The Kostyonki–Borshchyovo archaeological complex is a significant prehistoric site located in the Kursk Oblast region of western Russia. It is situated near the village of Kostyonki, about 550 kilometers south of Moscow.
This complex is renowned for its rich archaeological discoveries that provide valuable insights into the lives and activities of early human populations in the region.
The complex comprises two main sites: Kostyonki and Borshchyovo. The Kostyonki site has been extensively studied since the early 19th century, while Borshchyovo was discovered more recently in the 1970s. These sites represent the last glacial period, specifically the Middle to Upper Paleolithic transition, spanning a time period of approximately 50,000 to 20,000 years ago.
Excavations at Kostyonki–Borshchyovo have unearthed a wealth of stone tools, bone artifacts, and the remains of ancient human settlements. The tools found include various types of blades, scrapers, burins, and points, which were likely used for hunting, butchering, and other daily activities.
The bones discovered at the site belong to a range of animals, including mammoths, woolly rhinoceroses, horses, and other mammals that were prevalent during the Ice Age.

One of the most remarkable features of the Kostyonki–Borshchyovo complex is the abundance of art objects and figurines created by the early humans who inhabited the region.
These include sculpted animal representations, such as mammoths and birds, as well as humanoid figurines believed to have religious or symbolic significance. These artistic expressions offer glimpses into the cultural and spiritual beliefs of the ancient inhabitants, shedding light on their social complexity and cognitive abilities.
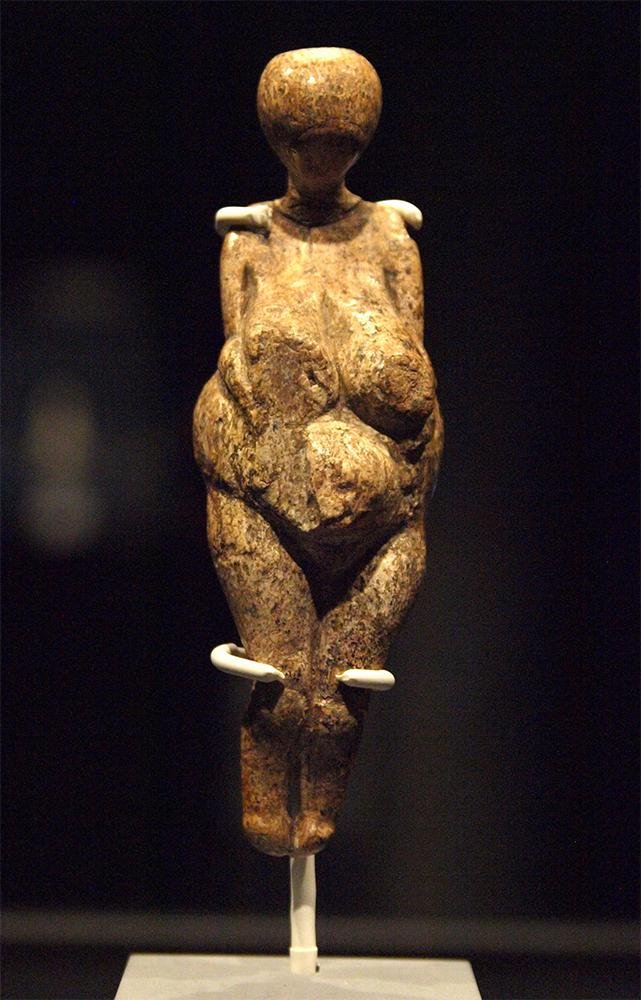

The archaeological findings at Kostyonki–Borshchyovo have played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of human evolution, as well as the behavioral and technological developments of early Homo sapiens.
The discovery of hearths and other evidence of long-term occupation suggests that these sites were not merely temporary camps, but rather established settlements where groups of people lived.
The site is a treasure trove of information about our ancient past. Its artifacts and remains continue to be studied and analyzed by archaeologists and anthropologists, helping to unravel the mysteries of our human ancestors and their way of life during the Paleolithic era.























Comments 0