Archaeologists excavating the ancient city of Tios, located near the modern Filyos Port in Zonguldak, Turkey, have uncovered a substantial Roman necropolis. This ancient Greek colony, believed to have been founded in the 7th century BCE by a Milesian priest named Tios, has remained relatively well-preserved, largely undisturbed by modern development.

Led by Professor Şahin Yıldırım from Bartın University, the excavation team of 44 members has unearthed a variety of burial structures, including 96 sarcophagi, 23 chamber tombs, seven cist graves, 60 tile graves, and over 1,300 funerary objects. Professor Yıldırım noted that the necropolis spans from the 5th century BCE to the 5th century CE, with its most active period during the 1st to 3rd centuries CE, when it flourished as a “city of the dead.”
“The necropolis was constructed with a planned layout, featuring streets, alleys, and terraces, much like a city,” explained Professor Yıldırım. A 500-meter avenue lined with sarcophagi suggests that these burials belonged to wealthy individuals, primarily from the 2nd to 3rd centuries CE.
The discovery has been supported by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the Ministry of Energy and Natural Resources, Türkiye Petrolleri (TPAO), and TP-OTC. Professor Yıldırım emphasized the significance of Tios, stating, “Tios is the only ancient city in the Black Sea region with no modern settlement on top of it. We have uncovered a vast necropolis extending from the late 5th century BCE to the 5th century CE. This area holds a very important place for Türkiye and Black Sea archaeology.”
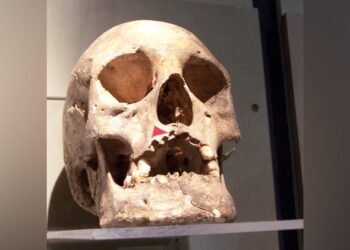
Artifacts discovered include tombstones and inscriptions from the reign of Emperor Marcus Aurelius, revealing that many inhabitants of Tios were granted Roman imperial citizenship. Human skeletons found in the graves suggest familial connections among those buried. The excavation also revealed that some chamber tombs were reused by the Byzantines in the 6th century CE.
The Tios necropolis stands out as a remarkably preserved site. “During the Gothic invasions, many tombs were looted, but the Romans later restored and continued to use the necropolis,” Yıldırım stated.