Recent research has revealed what may be the world’s oldest known lunisolar calendar, discovered at the ancient archaeological site of Göbekli Tepe in southern Turkey. Carved into a massive stone pillar nearly 13,000 years ago, the intricate markings likely record a catastrophic comet strike, an event that researchers believe played a pivotal role in the development of human civilization.
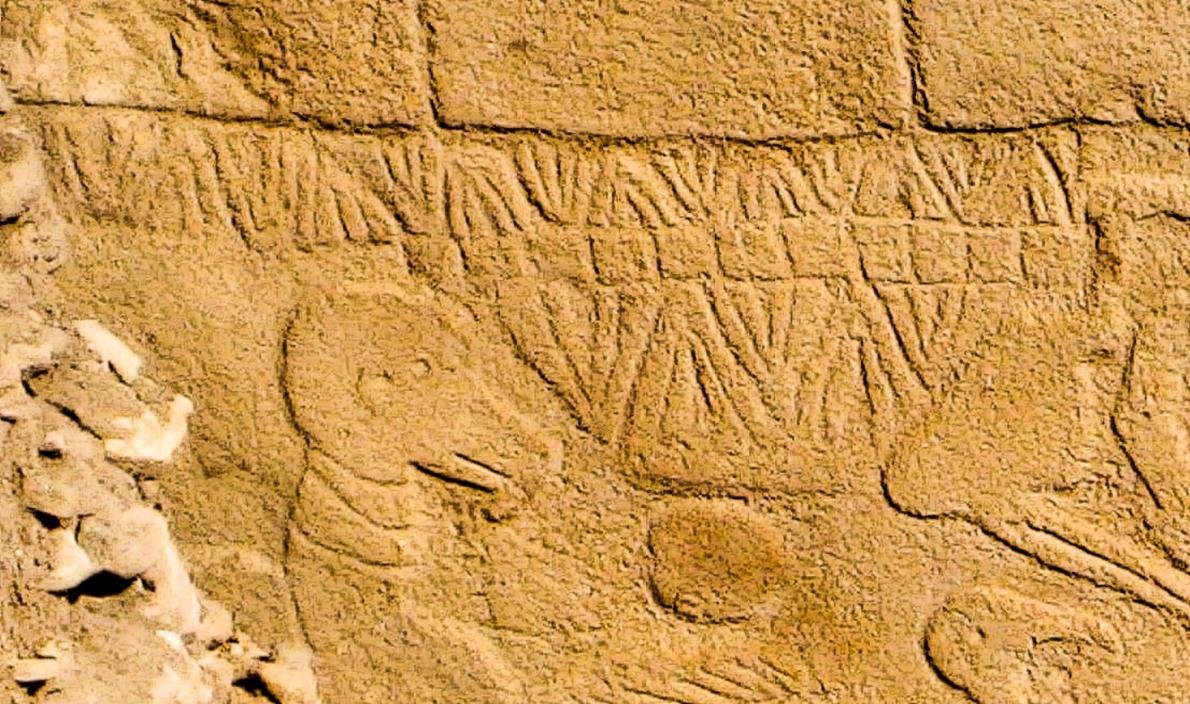

The new study, published in the journal Time and Mind by Dr. Martin Sweatman, an engineer at the University of Edinburgh, reveals that the V-shaped carvings found on the stone pillar at Göbekli Tepe could represent days in a solar calendar. This calendar, according to Sweatman, consisted of 12 lunar months and 11 additional days, closely tracking the phases of the sun, moon, and constellations. The calendar predates all previously known systems of this kind by thousands of years, positioning Göbekli Tepe as a crucial site for understanding early human astronomical knowledge.
Göbekli Tepe, often referred to as the world’s first temple, is a complex of temple-like enclosures adorned with intricately carved symbols. Discovered in the late 20th century and situated on a hill overlooking the Harran Plain, the site is located near the city of Şanlıurfa, historically known as Urfa. This area, rich in archaeological significance, is believed to be the birthplace of the Biblical patriarch Abraham.
The V-shaped carvings on the pillar at Göbekli Tepe are not mere decorations. According to Dr. Sweatman, they could represent the earliest attempt by humans to document the solar and lunar cycles. “We can be very confident indeed that it’s a date,” Sweatman stated. He further explained that one of the symbols, a V worn around the neck of a bird-like figure, might represent the summer solstice constellation at the time.
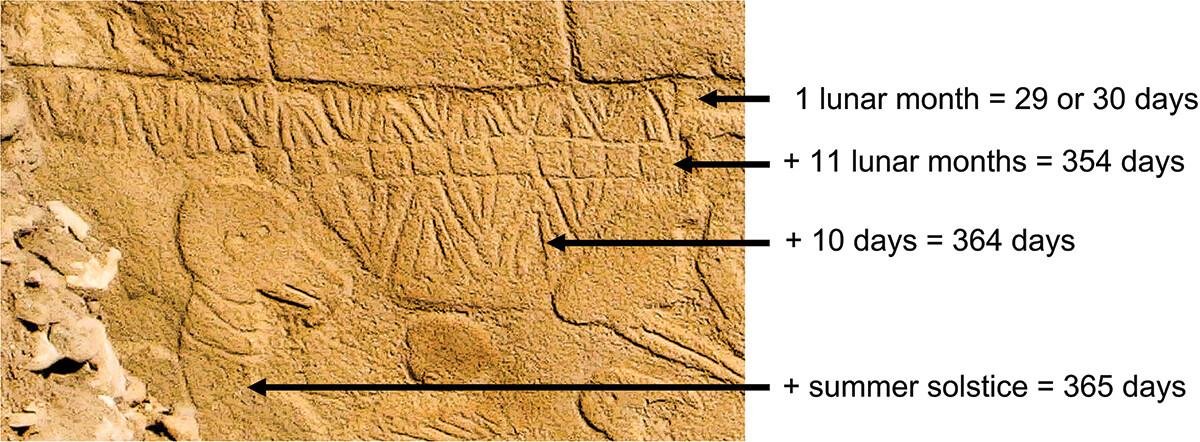
These findings suggest that the inhabitants of Göbekli Tepe were keen observers of the sky, likely driven by a world-shattering event. Researchers believe that the calendar was carved to memorialize a devastating comet strike around 10,850 BCE, which triggered a 1,200-year mini Ice Age. This comet strike is thought to have wiped out many large animal species and caused significant environmental changes that may have spurred the transition from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to agriculture in the Fertile Crescent of West Asia.
This comet impact theory is supported by evidence from soil sediments in North America and Greenland, where high levels of platinum and nanodiamonds, along with materials altered by extreme temperatures, have been found. These findings indicate that the comet strike had a global impact, leading to significant climatic shifts and possibly triggering the beginnings of human civilization as we know it.

Moreover, another pillar at Göbekli Tepe appears to depict the Taurid meteor stream, believed to be the source of the comet fragments. This stream, originating from the direction of the Aquarius and Pisces constellations, is depicted in a way that suggests ancient people could track the precession of the Earth’s axis. This ability to record such astronomical phenomena predates the documented discovery of precession by Hipparchus of Ancient Greece by at least 10,000 years.
Researchers suggest that the comet strike and the subsequent climate changes may have led to the formation of new religious practices or cults, which could have played a role in the development of human civilization. Dr. Sweatman noted, “This event might have triggered civilization by initiating a new religion and by motivating developments in agriculture to cope with the cold climate.” He also speculated that these early attempts to document celestial events could represent the first steps toward the development of writing, millennia later.

























Martin Sweatman is not a credible source. He is a chemical engineer who was inspired by Graham Hancock, a prominent pseudoarchaeologist who once claimed that Atlantis existed as a globe-spanning, technologically sophisticated society in Antarctica that was wiped out by a global catastrophe that shifted the entire continent down to the southern pole. Hancock postulated in his book, The Fingerprints of the Gods, that the survivors of Atlantis seeded other cultures with warnings that a similar event would occur in 2012. (Obviously, that didn’t happen.)
Sweatman has been promoting his ridiculous claims about the solar calendar on YouTube for years. In 2020, David Miano, an actual historian and researcher of ancient civilizations in the Middle East, debunked Sweatman’s claims and even did a follow up video in 2021 in response to Sweatman taking umbrage with his frank analysis of his views (links below).
Is the Zodiac at GOBEKLI TEPE? | Pillar 43 and the Evidence for Constellations (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vUdJCVwqJNM)
Lies & Statistics and Gobekli Tepe | A Response to Martin Sweatman (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C_7Jl6GExnM)
Sweatman recently appeared in Hancock’s Netflix series, Ancient Apocalypse. In the series, Hancock has abandoned the belief that Atlantis is in Antarctica. Instead, he uses Sweatman’s ‘research’ to bolster his claim that Atlantis is now sunken off the coast of Europe.This series has been absolutely blasted by the archaeological community, many of whom have complained they were quoted out of context in the series. They even wrote a letter to Netflix asking them to reconsider airing the series.