A new study published in the Journal of Human Evolution has shown remarkable similarities between how modern chimpanzees and early human ancestors pick tools, giving us fresh insights into the evolution of tool use.
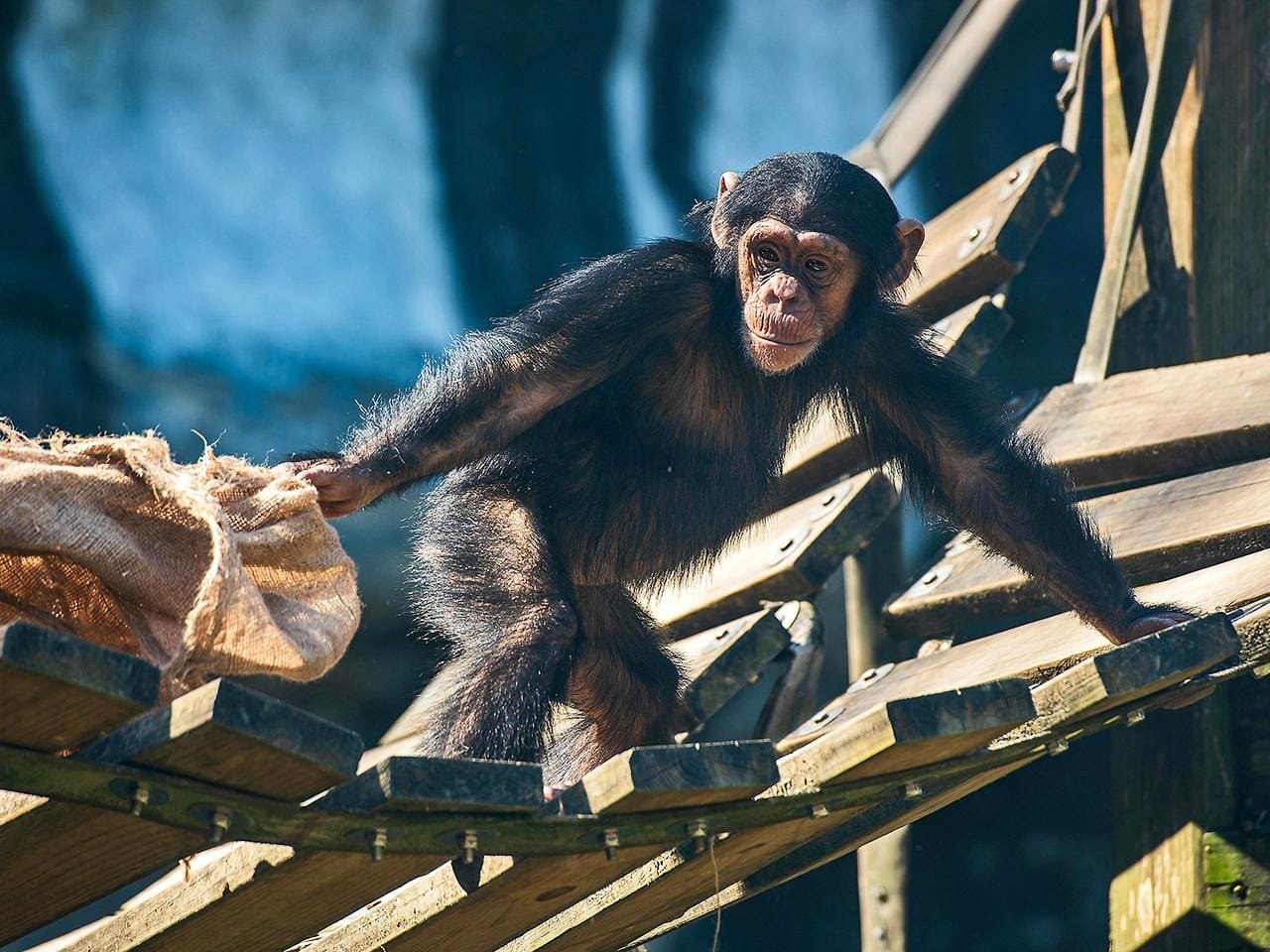

An international team of paleobiologists, anthropologists, and behavioral scientists carried out this research. Their work shows that the way chimpanzees choose stones to crack nuts is very similar to the purposeful and practical approach used by Oldowan hominins over 2.5 million years ago.
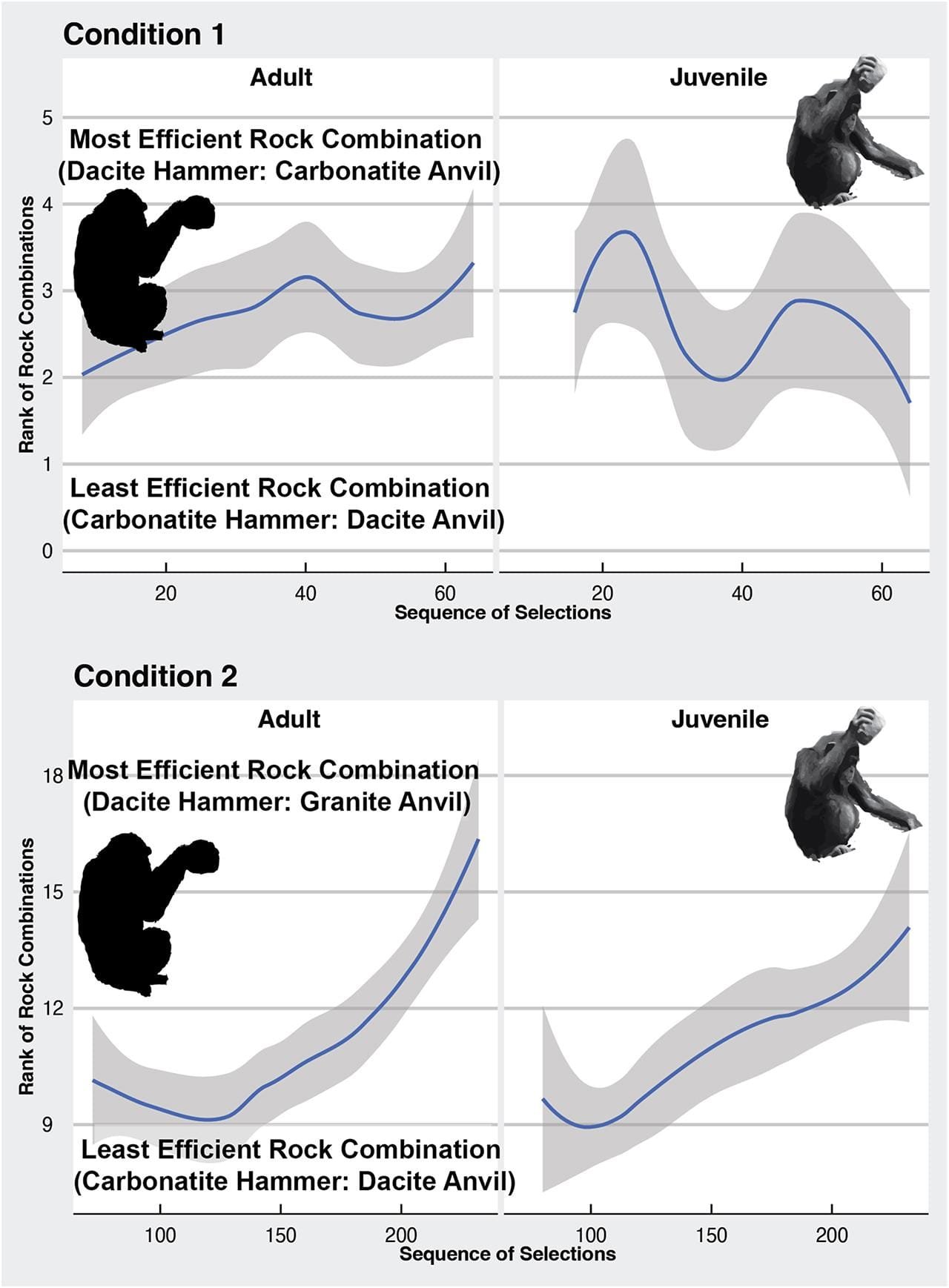
Scientists watched chimps in Bossou, Guinea, crack nuts using two tools: a hammer to hit the nut and an anvil to hold it steady. The team gave the chimps stones of different hardness, bounce, weight, and shape to see how they chose their tools. The study showed that chimps always picked harder stones for hammers and softer, more stable ones for anvils. They made these choices based on mechanical properties of stones, not how they looked or felt. The way they selected them suggests that they must have had an understanding of their practical utility.
These discoveries resemble how Oldowan hominins used tools. They were some of the first we know about to use stone tools. People started using Oldowan tools about 2.5 million years ago to chop, cut, and scrape. Studies show these early human ancestors picked stones with specific useful features on purpose, getting better at choosing over time. Just like the chimps, they cared more about how well tools worked and their mechanical benefits than how they looked on the surface.
Notably, Oldowan hominins moved stones long distances so they had a good understanding of material properties.
The study also reveals the social dynamics of tool use in chimpanzees. Younger chimps would mimic the tool choices of older, more experienced chimps, forming a type of cultural transmission. This is how early human societies passed down survival skills and tool-making techniques, which were essential for technological advancement and adaptation.
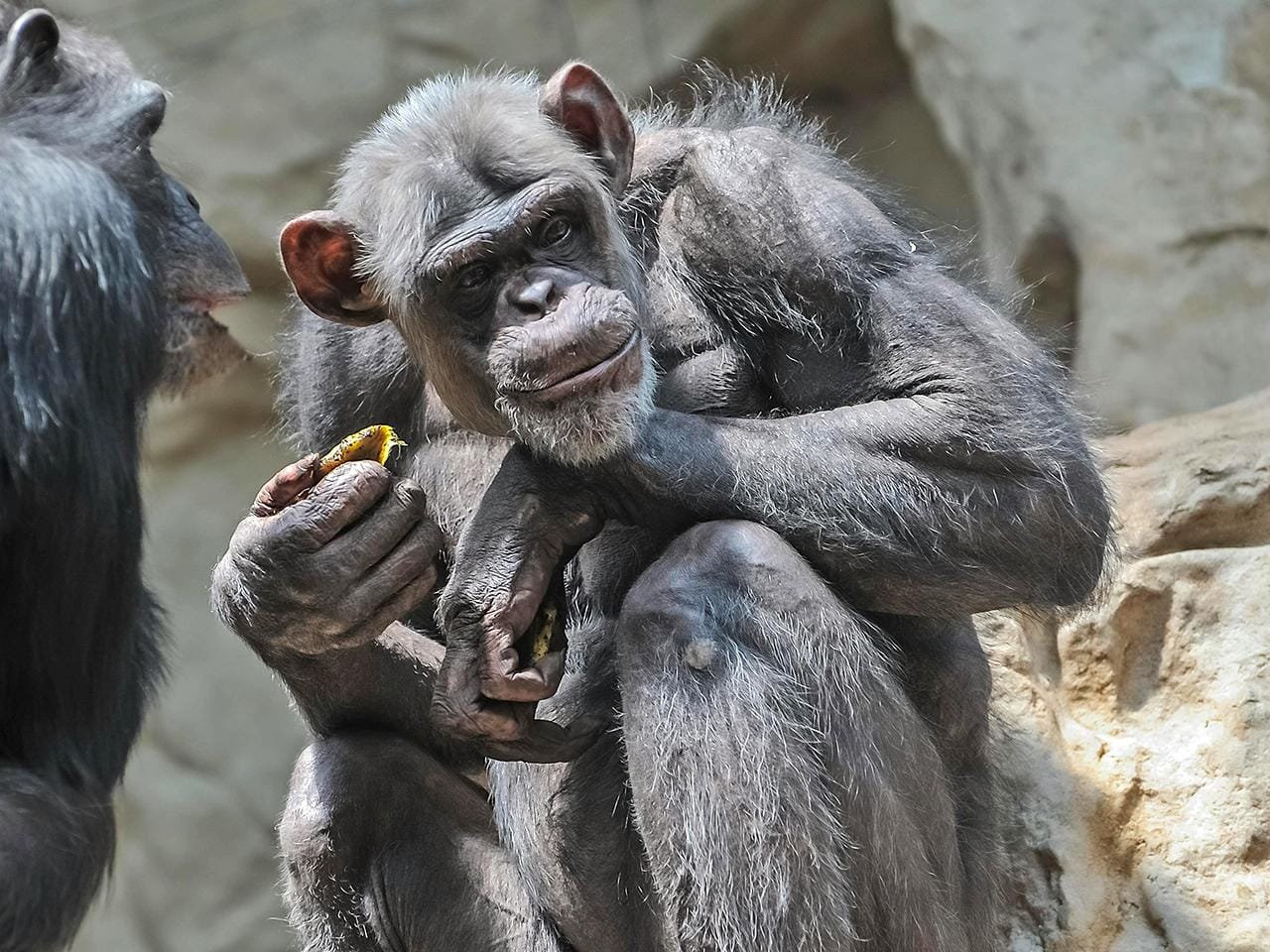

The findings add to the expanding area of primate archaeology, which connects behavioral research on modern primates with the archaeological evidence of ancient hominins. By examining chimpanzees—our nearest living relatives who have about 98% of our DNA in common—researchers can guess at the social and environmental factors that shaped how early humans started to use tools.