Archaeologists have employed advanced lidar technology to unveil an ancient civilization hidden beneath the dense vegetation of the Upano Valley in eastern Ecuador.
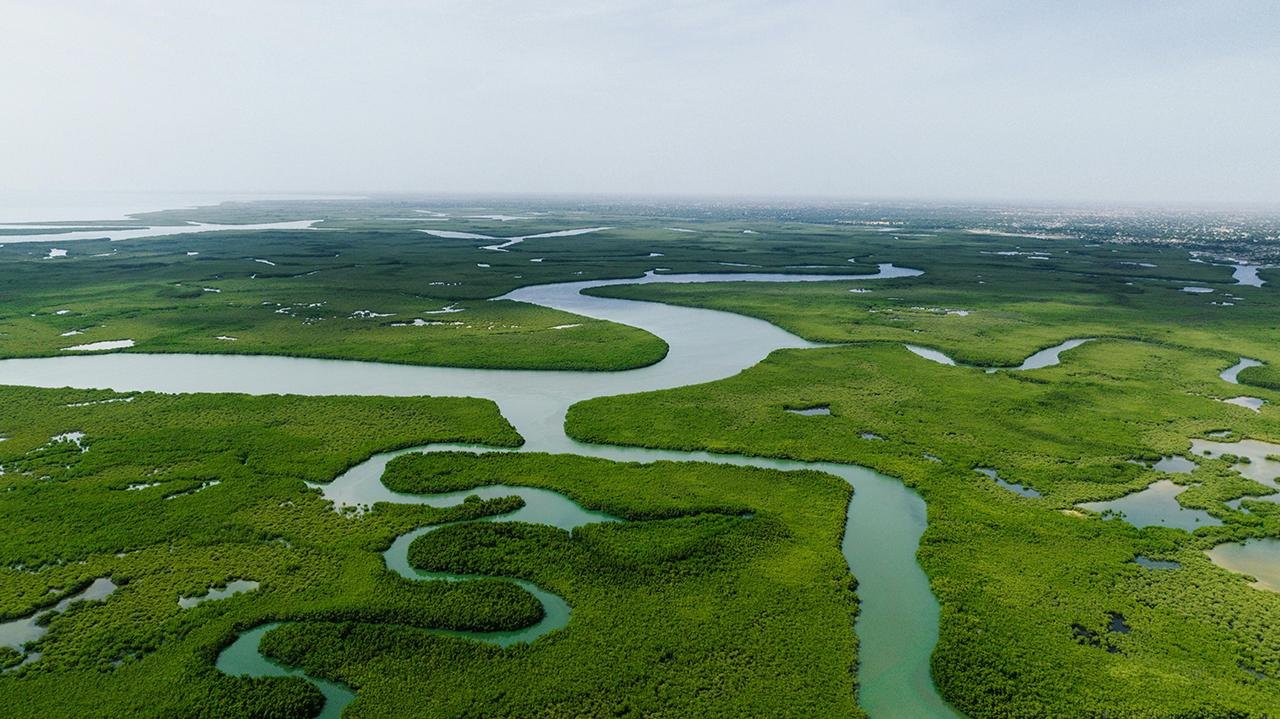

The findings, published in the journal Science, showcase a complex network of interconnected cities, roads, and agricultural structures dating back 2,500 years, making it the oldest and largest example of an agricultural civilization in South America’s Amazon rainforest.
The Upano Valley site, which spans approximately 230 square miles, was occupied by the pre-Hispanic Kilamope and Upano cultures, followed by the Huapula culture. Lidar imaging, a method using airborne lasers to penetrate the forest canopy, revealed more than 6,000 rectangular earthen platforms, plaza structures, and mounds connected by an extensive gridwork of straight roadways and footpaths.
The lead study author, Stéphen Rostain, an archaeologist and director of research at the French National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS), emphasized how lidar provided a unique perspective, allowing researchers to overcome the limitations of on-foot exploration hindered by the forest’s dense foliage.
The settlements in the Upano Valley, including Sangay and Kilamope, exhibited a high degree of urban planning, with large mounds reaching up to 492 feet in length and 26 feet in height. The complexity of the site drew comparisons to Maya urban systems in Central America, challenging previous beliefs about the Amazon’s historical civilizations.
“We believe that it is crucial to thoroughly revise our preconceptions of the Amazonian world and, in doing so, to reinterpret contexts and concepts in the necessary light of an inclusive and participatory science,” the study authors wrote in their paper.
According to Science Journal, the use of lidar technology has revolutionized the understanding of pre-Columbian Amazonian cultures, revealing a diverse range of complex societies that predate European colonization.
The Upano Valley discoveries, surpassing 2,000 years in age, underscore the long-unrecognized diversity of ancient Amazonian cultures. The network of roads connecting the Upano sites, covering an expansive area of 300 square kilometers, suggests contemporaneous existence, challenging prior assumptions about the Amazon’s historical settlement patterns.
The settlements in Upano are more than a millennium older than other complex Amazonian societies, such as the recently discovered Llanos de Mojos in Bolivia. Researchers emphasize the sophistication of the Upano Valley road network, which includes wide, straight roads and right angles, suggesting advanced planning and engineering.
The lidar survey also uncovered hillside terraces, rectangular agricultural fields, and evidence of water management systems, including canals and causeways. The extent of landscape modification in the Upano Valley rivals other ancient civilizations, such as the Classic Maya. Despite the impressive findings, many questions remain unanswered, including the population size, trade networks, and governance structures of the Upano people.
“It changes the way we see Amazonian cultures. Most people picture small groups, probably naked, living in huts and clearing land – this shows ancient people lived in complicated urban societies,” explains co-author Antoine Dorison
The vast archaeological potential in the Ecuadorian Amazon, still largely unexplored, raises anticipation about future discoveries of the region’s ancient civilizations.






















Disclaimer: This website is a science-focused magazine that welcomes both academic and non-academic audiences. Comments are written by users and may include personal opinions or unverified claims. They do not necessarily reflect the views of our editorial team or rely on scientific evidence.
Comment Policy: We kindly ask all commenters to engage respectfully. Comments that contain offensive, insulting, degrading, discriminatory, or racist content will be automatically removed.
Graham Hancock has been stating that there were cities with millions of inhabitants in the Amazon for years. Now the evidence comes to light reinforcing his claims.