In a recent study conducted by researchers from the Collaborative Research Center (CRC) 1266 at Kiel University, the culinary habits of early inhabitants in Eastern Holstein, Germany, have been brought to light through the analysis of burnt food residues on ceramic vessels.
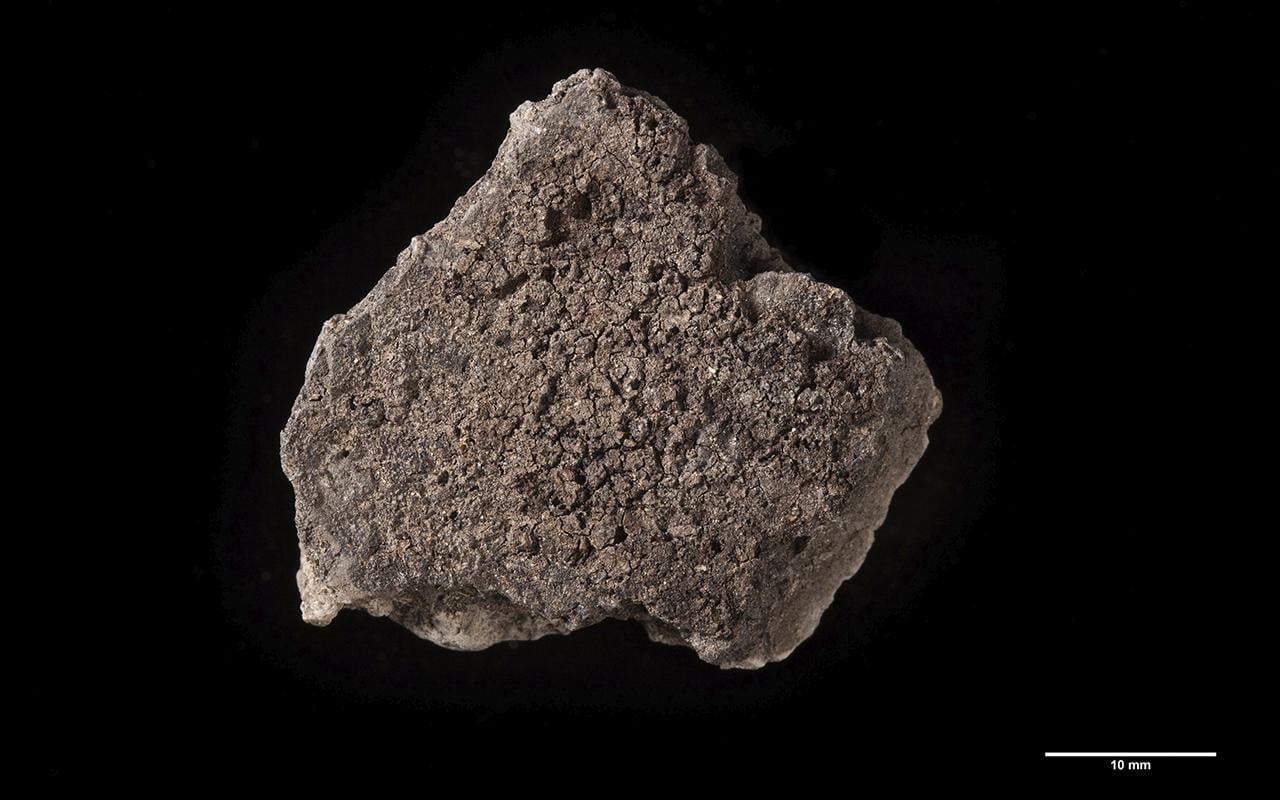

This marks the first archaeobotanical exploration of such residues, offering a unique glimpse into the diverse meals prepared in the Neolithic settlement of Oldenburg LA 77 around 5,000 years ago.
Published in PLOS ONE, the study employed scanning electron microscopy and chemical analysis to unveil the complex preparation of plant-based foods in this ancient community. The ceramic vessels, originating from one of the oldest villages in Schleswig-Holstein, revealed a sophisticated combination of cereals and wild plants in the meals of these early farmers.
The “food crusts” discovered on the ceramic shards contained tissue remnants of emmer and barley grains, along with seeds from the white goosefoot, a wild plant rich in starchy seeds.

Dr. Dragana Filipović, research associate at the CRC 1266, highlighted the significance of the findings, stating, “Charred grains and chaff from emmer and barley, as well as seeds from white goosefoot, have already been documented by archaeobotanical analyses of soil samples from this Neolithic settlement.”
The study further illuminated that the Neolithic diet was not monotonous but rather diverse. The barley, harvested at the milky-ripe stage, was processed similarly to green spelt traditionally produced in Baden-Württemberg, while emmer was processed in a sprouted state, imparting a sweet flavor to the porridge.
Dr. Lucy Kubiak-Martens, a cooperation partner of BIAX Consult and the study’s first author, highlighted the intentional nature of this culinary experiment, stating, “It looked like someone had mixed cereal grains with the protein-rich seeds and cooked it with water. It wasn’t incidental, it was a choice.”

Moreover, a separate pottery shard containing animal fat residue, likely milk, provided insights into the ingredients used during this ancient cooking episode. Dr. Kubiak-Martens said: “While the animal fats are absorbed into the ceramic and leave a signal there, the plant food components can only be detected in the burnt food crust.”
Complementing these findings, an integrated botanical and chemical approach was employed in a study on Funnel Beaker ceramics from Oldenburg LA 77, as reported by researchers in northern Germany. The study, incorporating scanning electron microscopy, attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and direct time-resolved mass spectrometry, offered detailed information about the ingredients, cooking methods, and seasonal timing of Neolithic food preparation.