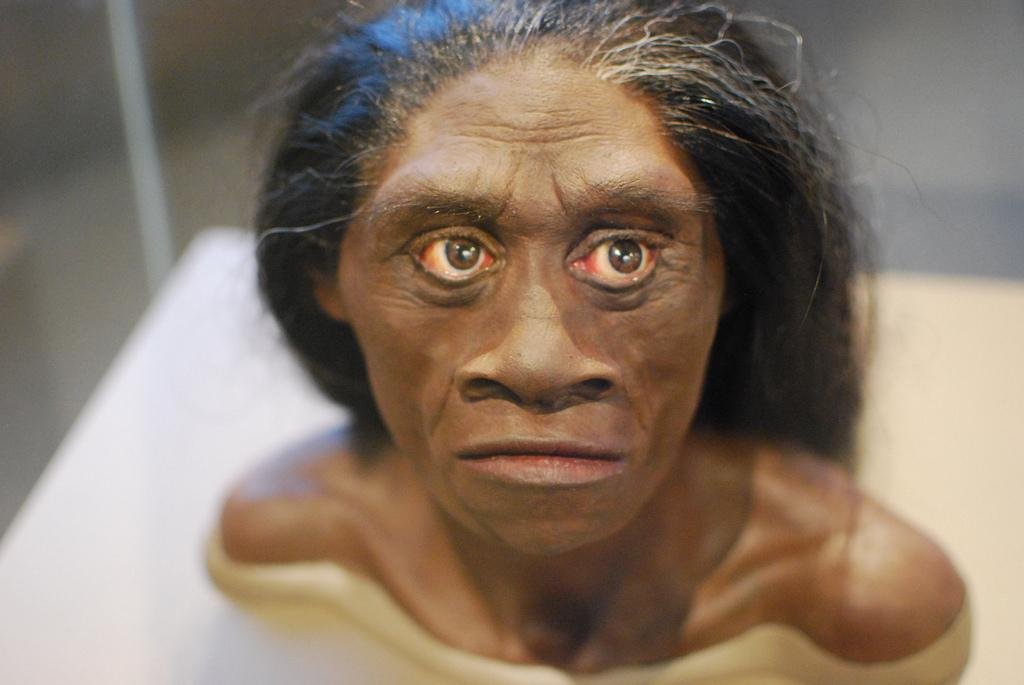
Recent fossil discoveries on the Indonesian island of Flores have revealed that the ancient human species, Homo floresiensis, commonly referred to as “hobbits” due to their small stature, were even tinier than previously thought.
Homo floresiensis was first discovered in 2003 in the Liang Bua cave on Flores. The initial fossils indicated that these small-brained humans lived on the island as recently as 50,000 years ago, while Homo sapiens had already established themselves in nearby regions. The original specimens suggested that individuals of this species grew to about 3 feet 6 inches tall, with small brains and relatively large teeth.
The origin of Homo floresiensis has been a subject of much debate. Some researchers believed they were a dwarfed version of Homo erectus, an early human ancestor that lived in Asia. Others speculated that they might be a remnant of an even more ancient small-statured human ancestor from Africa predating Homo erectus.
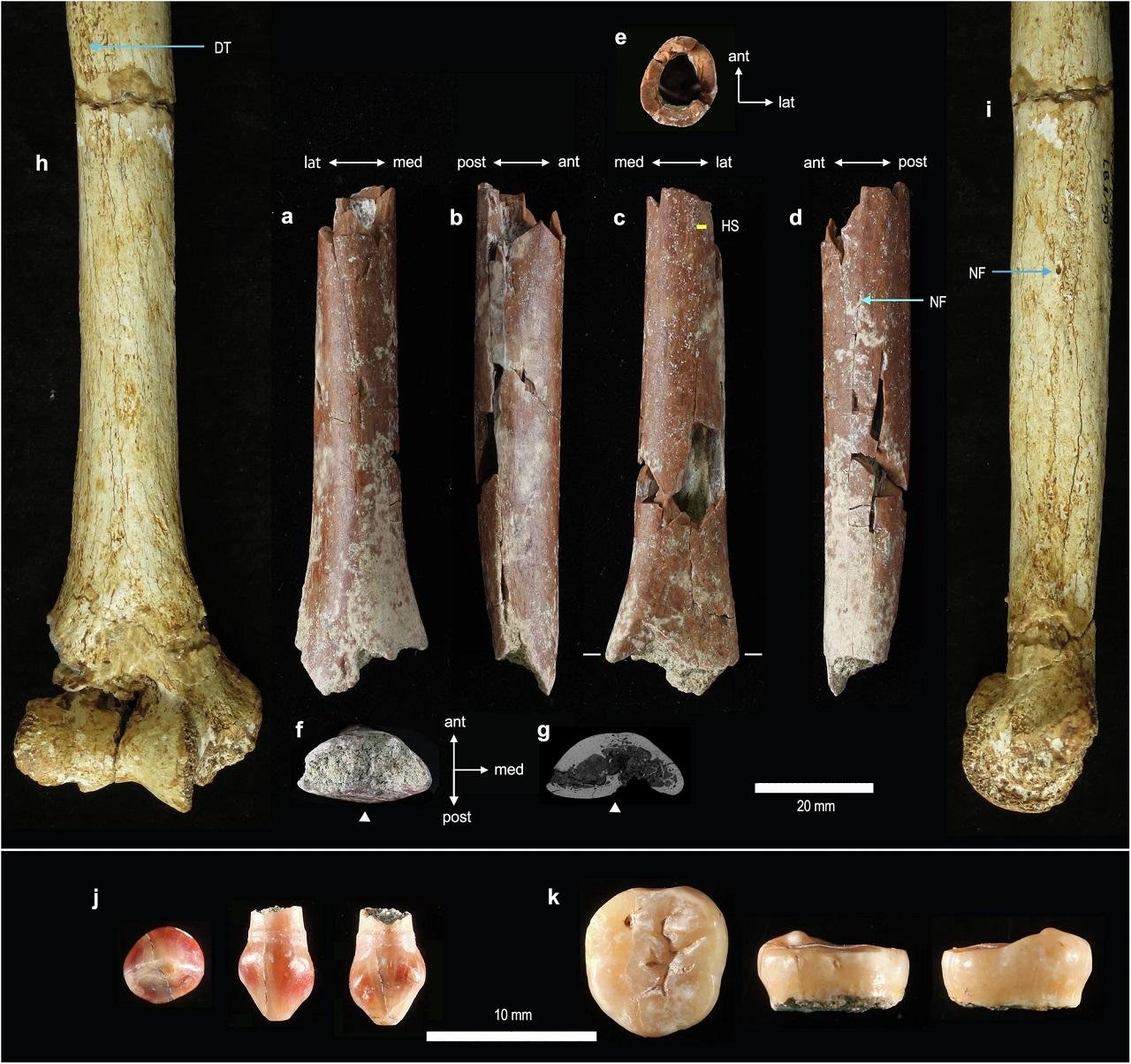
At a site called Mata Menge, approximately 45 miles from the Liang Bua cave, researchers have uncovered new fossils dating back 700,000 years. These include a tiny adult humerus bone, jaw fragments, and teeth, suggesting that the ancestors of Homo floresiensis were even smaller, standing around 3 feet 3 inches tall. This is about 2.4 inches shorter than previously estimated.

Adam Brumm, a co-author of the study and an archaeology professor at Griffith University’s Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, noted, “This 700,000-year-old adult humerus is not just shorter than that of Homo floresiensis; it is the smallest upper arm bone known from the hominin fossil record worldwide.”
The diminutive size of Homo floresiensis is thought to be a result of phyletic dwarfism, an evolutionary process where species evolve smaller body sizes when isolated on islands with limited resources and no significant predators. This phenomenon is well-documented in other island species, such as elephants, deer, and cattle.
Yousuke Kaifu, a professor of anthropology at the University of Tokyo and lead author of the study, told the Associated Press news agency “We did not expect that we would find smaller individuals from such an old site.” He also told Live Science that the small body size of Homo floresiensis likely evolved within the first 300,000 years of their history on the island and remained consistent for over 600,000 years.
The new fossils provide compelling evidence that Homo floresiensis evolved from Homo erectus through a dramatic reduction in body size. Despite these advances, many questions about Homo floresiensis remain unanswered. Researchers are still uncertain about the exact timeline and mechanisms of their evolution.























