Aerial archaeology, also known as airborne archaeology or remote sensing, is a branch of archaeology that utilizes aerial platforms and remote sensing technologies to study and interpret archaeological sites and landscapes. By capturing images and data from above, aerial archaeologists are able to uncover hidden features, patterns, and structures that are not easily visible from the ground.
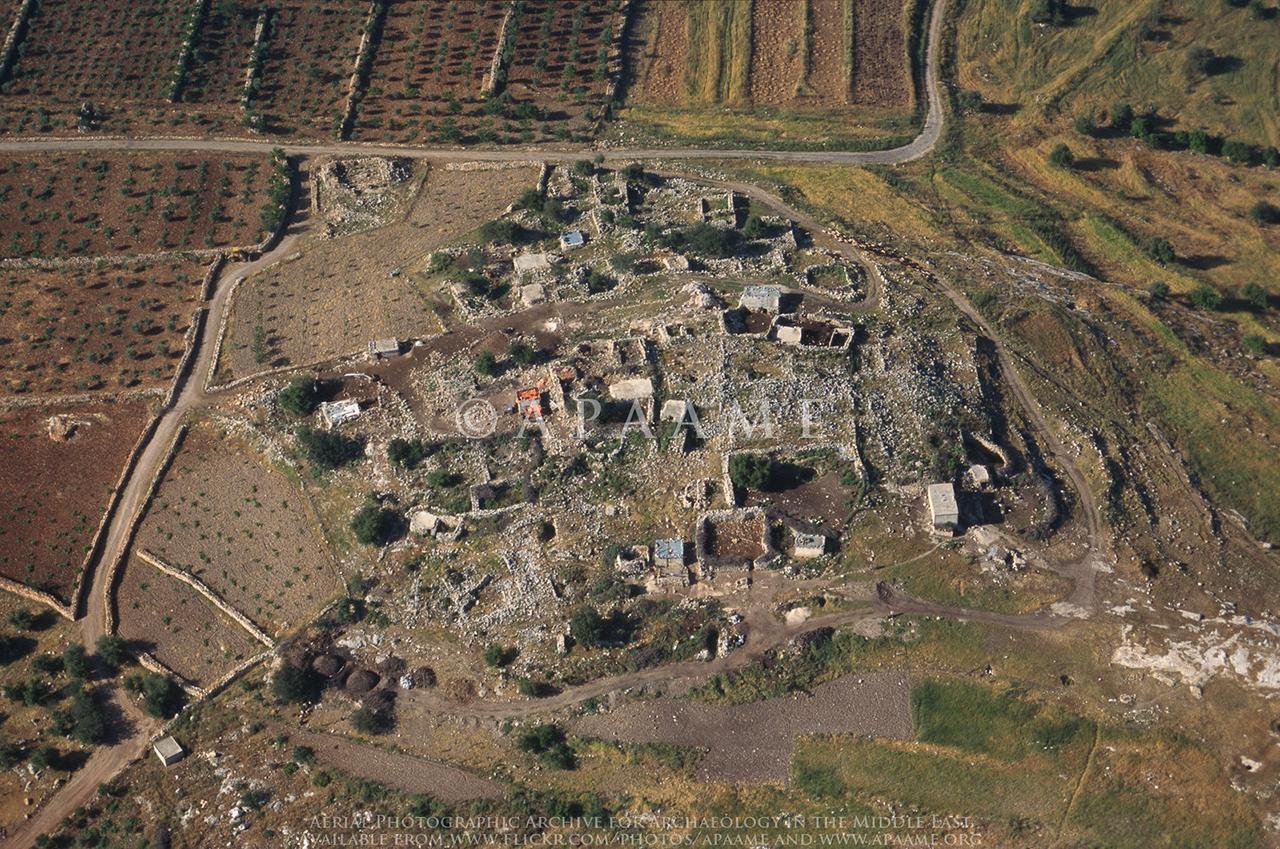

History of Aerial Archaeology
The origins of aerial archaeology can be traced back to the early 20th century when pilots and photographers began taking aerial photographs of archaeological sites. However, it was not until the 1970s that the field really took off with the advent of new technologies, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), which allowed for more accurate and detailed data collection.
One of the pioneers of aerial archaeology was O.G.S. Crawford, an English archaeologist who recognized the potential of aerial photography for archaeological research. Crawford conducted extensive surveys of the English landscape from the air and published numerous articles and books on the subject. His work laid the foundation for the development of aerial archaeology as a scientific discipline.
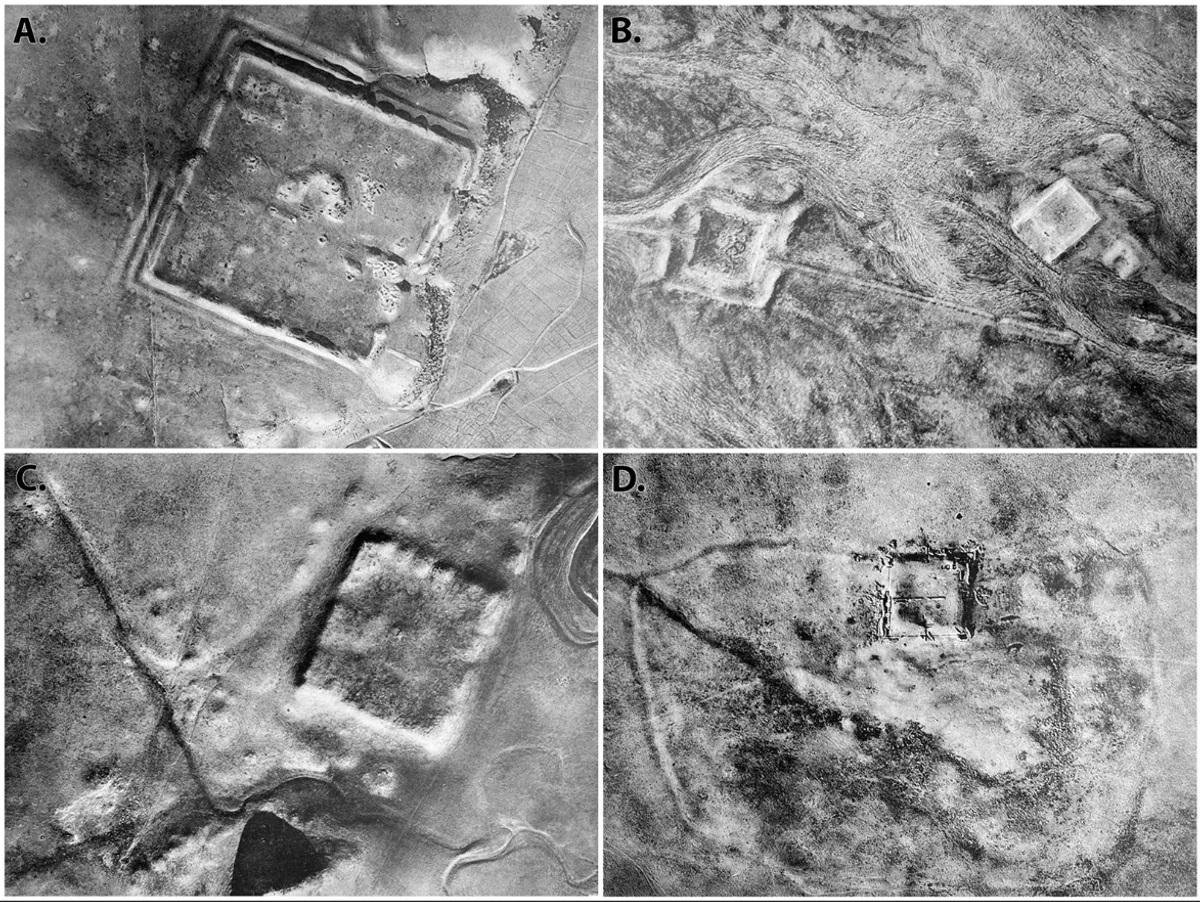

Methods and Technologies
Aerial archaeology encompasses a range of methods and technologies, each with its own strengths and limitations. Some of the most commonly used techniques include:
Aerial Photography
Aerial photography involves capturing images of the Earth’s surface from an elevated position. These photographs can reveal features and structures that are not easily visible from the ground, such as crop marks, soil marks, and shadow marks. Aerial photographs can be taken using various types of cameras, including digital cameras, infrared cameras, and multispectral cameras.
LiDAR
LiDAR is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D models of the Earth’s surface. LiDAR can penetrate vegetation and other obstructions, allowing archaeologists to see beneath the surface and identify buried structures and features. This technology has revolutionized the field of aerial archaeology, enabling researchers to map large areas quickly and efficiently.
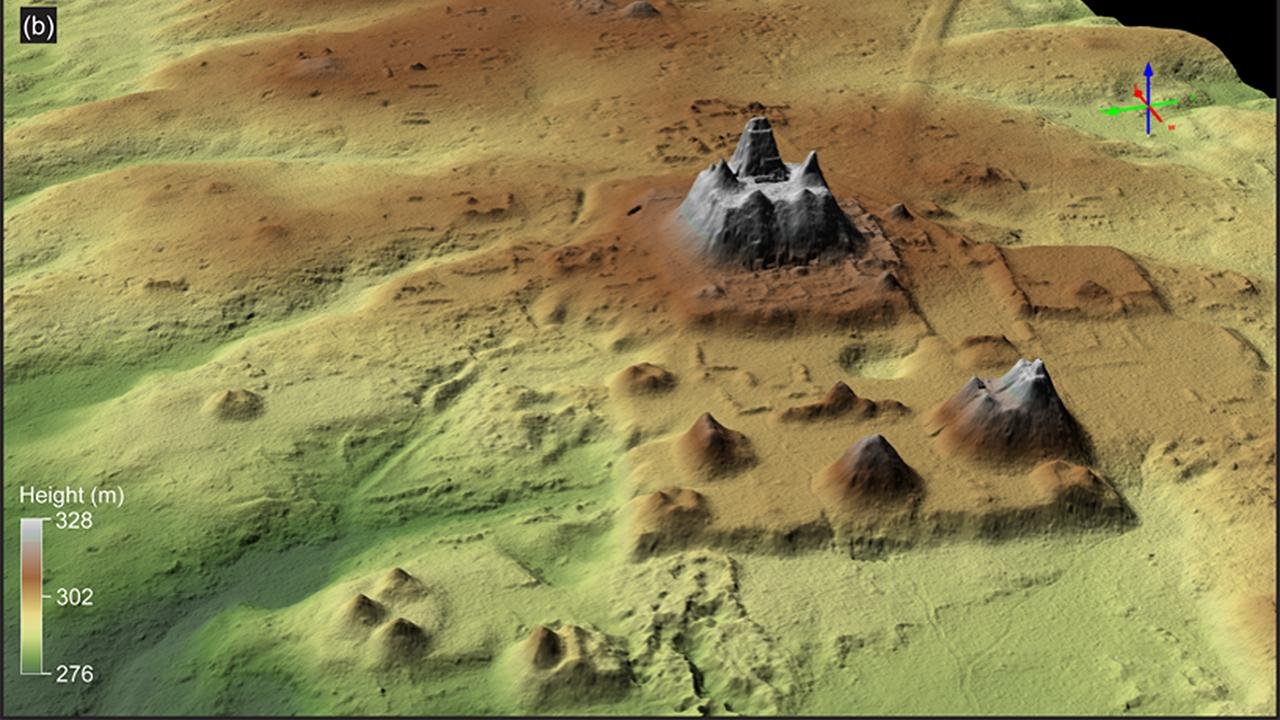

Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery has become an increasingly important tool in aerial archaeology. High-resolution satellite images can provide valuable information about archaeological sites and landscapes, especially in remote or inaccessible areas. Satellite imagery can be used to identify potential sites for further investigation, monitor changes over time, and create detailed maps.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging uses infrared technology to detect differences in temperature. This can be particularly useful in aerial archaeology as buried structures and features often retain heat differently from the surrounding soil. By capturing thermal images from the air, archaeologists can identify hidden features, such as underground chambers or walls, that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Applications of Aerial Archaeology
Aerial archaeology has a wide range of applications and can contribute significantly to our understanding of the past. Some of the key areas where aerial archaeology has been used include:
Site Discovery and Mapping
Aerial surveys can help archaeologists identify and map new archaeological sites. By capturing images from above, researchers can detect subtle changes in vegetation and soil patterns that may indicate the presence of buried structures or archaeological features. This can be particularly useful in areas where dense vegetation or urban development makes ground-based surveys difficult.
Landscape Analysis
Aerial archaeology allows for the study of entire landscapes, providing insights into how ancient civilizations interacted with their environment. By analyzing patterns of settlement, land use, and infrastructure, researchers can gain a better understanding of past societies and their relationship with the natural world. This can help answer questions about agricultural practices, trade routes, and social organization.
Conservation and Management
Aerial archaeology plays a crucial role in the conservation and management of archaeological sites. By monitoring changes in the landscape over time, researchers can identify areas at risk of damage or destruction. This information can be used to develop strategies for site protection and to prioritize areas for excavation or further investigation.
Cultural Heritage Documentation
Aerial archaeology is also valuable for documenting and preserving cultural heritage. By creating detailed maps and 3D models of archaeological sites, researchers can record and analyze important cultural and historical information. This documentation can be used for educational purposes, public outreach, and future research.
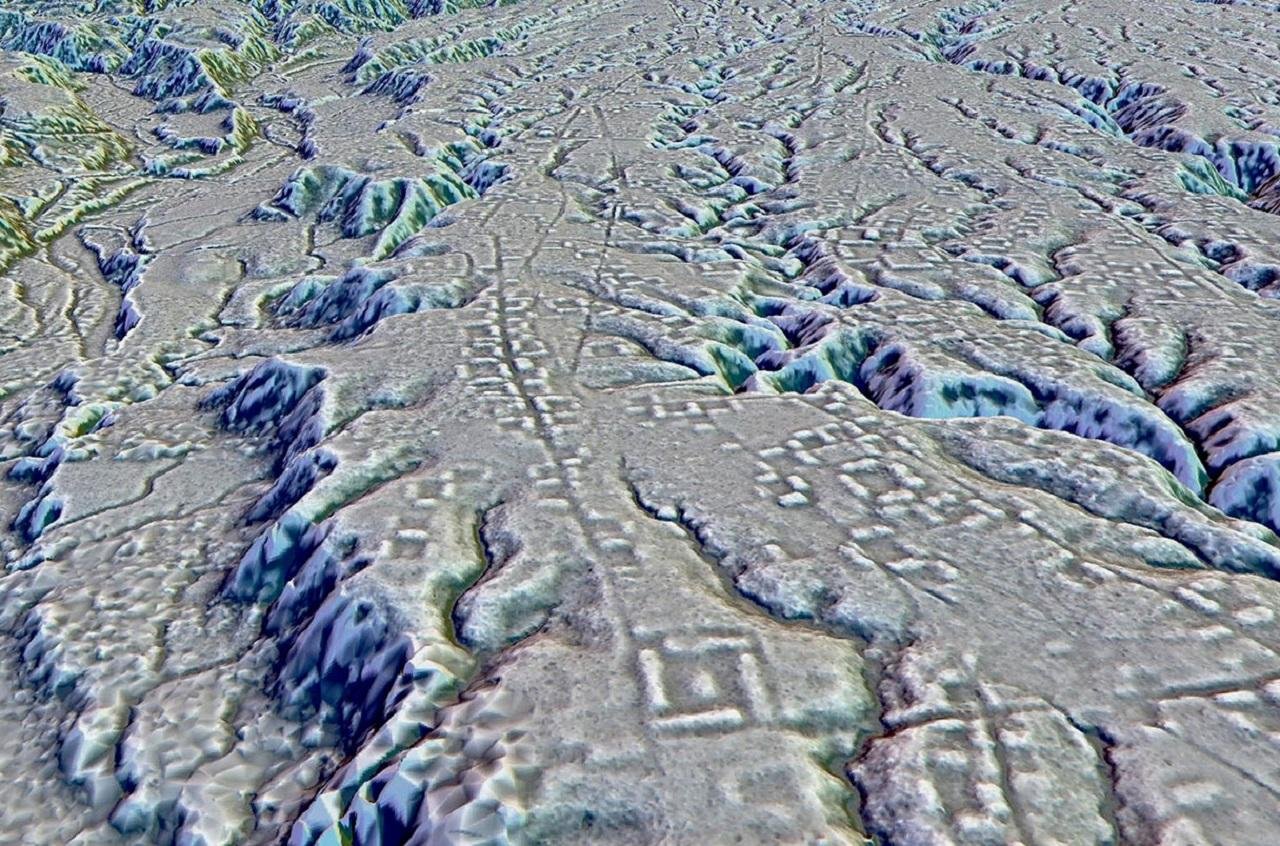

Challenges and Future Directions
While aerial archaeology has revolutionized the field of archaeology, it is not without its challenges. Some of the key challenges include:
Weather and Environmental Conditions
Aerial surveys are highly dependent on weather and environmental conditions. Poor weather, such as rain or fog, can limit visibility and hinder data collection. Additionally, dense vegetation and urban development can make it difficult to capture clear images from the air.
Data Processing and Analysis
The large amount of data collected through aerial surveys can be overwhelming. Processing and analyzing this data requires specialized software and expertise. It can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring collaboration between archaeologists, geographers, and computer scientists.
Cost and Accessibility
Aerial archaeology can be expensive, especially when using advanced technologies such as LiDAR or satellite imagery. Access to these technologies may also be limited in some regions, particularly in developing countries. This can pose challenges for researchers working in these areas.
Despite these challenges, the future of aerial archaeology looks promising. Advances in technology, such as the development of smaller and more affordable drones, are making aerial surveys more accessible. Furthermore, the integration of aerial data with other archaeological methods, such as ground-based surveys and excavation, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of archaeological sites and landscapes.
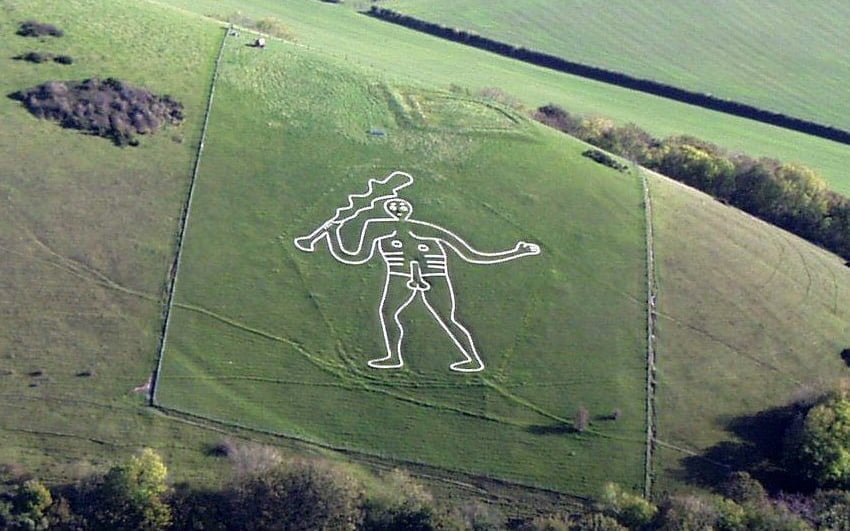

Aerial archaeology has transformed the field of archaeology, allowing researchers to explore and interpret the past from a new perspective. Through the use of aerial platforms and remote sensing technologies, archaeologists can uncover hidden features and map landscapes. As technology continues to advance, aerial archaeology will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in our understanding and preservation of the world’s cultural heritage.





















Comments 0