Italian researchers have unearthed over 3,000 Roman coins and 50 gems in the ancient Roman city of Claterna, near modern-day Bologna.

Claterna, once a thriving hub of culture and commerce, dates back to the second century BCE and continued to flourish until the collapse of the Roman Empire.
Previous excavations led by the Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape Superintendency revealed remnants of a forum, sculptures, bathhouses, streets, and domus adorned with vibrant-colored marbles and mosaics.
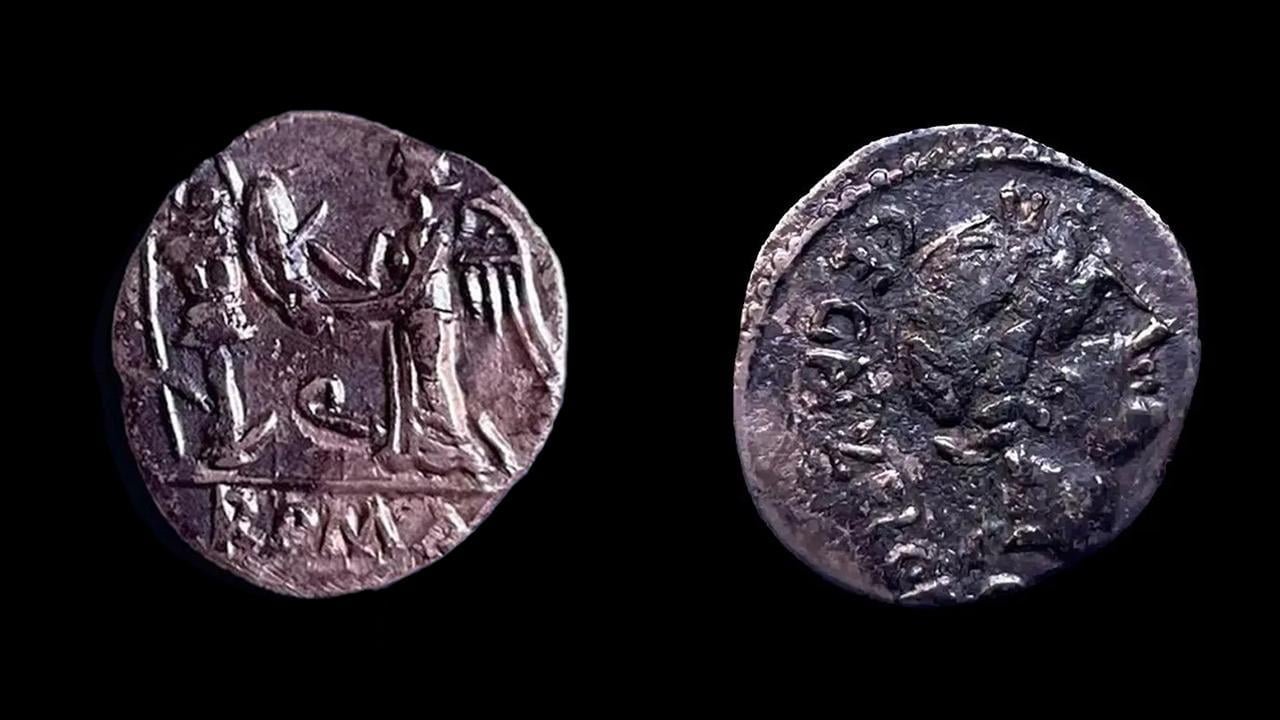
The recent excavations, conducted on a mere tenth of the 44-acre site, have exposed the largest non-stratified archaeological area in Northern Italy. Among the treasures discovered are over 3,000 Roman coins, predominantly silver and bronze, and numerous gems engraved with images honoring Roman deities. Notably, a rare silver quinary from 97 BCE was found in the corridors of a newly discovered theatre complex.

Italian Undersecretary of State Lucia Borgonzoni highlighted the newfound importance of Claterna, stating, “Given the importance and quantity of finds brought to light so far, we can probably speak of a Pompeii of the North.” Contrary to previous assumptions, the discoveries challenge the notion that Claterna was merely a transit town, revealing it to be a significant trading center with direct ties to Rome.
Francesca Tomba, the superintendent of Bologna, emphasized the ongoing potential of the site, stating, “A large part of the site is still yet to be discovered.” The extensive excavation efforts have uncovered only one-tenth of the city, leaving much more to be explored and understood about Claterna’s past.
The unearthed coins and gems provide valuable insights into the city’s economic and cultural significance. The coins, including the rare quinarius, suggest Claterna was a bustling center of commerce rather than just a pilgrimage site. Borgonzoni noted, “It was a trading center with direct contacts with Rome,” emphasizing the economic ties that existed between Claterna and the capital.
The gems, engraved with depictions of Roman deities and structures, further showcase the city’s rich cultural history. Plans are underway to restore Claterna’s ancient theatre for future use, allowing visitors to experience the entertainment spectacles that once took place over 2,000 years ago.

The ongoing collaboration between Italy’s Cultural Ministry, the superintendency of Bologna, and local institutions aims to educate the public about Claterna’s historical significance. Lucia Borgonzoni expressed the intention to implement activities that “bring knowledge of this magical place rich in history to young people” and attract visitors from around the world.