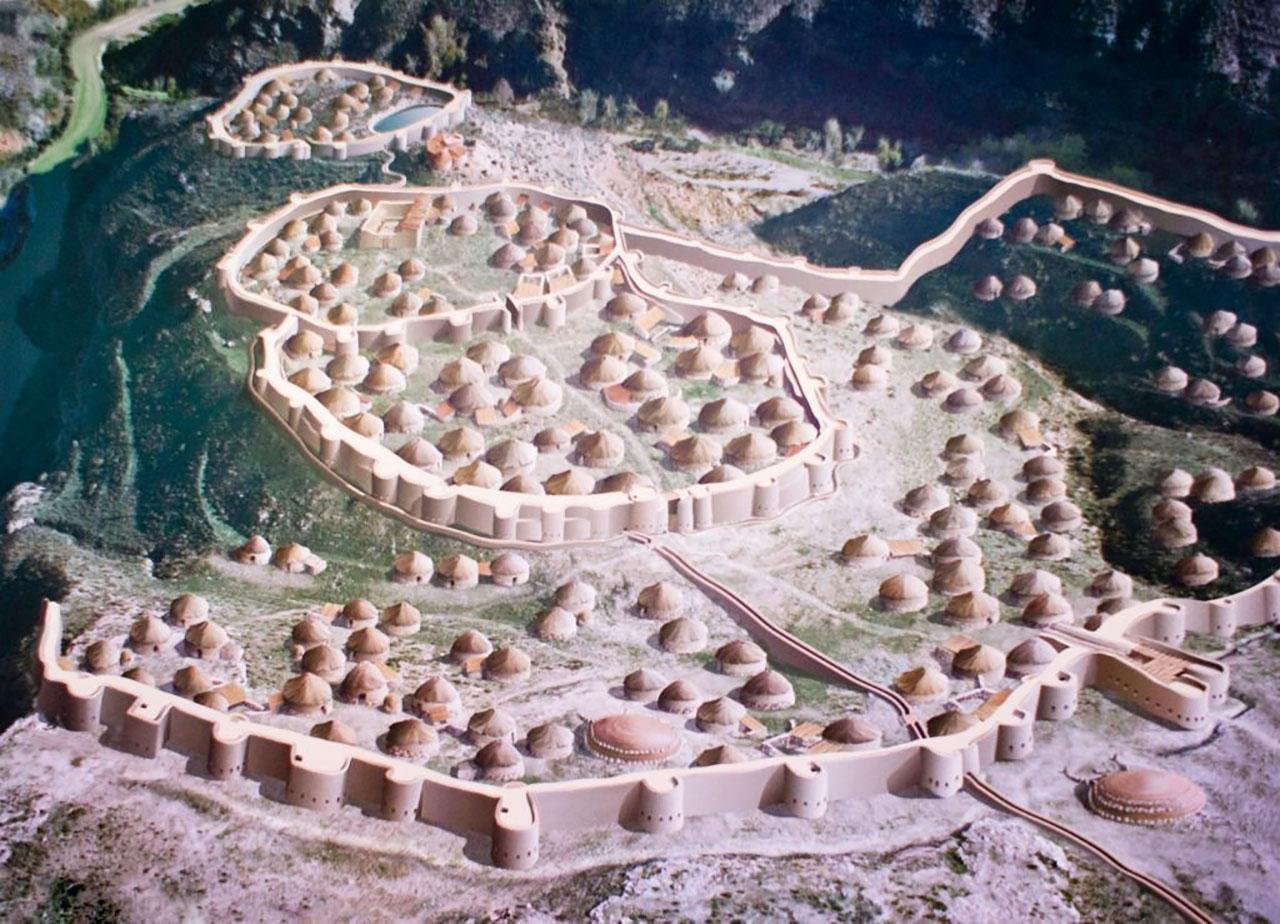
New excavation of the Valencina de la Concepción Chalcolithic site in Seville, Spain, is defying old assumptions regarding its purpose and social structure. Not a temporary gathering point or reserved for ritual activity, but rather, a recent Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) research published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports reveals Valencina to have been a thriving, permanent settlement occupied continuously for well over a millennium—from around 3300 to 2150 BCE.

Researchers analyzed 635 macrolithic tools from the site’s northern section, an area long comparatively overlooked relative to the site’s more prominent necropolis. It was part of the larger Valencina Nord Project, undertaken in collaboration with the German Archaeological Institute in Madrid, the University of Würzburg, and the Autonomous University of Madrid. Excavations focused on sites such as Cerro de la Cabeza and Pabellón Cubierto, examining habitation structures, workshops, and storage pits.
According to Marina Eguíluz, a predoctoral researcher at the Department of Prehistory of UAB and lead author of the study, “This indicates a permanent occupation of the settlement. The only observable changes between the three major phases of occupation could be due to the density of occupation of the area.”
The findings reveal a stable and sustainable way of life centered on diversified domestic and subsistence tasks. These included grain processing, animal husbandry, leather work, fiber work, and working with organic and inorganic materials. The tools were built using locally sourced raw materials—within a 30-kilometer radius—and revealed extensive evidence of use and reuse, indicating a connection to local environments and efficient resource management.
Significantly, no traces of surplus accumulation or central storage were identified by the study, and this convinced scholars that the inhabitants practiced an egalitarian and cooperative economy. UAB prehistorian Roberto Risch, the coordinator of the study, explained: “The observed continuity highlights the sustainability of the socioeconomic model present during the Copper Age, based on cooperativism and the lack of accumulation and centralization.” In his view, these findings reinforce the theory of “cooperative societies of abundance,” contrary to typical models which locate prehistoric society as having taken a linear path toward hierarchy and state formation.
Previous interpretations of Valencina have given great emphasis to its necropolis and elite burials and burial goods, often overlooking the settlement area. Stone tools had been viewed primarily in ritual terms before because they were fragmented. But this research turns the spotlight onto daily life and economic activity, rewriting our knowledge of one of the biggest Copper Age sites in Europe, covering a remarkable 450 hectares.
Autonomous University of Barcelona