Scientists from the University of Bristol discovered that early Jurassic ichthyosaur juveniles have predatory specializations.
Their findings, which were published in the Journal of Anatomy, suggest that physical differences in their snouts indicate that they evolved to have different diets and were not competing for the same resource.
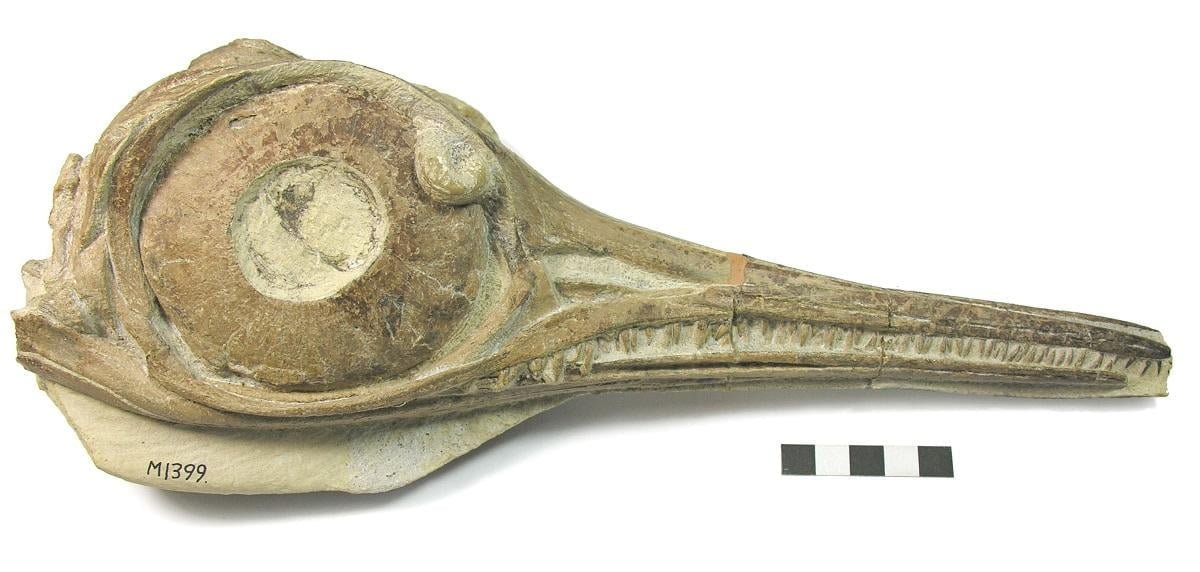

The classic’sea dragons,’ ichthyosaurs, were dolphin-shaped marine predators that fed on fish and squid-like swimming shellfish.
The Lower Jurassic ichthyosaurs are renowned since the first specimens were discovered over 200 years ago at Lyme Regis in southern England by the great fossil collector and palaeontologist Mary Anning. Her specimens have long, slender snouts on some, and short, broad snouts on others.
“Functional studies need excellent three-dimensional specimens,” said Matt Williams of the Bath Royal Literary and Scientific Institution, “and the Lower Jurassic ichthyosaur fossils from Strawberry Bank in Ilminster are just that. Mary Anning’s fossils are amazing, but they are mostly squashed flat.”
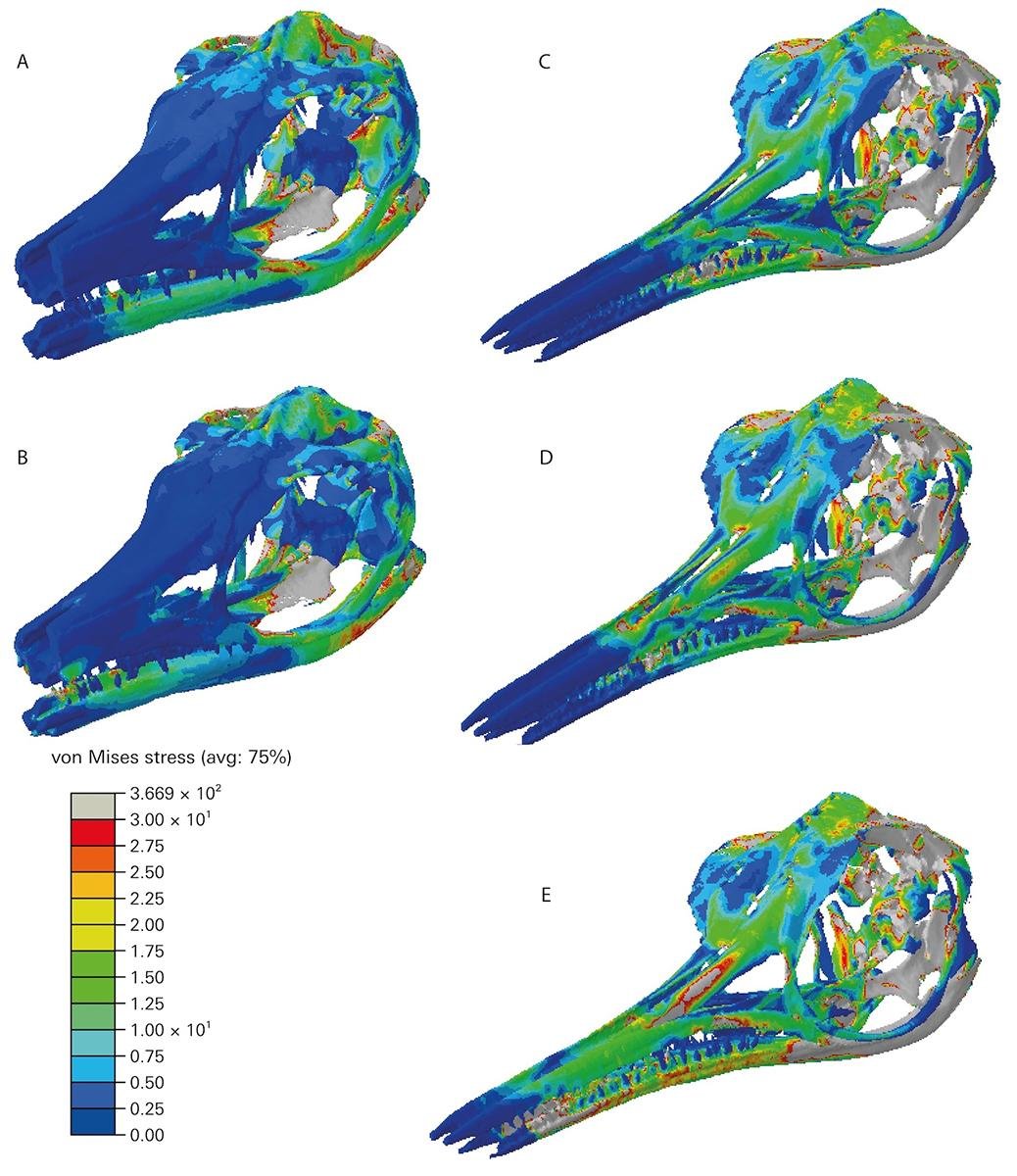
“Our idea was to CT scan the specimens,” said Dr Ben Moon, of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences and a supervisor of the study. “The scans allow us to make a detailed, 3D model of the skull in the computer, and it can then be tested for the likely forces experienced during biting.”
“After we had the models, we could stress test them,” supervisor Andre Rowe said. “We tested and confirmed the hypothesis that the slender-snouted ichthyosaur had a quick but weak bite, and the broad-snouted ichthyosaur had a slow but powerful bite.”
“Confirming the supposition was important,” author Professor Michael Benton remarked. “It’s important we apply rigorous scientific approaches such as these engineering analyses. The two species of ichthyosaur presumably chased fast-moving prey (the fast biter) and slower, tough-shelled prey (the slow, powerful biter).
“I learned about CT scanning, model construction, and biomechanical testing using standard engineering software that is used to test how buildings and large structures bend,” said Sarah Jamison-Todd, who completed the work as part of her MSc in Palaeobiology.
Prof Benton concluded: “Modern predators like sharks and killer whales tend to eat anything they can, so it is exciting to be able to show that in the Jurassic there were definite specializations. The work can be extended to explore other marine reptiles such as plesiosaurs and crocodiles, so we get a detailed picture of these amazing and alien worlds of the Jurassic oceans.”
Provided by University of Bristol
More information: Sarah Jamison‐Todd et al, (2022). Dietary niche partitioning in Early Jurassic ichthyosaurs from Strawberry Bank, Journal of Anatomy. DOI: 10.1111/joa.13744