Archaeologists from Durham University in the UK and the University of Al-Qadisiyah in Iraq have successfully identified the site of the pivotal 7th-century Battle of al-Qadisiyyah. By cross-referencing declassified Cold War-era satellite images with historical texts, the researchers believe they have located the battlefield approximately 30 kilometers south of Kufa, in Iraq’s Najaf Governorate. This battle, dating to 636 or 637 CE, played a central role in the early Islamic expansion, leading to a decisive Arab Muslim victory over the Sasanian Empire and clearing the way for Islam’s spread into Persia and beyond.
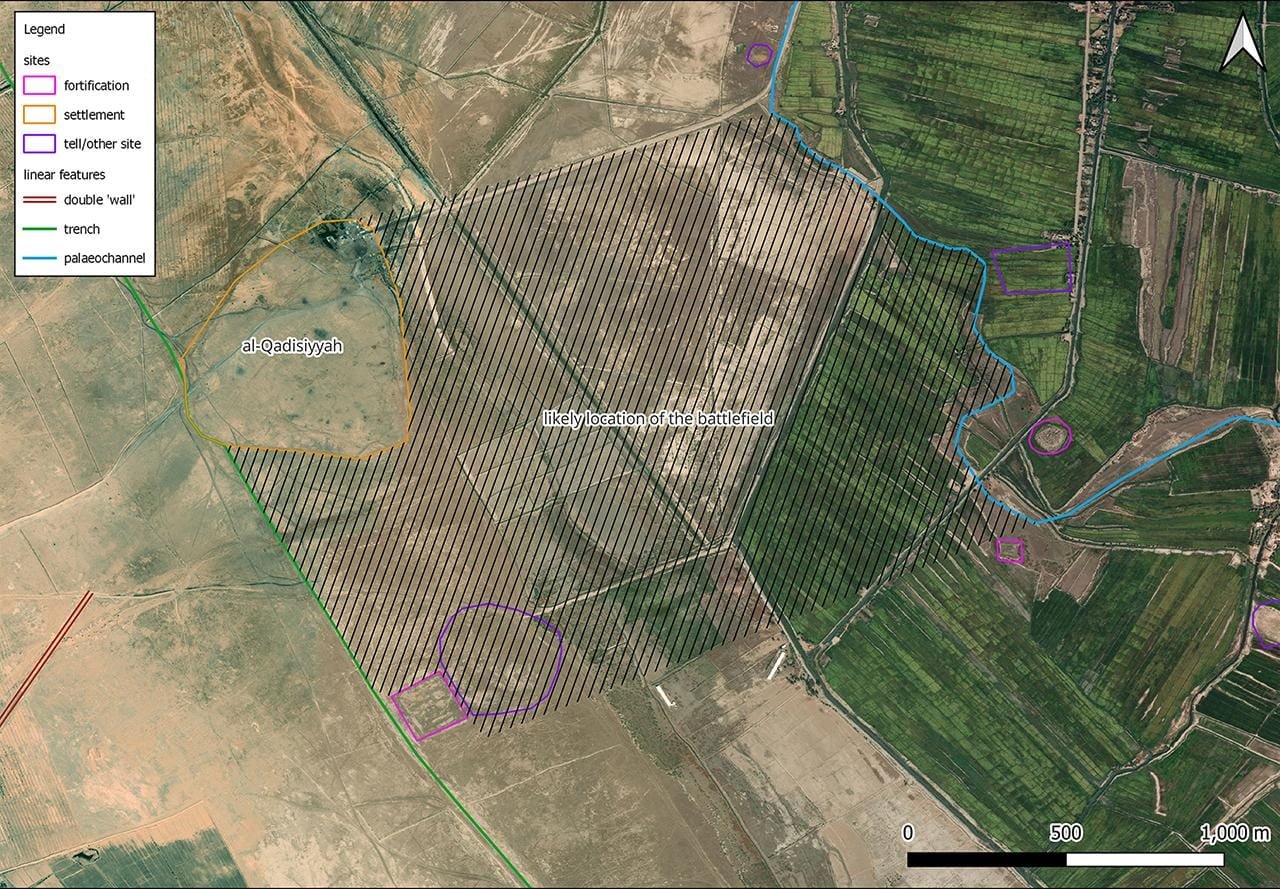
The discovery arose from an ambitious archaeological survey led by Dr. William Deadman, an expert in archaeological remote sensing at Durham University. Initially, Deadman’s team aimed to map the Darb Zubaydah, a historic pilgrimage route running from Kufa to Mecca, using both 1970s U.S. spy satellite images and modern photos. During the analysis, Deadman noted structural features on the satellite images that appeared to match descriptions in ancient texts of the al-Qadisiyyah battlefield. “I thought this was a good chance at having a crack at trying to find it,” he told CNN.
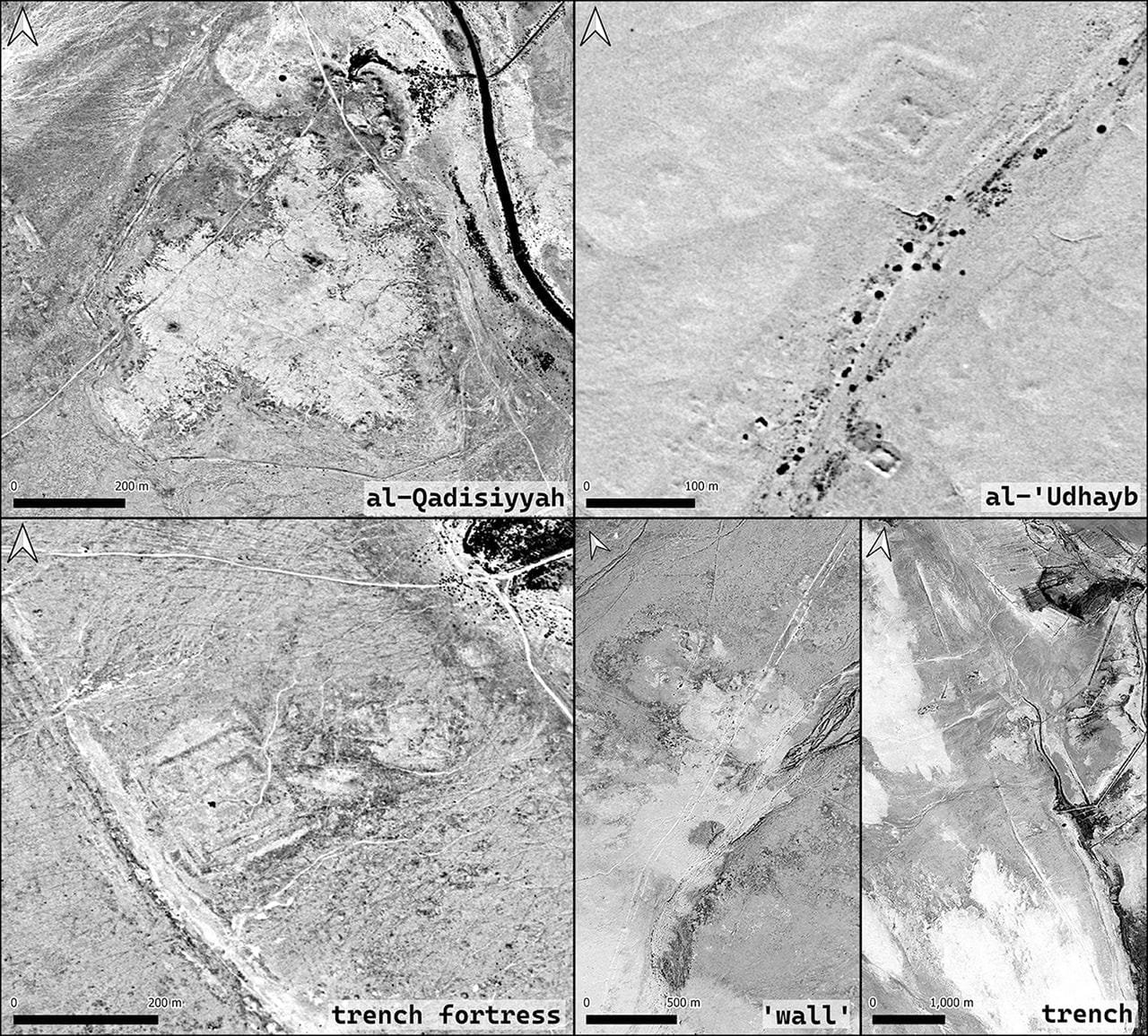
The team’s findings centered on a unique six-mile double wall feature, which they believe was instrumental during the battle. This structure linked a desert military outpost with a settlement on the edge of Mesopotamia’s southern floodplain, closely corresponding to historical descriptions of the battle site. Dr. Deadman described his reaction to the discovery as “gobsmacked,” adding that he was “extremely confident” that the site matched historical records.
On-the-ground investigations conducted by archaeologists from the University of Al-Qadisiyah provided additional confirmation, uncovering pottery shards and other artifacts consistent with the era of the battle. These artifacts, along with features such as a deep trench, fortresses, and remnants of an ancient river ford once traversed by elephant-mounted Persian troops, offer a tangible link to the historical accounts.

The Battle of al-Qadisiyyah marked a crucial turning point in Islamic history, leading to the eventual fall of the Sasanian Empire. “The decisive battle heralded the end of the Sasanian Empire into the abyss and the expansion of Muslim territory into Mesopotamia, Persia, and beyond,” commented Mustafa Baig, a lecturer in Islamic Studies at the University of Exeter, to CNN.
The research team’s use of Cold War-era satellite imagery—technology typically employed to view terrain now hidden by modern agricultural and urban developments—highlights the critical role of remote sensing in archaeology. Deadman noted, “The amazing thing about this spy imagery is that it allows us to wind back the clock 50 years,” making previously obscured features accessible to modern archaeologists.
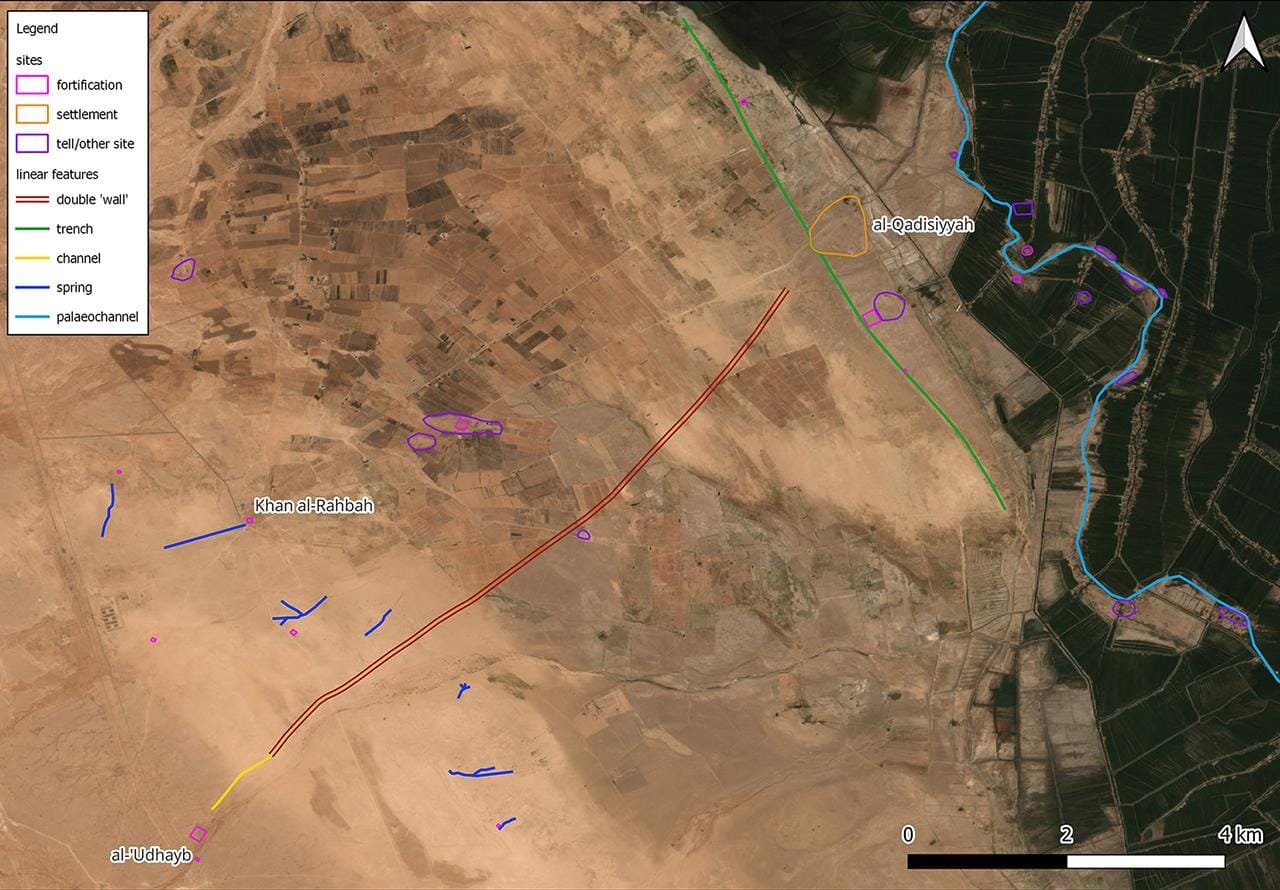
The findings also enhance understanding of the Darb Zubaydah pilgrimage route. The team successfully identified two significant waypoints along the route, al-Qadisiyyah and al-‘Udhayb, used by armies and pilgrims alike. These stopping points not only aided Muslim forces but also later provided logistical support for pilgrims journeying from Iraq to Mecca.
The findings were published in the journal Antiquity.























