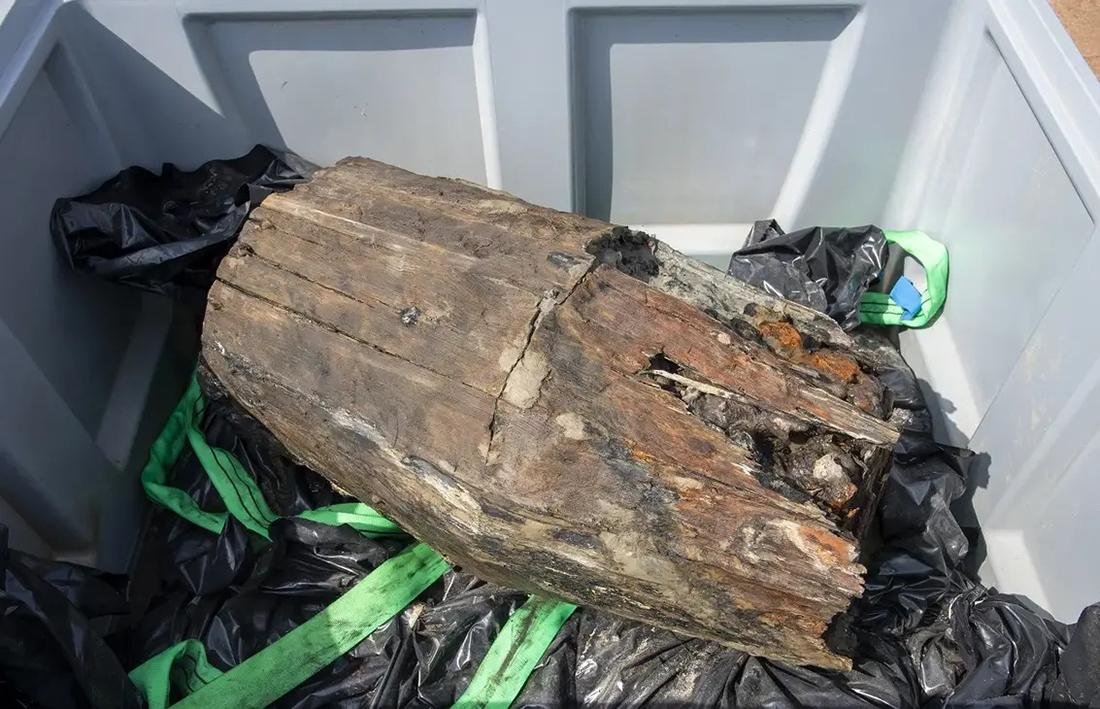
Marine archaeologists from Vrak – Museum of Wrecks have raised a wooden barrel containing osmond iron from a 16th-century shipwreck off the Baltic coast of Sweden. This remarkable find marks the first time in nearly 500 years that such a cargo has been retrieved.

The shipwreck, dubbed the “Osmond Wreck” after its primary cargo, was initially discovered in 2017 by Vrak archaeologists north of Dalarö in the Stockholm archipelago. This vessel is a clinker-built ship, characterized by overlapping hull planks, a common design in medieval ship construction. Notably, the ship remains in an exceptional state of preservation, with the mainmast still standing and much of its cargo intact.
Dendrochronological analysis has dated the ship’s construction to the 1540s in Stockholm, with repairs made in 1553 using wood from southern Finland. This analysis indicates the ship sank shortly after these repairs, likely in the 1550s or 1560s.
Osmond iron, produced by melting pig iron in specialized hearths, was a significant Swedish export from the Middle Ages until the early 17th century. Sweden was a major producer of this iron, which was essential for forging tools and weapons. However, the trade and production processes of osmond iron remain poorly understood, making this discovery particularly valuable.

The recently recovered barrel, which contains fist-sized lumps of osmond iron, was raised from a depth of 28 meters by marine archaeologists. The operation, led by Jim Hansson, project manager and marine archaeologist at Vrak, was challenging due to the barrel’s weight and the depth at which it was found. “It was incredibly difficult to get it out and get it off – the barrel is so heavy and it’s a great depth,” Hansson explained.
The raised barrel is now undergoing conservation and further examination. Researchers aim to determine the specific use of the osmond iron and its intended destination.
Underwater studies have identified 30 barrels at the wreck site, 20 of which contain osmond iron. The remaining barrels hold tar, ash, and butter, highlighting the diverse nature of the cargo. Excavations have also revealed large quantities of fish bones and deer antlers, likely intended for export to produce items such as combs. Personal belongings of the sailors, along with galley utensils like kettles, were also found.
The excavation is a collaborative effort between Vrak and Jernkontoret, the Swedish iron and steel producers’ association. Funded by a £120,000 grant from the Voice of the Ocean Foundation, the project aims to explore the early Swedish iron industry and its trade networks. Researchers are particularly interested in understanding whether all osmond iron originated from the same location and if historical records about the uniform size of osmond lumps hold true.
“This is a unique opportunity to study 16th-century iron,” said a Vrak spokesperson. “We hope to uncover many more clues about early Swedish iron production and its impact on European trade.”