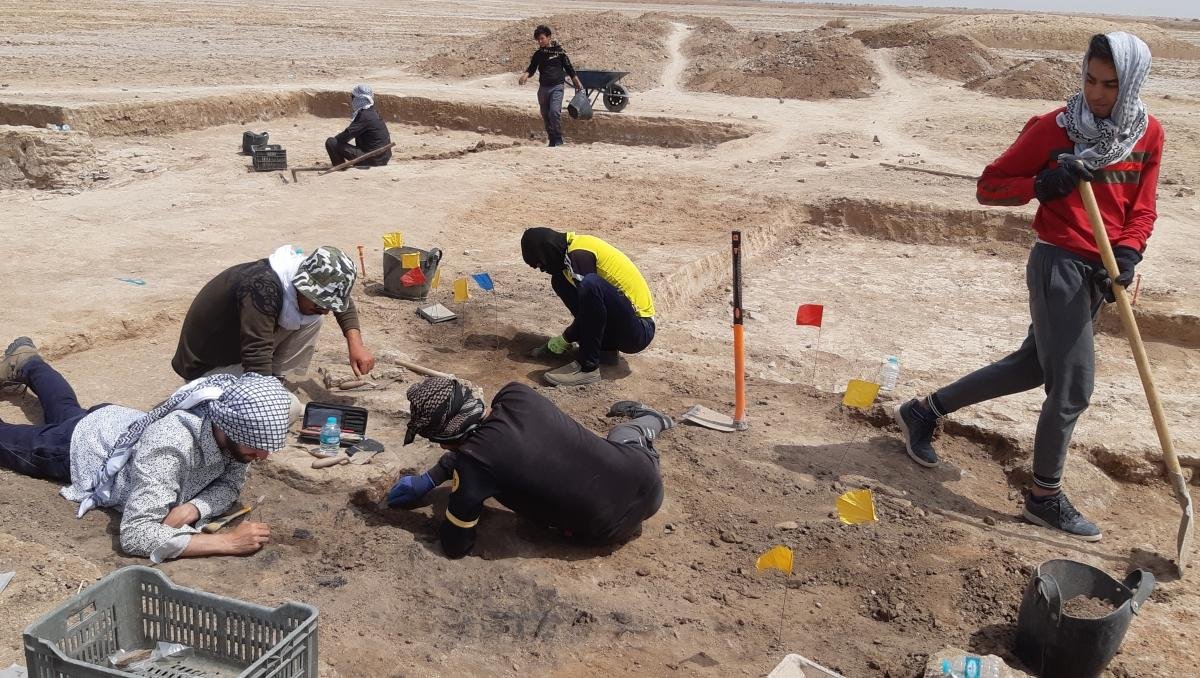

Work at Jebel Khayyaber fills a gap in the history of Mesopotamia during centuries with limited written records. Ongoing projects aim to refine the city plan, date the construction phases, and link urban growth with trade and environmental change. Excavation will follow when funding and field conditions allow. Noninvasive research already places Alexandria on the Tigris among the largest known cities of the Hellenistic and Parthian Near East.























Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.