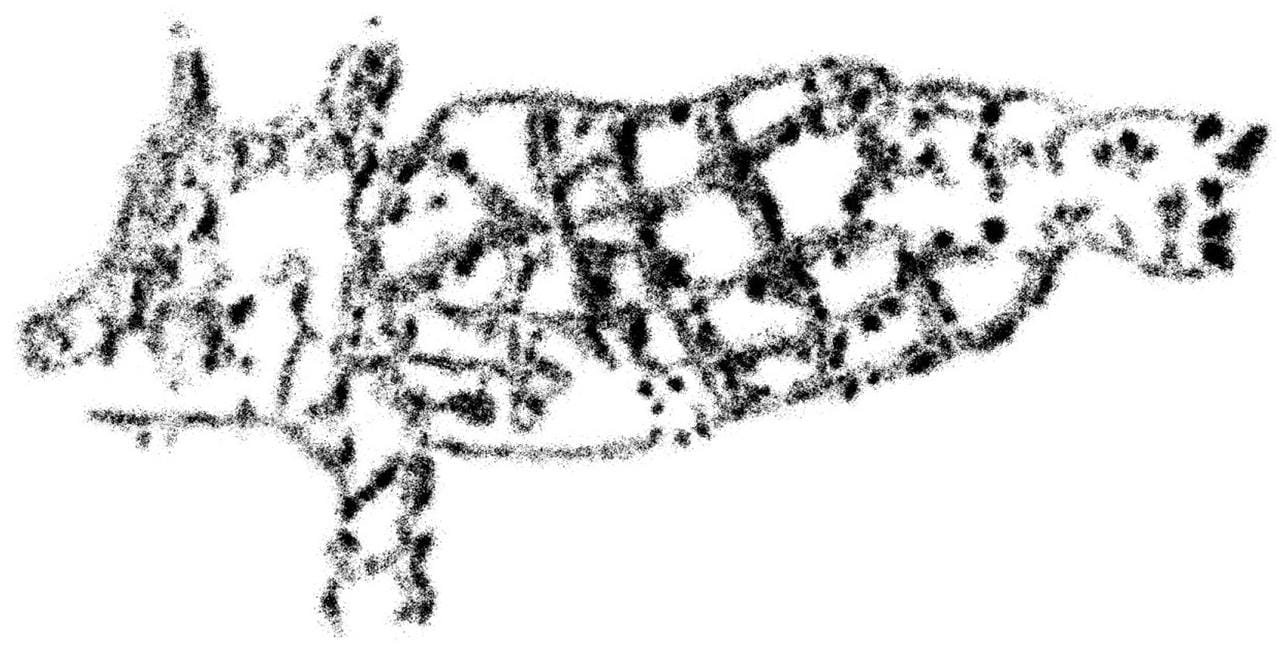
Researchers have identified a unique petroglyph in Egypt’s el-Hosh region that likely represents the zodiac sign Capricornus, a hybrid creature with the forequarters of a goat and the hindquarters of a fish. This discovery, led by Dr. Linda Evans of Macquarie University, Australia, and her colleagues, has been documented in the Journal of Egyptian Archaeology. It represents the first known instance of a zodiac symbol in Egyptian rock art.
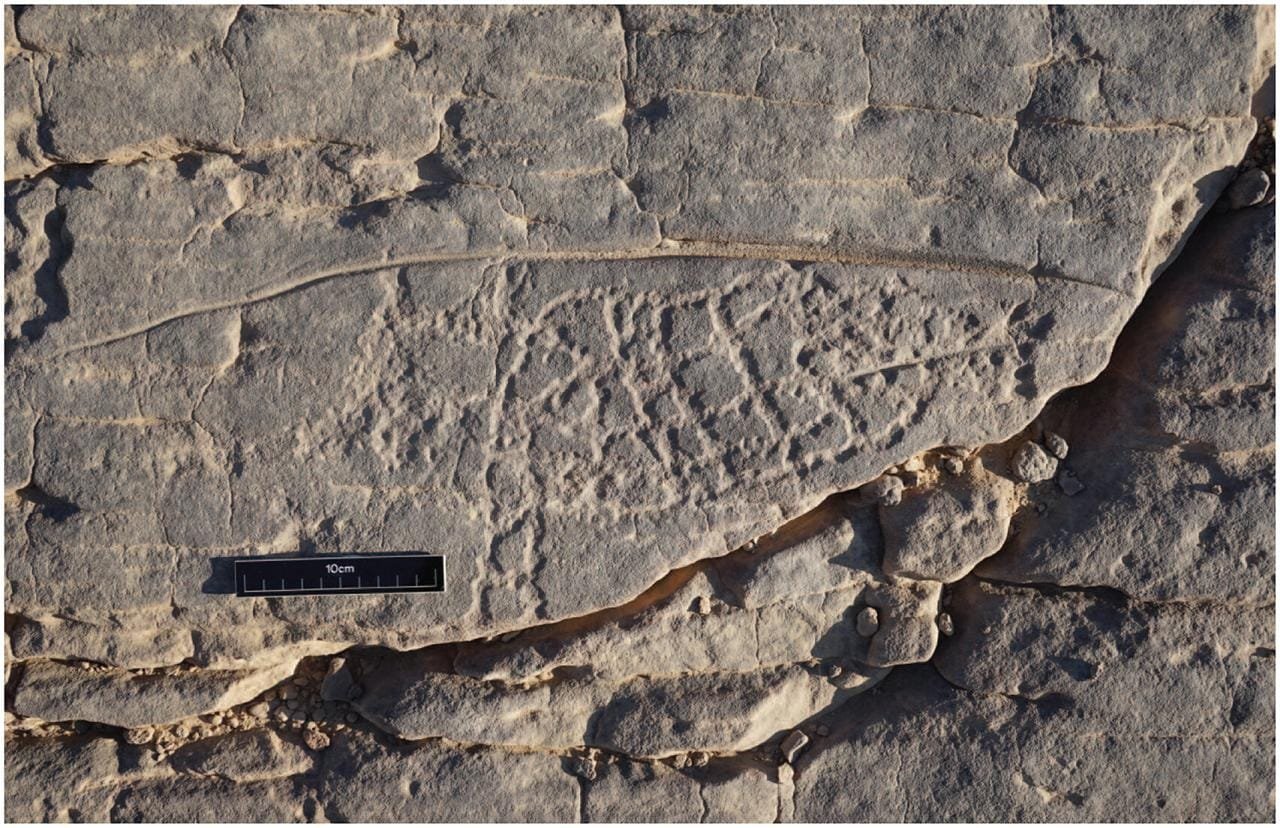

The Capricornus carving was initially identified during fieldwork by Dr. Frederick Hardtke, who described its unique placement: “The goat-fish was found in a locality of el-Hosh, which hosts a large number of petroglyphs and texts, much of it Predynastic, but also material from the Graeco-Roman and Islamic periods. It was located adjacent to another highly unusual image we believe to be a chameleon, making the panel enigmatic.”
Dr. Evans was struck by the resemblance of the hybrid creature to Capricornus and began investigating its origins. “We had described it in an earlier paper as a mythical animal, but after more research, I realized it resembled the goat-fish, leading me to study its history as an astrological sign,” she explained.
Capricornus originates in Mesopotamia, where it symbolized the Sumerian god Enki (and later, the Akkadian Ea), both associated with water and wisdom. By the late third millennium BCE, this imagery evolved into the recognizable goat-fish hybrid depicted on Mesopotamian seals. The zodiac, as a system of celestial symbols influencing human affairs, spread from Mesopotamia to Greece in the 5th century BCE and eventually reached Egypt through Greek and Roman influences during the Ptolemaic and Roman periods (3rd century BCE to 2nd century CE).
In Egypt, zodiacs first appeared on temple ceilings, coins, and coffin lids during the Greco-Roman period. “Even though such symbols were primarily associated with elite contexts, they eventually permeated broader society, as seen in horoscopes made for individuals like the weaver Tryphon in the first century CE,” said Dr. Evans.
The petroglyph’s style and characteristics suggest it was created during the Graeco-Roman period, between the first century BCE and the second century CE. Supporting this conclusion, Dr. Hardtke noted, “Overall, we observe a gradual decline in both frequency and quality of pictorial rock art in Egypt with the advent of writing.”
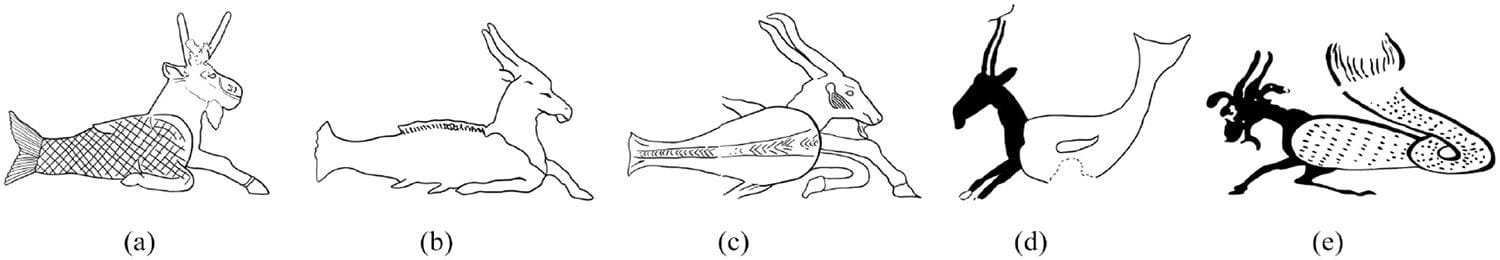
Key details in the carving, such as the depiction of a straight tail, also date it to before the second century CE, when Roman variants of Capricornus began showing looped tails. Stylistic similarities between the Capricornus and the nearby chameleon petroglyph suggest both were carved by the same individual during this era.
The precise purpose of the Capricornus petroglyph remains uncertain. It could have served as a navigational marker, given the importance of stars in desert travel. Alternatively, its creator may have been captivated by its astrological and astronomical significance, potentially reproducing it from memory or a coin.
Dr. Hardtke further explained that Greco-Roman influences on Egyptian rock art were not uncommon during this period: “Occasionally, we find Greek inscriptions, dedications to gods, and figural depictions alongside texts. This context makes the Capricornus carving even more plausible as a product of cultural exchange.”























Comments 0