Archaeologists from Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have recently made a significant discovery in the dense forests of the Balamkú Ecological Reserve in the Mexican state of Campeche.

Using high-resolution photography and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, researchers uncovered a previously unknown Maya city named Ocomtún, which means “stone column” in the Mayan language. The site spans approximately 123.5 acres and primarily dates to the Classic Period (250–1000 CE).
LiDAR technology works by emitting pulsed laser light to measure distances to the Earth’s surface, generating a detailed 3D digital map of the terrain. This method enabled archaeologists to penetrate the thick jungle canopy and reveal hidden features of the ancient city.
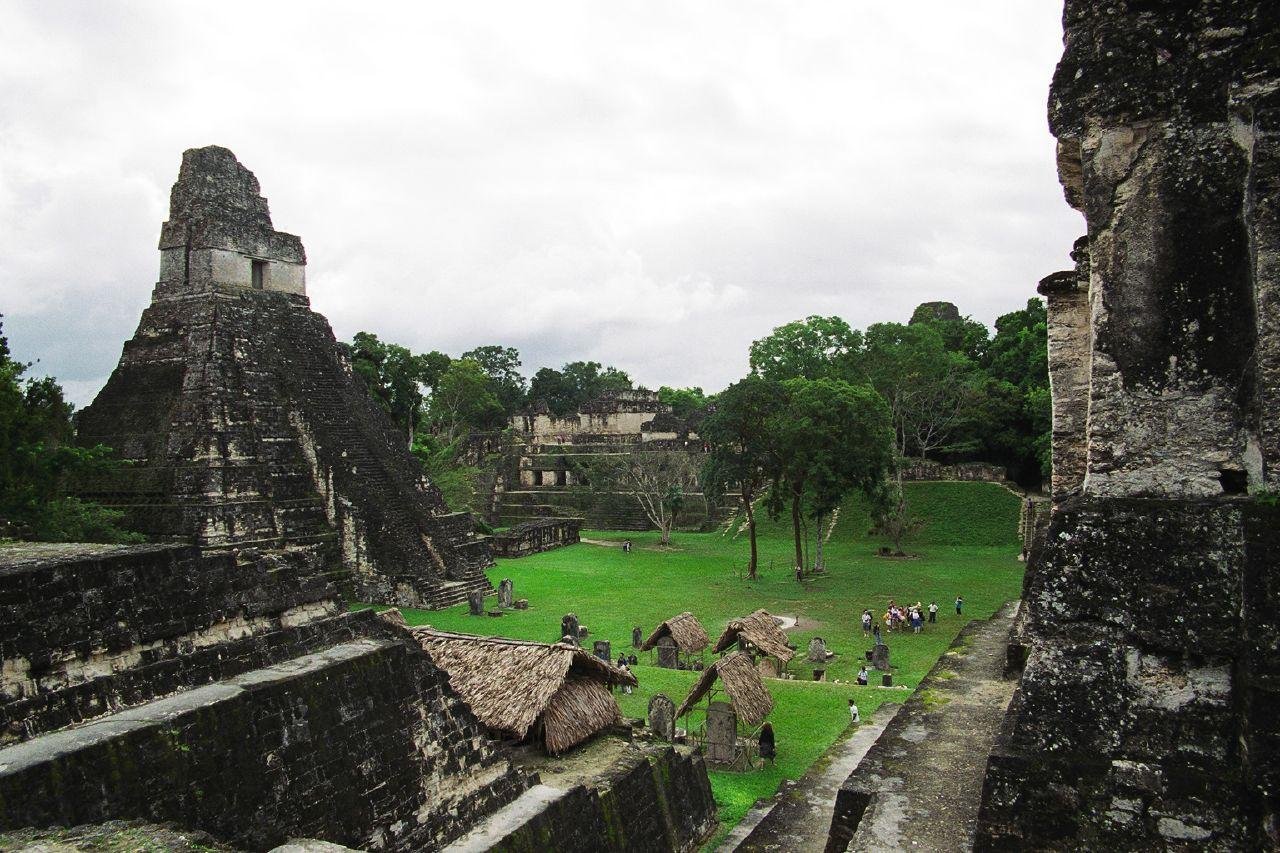
Located on a peninsula surrounded by wetlands, the site contains a dense concentration of pre-Hispanic structures. These include pyramidal buildings over 15 meters tall, broad plazas, and elongated structures arranged in concentric circles, as well as a ballgame court—a hallmark of Mesoamerican civilizations. The discovery also includes an 80-meter-long rectangular acropolis and a 25-meter-high pyramid.
Ocomtún played an important role during the Classic Period, and the site experienced further development during the Terminal Classic (800–1000 CE), when shrines, terraces, and ceremonial plazas were constructed. However, by the 10th century CE, the population sharply declined, and the city was eventually abandoned. This decline coincides with the broader Maya collapse, a period during which many southern lowland Maya cities were deserted.
The discovery of Ocomtún adds valuable insight to the expanding body of research on the Maya civilization, which was renowned for its achievements in architecture, astronomy, mathematics, writing, and calendrical systems. The Maya once dominated a vast region of Mesoamerica, encompassing much of what is now southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and parts of Honduras and El Salvador.
The so-called Maya collapse, which peaked in the 9th century CE, is believed to have been caused by a combination of factors, including political instability, prolonged drought, overpopulation, and environmental degradation.
The dense jungles of the Yucatán Peninsula have long obscured ancient Maya sites, but with the application of LiDAR, many previously unknown settlements are now being brought to light. In addition to aerial surveys, ground-level excavations are underway to recover artifacts and gain deeper insights into the daily lives, rituals, and social structures of the Maya people.
The significance of Ocomtún lies not only in its architectural complexity but also in its potential to enhance our understanding of Maya political geography, ceremonial practices, and regional interactions. Future research, including the analysis of ceramic fragments and construction materials, will shed further light on the period during which the city flourished.
This discovery underscores how advanced technologies, like LiDAR, are revolutionizing archaeological exploration and enabling scholars to reconstruct the rich and complex histories of ancient civilizations like the Maya.