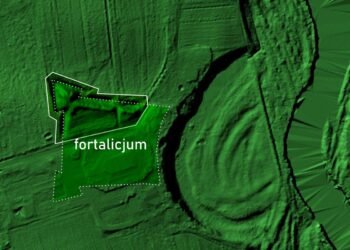
After an extensive two-year excavation project in Egypt, archaeologists have discovered the pyramid of an unidentified queen from ancient Egypt, along with a collection of coffins, mummies, artifacts, and an interconnected network of tunnels.

This remarkable find took place in the ancient necropolis of Saqqara, situated in Giza, just 20 miles south of Cairo. The significant discoveries were made on November 4, coinciding with the 100th anniversary of the uncovering of King Tut’s tomb.
Given their close proximity to King Tut’s tomb, researchers believe that the mummies found likely belonged to his most trusted generals and advisors who served during his reign from 1333 B.C. to 1323 B.C.
Egyptologist Zahi Hawass, the former Minister of Antiquities, explained that Teti, a revered figure in the New Kingdom era, was worshipped as a deity, attracting people to seek burial near him.
Until now, Saqqara was predominantly known for burials from either the Old Kingdom or the Late Period. However, this recent discovery of 22 shafts, ranging from 30 to 60 feet (9 to 18 meters) deep, exclusively containing New Kingdom burials, has rewritten the historical understanding of the site.
According to Hawass, archaeologists made an astonishing discovery during their excavation, unearthing a massive sarcophagus made of limestone, along with 300 exquisite coffins from the New Kingdom period.
This finding is particularly significant because New Kingdom burials were not previously known to be prevalent in this area, making it entirely unique to the site.
The coffins themselves are remarkable, featuring distinct facial features that vary from one another, enabling differentiation between men and women. They are adorned with intricate scenes from the Book of the Dead, adding to their beauty and historical significance.
Additionally, a pyramid dedicated to an unknown queen named Neith was found, shedding new light on Egyptian history. Prior to this discovery, Neith’s existence was completely absent from historical records, making this revelation truly remarkable and rewriting our understanding of the past.
The condition of the mummies within the coffins surprised the researchers, as they were remarkably well-preserved after centuries. This preservation is a testament to the advanced mummification techniques of the New Kingdom period.
Some of the coffins even had two lids, and the most extraordinary find thus far was a coffin featuring a solid gold mask of a woman, showcasing the exceptional craftsmanship of the time.
He further explained that within the coffins and underground burial chambers, a diverse array of artifacts were discovered. These included ancient games like Senet, shabtis (funerary figurines), statues depicting the deity Ptah-Sokar, and even a metal axe held by a soldier.
Some of these remarkable artifacts will be showcased in the forthcoming Grand Egyptian Museum in Giza, set to open in the following year.