In an exploration of ancient dietary habits and health in the city of Pergamon, located in western Turkey, recent research and examination of unearthed skeletons dating back 2,000 years have provided intriguing insights into the lives of its inhabitants.
This comprehensive study, led by an international team of Turkish and German scientists, delves into the dietary disparities, dental issues, and sinus problems experienced by the residents of this ancient city.
Professor Wolf Rüdiger Teegen, a renowned specialist in Prehistoric Protohistory and Roman Archaeology at Munich’s Ludwig Maximilians University, has been instrumental in uncovering these findings.
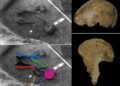
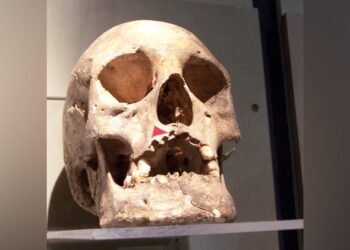
His extensive work in Bergama, the modern town near the ancient city of Pergamon, spans over a decade, with a focus on the analysis of fossilized bone remains. The research encompassed the examination of 300 skeletons and bone fragments, spanning across both the Roman and Byzantine eras.
As Professor Teegen explains, a critical aspect of their findings revolves around the dietary habits of the people of Pergamon. Through the analysis of ancient teeth, they have been able to discern that carbohydrates and plant-based foods predominantly constituted the diet of the city’s residents. Staples such as bread and porridge were commonplace in their meals, reflecting a carbohydrate-rich regimen.
However, it’s also evident that meat consumption was not uniform. Those with greater financial means had greater access to meat, a diet dependent on social status. “Those who had money were able to eat meat or fish,” Teegen emphasizes. During the Roman Empire, beef was relatively affordable compared to pork, which was a highly popular choice. Remarkably, rabbit meat was considered the most expensive meat during that era.
In their meticulous studies, Teegen’s team paid special attention to age and sex, shedding light on patterns of life and death in ancient Pergamon. “It is impossible to determine gender in some skeletons,” he notes. “Age determination is much more possible.” Their research has unveiled that people in Pergamon typically lived between the ages of 20 and 40. The older age group experienced a notably lower death rate. Notably, women often did not survive past the age of 40, owing to factors like pregnancy and childbirth.
These findings align with broader trends seen in both Roman and Hellenistic periods. The research underscores the fact that diseases characterized by symptoms like fever or diarrhea left no discernible marks on the skeletons, making it challenging to ascertain the causes of death beyond traumatic injuries.
Focusing on the health of Pergamon’s ancient residents, Teegen reveals the prevalence of specific health issues within this population. Abscesses and tooth loss were two of the most common health problems encountered. These ailments notably affected individuals during their childhood and youth, underlining the impact of such conditions on the lives of the city’s inhabitants.
The research conducted on skeletons from ancient Pergamon has illuminated the dietary disparities based on social status and the health issues prevalent in this population.