In a discovery from the San Lázaro rock shelter in central Spain, near Segovia, archaeologists have unearthed what is thought to be the earliest known human fingerprint, challenging long-standing assumptions about the symbolic and artistic capabilities of Neanderthals. The find—an ocher-stained granite pebble with a well-defined fingerprint and arranged facial features—foretells an intentional attempt at symbolic expression some 43,000 years ago.

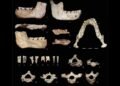
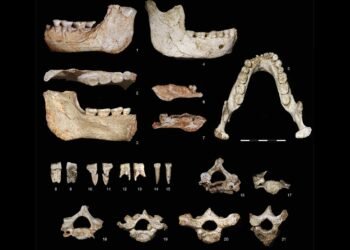
The research, led by a team from the Complutense University of Madrid, the Geological and Mining Institute of Spain, the Spanish National Police’s Scientific Police Unit, and the University of Salamanca, was published in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences. The researchers examined the granite rock using a range of scientific tools, including 3D scanning with lasers, multispectral imaging, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which ultimately revealed an unmistakable human fingerprint embedded in red ocher pigment.
“This is a contribution to our understanding of Neanderthals’ capacity for abstraction, and how it could have been one of the earliest human facial symbolizations in prehistory,” the study authors said. The fingerprint, forensic specialists confirmed, retains full ridge patterns, bifurcations, and convergence points—clear evidence of intentional application by a human, likely a male Neanderthal.
The 21-cm-long stone, geologically inconsistent with the immediate cave environment, appears to have been transported from the River Eresma approximately 5 kilometers away. It lacks utilitarian markings, and its unique size and shape are distinct from the other Mousterian-era tools discovered in the same layer.

Most striking is the arrangement of features: two small, symmetrical indentations above a central larger indentation, with a precisely situated red ocher dot between them. Monte Carlo statistical simulations revealed that there existed only a 0.31% probability that the red dot’s alignment coinciding with the indentations occurred by chance, thereby making it more likely that the Neanderthal was trying to depict a human face.
Although interpretations vary, with some scientists wondering whether the work can actually be considered symbolic art, the authors believe the placement of pigment and choice of stone suggest symbolic activity. The researchers wrote: “It is not just a fingerprint; it is the signature of an individual who manipulated this object with a purpose that goes beyond the utilitarian.”

Spanish cultural official Gonzalo Santonja praised the discovery at a recent press conference, calling it “the oldest portable object to be painted on the European continent” and “the only object of portable art painted by Neanderthals.”
The find contributes to growing evidence—La Pasiega and Maltravieso cave art, for instance—that Neanderthals, once thought incapable of abstract thought or artistic expression, may have had a more complex symbolic culture than was once believed. It doesn’t compare with the elegant cave paintings of early Homo sapiens at France’s Chauvet Cave, of course, but the San Lázaro pebble is one example of a seeming sea change in scientists’ understanding of the cognitive lives of Neanderthals.
Whether as ritual, decoration, or the first hint of a Neanderthal signature, this fingerprinted stone is strong proof that imagining, symbolizing, and creating were not exclusive to modern humans.


















Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
I know nothing about fingerprints so this may be an ignorant question, but I wonder if this print differs from modern man? If it was put in a database of fingerprints, would it stand out from all the others? Quite an interesting find especially if this person was conveying an artistic expression, which I’m not convinced of but certainly does pose a fascinating question. If they are capable of deliberately making tools for different survival techniques, then I question why not then, for personal expression? How could they not see the similarities of nature mimicking (as in this case) man? And if this was the case in this example, this person went on to deliberately complete the image formed from an idea that struck them at that moment. Was this person with a group and was this object passed around and they all smiled and instantly related to it? Hope to hear about more finds like this!