The enigmatic “Screaming Woman” mummy, discovered in 1935 near Luxor, Egypt, has long perplexed researchers due to her haunting open-mouth expression. New findings published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine suggest that the woman may have died in excruciating pain, resulting in a cadaveric spasm that locked her face in a permanent scream.

The mummy was unearthed by a Metropolitan Museum of New York archaeological expedition while excavating the tomb of Senmut, the chief architect for Queen Hatshepsut. Senmut’s tomb also housed a burial chamber for his mother and other relatives, where the Screaming Woman was found. Despite her noble burial with luxurious materials, her identity and the cause of her agonized expression remained a mystery for nearly nine decades.
Researchers, led by radiologist Dr. Sahar Saleem of Cairo University and anthropologist Samia El-Merghani of the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities, conducted a detailed examination of the mummy using CT scans, infrared imaging, and other advanced techniques. Their virtual autopsy provided significant information about her physical condition and the possible causes of her death.
The analysis revealed that the Screaming Woman was around 48 years old, approximately 5 feet tall, and suffered from mild arthritis. Surprisingly, her brain, diaphragm, heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, and intestines were intact, deviating from the common practice of organ removal during mummification in the New Kingdom era (circa 1550-1070 BCE).
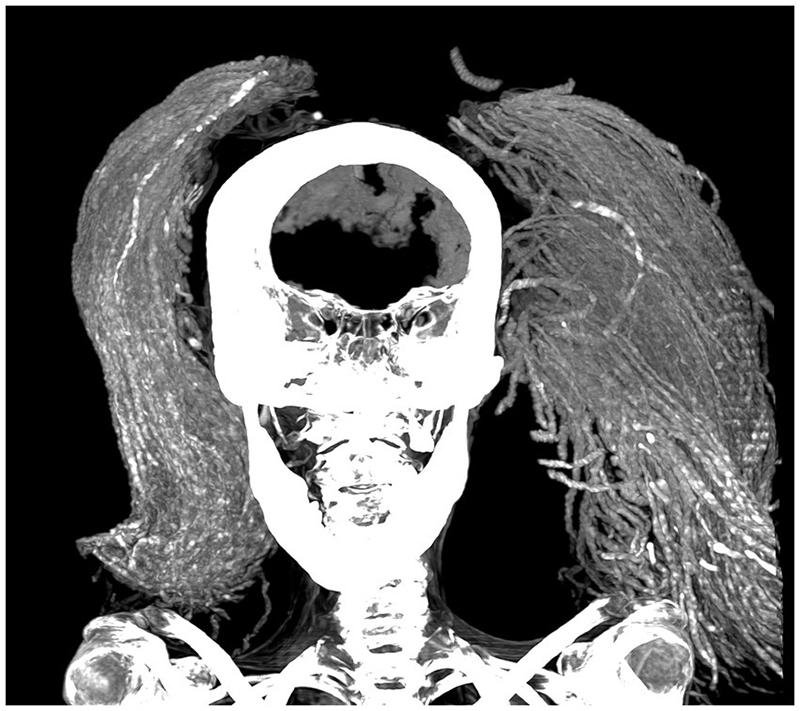
Contrary to initial beliefs that her open mouth was due to poor mummification, the study showed that the Screaming Woman was embalmed with expensive, imported materials such as juniper resin and frankincense. These substances, likely sourced from the Eastern Mediterranean and East Africa or Southern Arabia, were used to prevent decay caused by bacteria and insects.
Her burial also included a black wig made from date palm fibers, treated with quartz, magnetite, and albite crystals to stiffen and color the hair, mimicking natural locks. Additionally, she wore two rings adorned with carved jasper scarabs, indicating her high social status.
The researchers proposed several theories for her gaping mouth. Dr. Saleem suggested that the expression could be the result of a cadaveric spasm, a rare condition where muscles that were heavily used before death lock in place, indicating that she might have died in severe pain or emotional distress.
“Embalmers likely mummified the contracted body of the woman before it decomposed or relaxed, thus preserving her opened mouth position at death,” Dr. Saleem explained. This condition is controversial among scientists, with some doubting its occurrence.
Despite the advancements in understanding the Screaming Woman, her exact cause of death remains unknown. The study’s findings challenge previous assumptions.
“This type of study humanizes the mummy and lets us look to her as a human being,” Dr. Saleem remarked. The ongoing research aims to use more sophisticated techniques to uncover additional details about her life and death.
The Screaming Woman’s mummy is currently housed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo, while her coffin and rings are displayed at The Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City. Her story, though still shrouded in mystery, continues to intrigue scientists and the public alike.























